There is an opinion that after training, namely within a quarter or half an hour, it is necessary to take a portion of fast simple proteins along with carbohydrates, or, as an alternative, consume these products separately. Some sources report the formation of a protein-carbohydrate window at this time. This phenomenon is also called the anabolic or post-workout window. It is believed that fast carbohydrates after training are immediately consumed for the purpose of muscle recovery and growth. We propose to examine this topic in more detail, defining the true role of proteins and carbohydrates in building a beautiful muscular structure of the body.
General information about closing windows
During training, the body is subjected to serious stress. In particular, during intense exercise, it loses sugar from the blood, glycogen from the liver and muscle tissue. As a result, a state of hunger sets in, in which the body will optimize its own resources - burn muscle and fat tissue. However, these processes do not occur immediately after training, but during the period of restructuring of systems. Approximately - in 20-30 minutes (source - Wikipedia).
If during this time the body is provided with a sufficient amount of nutrients (nutrients), then instead of optimization processes it will switch to the mode of adaptation processes: building up new muscle and energy structures to withstand stress.
This is why athletes close their protein and carbohydrate windows after training. It is best to cover them with gainers, since they have a high glycemic index and almost do not participate in the digestive processes, which means they quickly restore depleted resources and prevent catabolic processes.
Eating carbs after a workout won't hurt you
Many people worry that carbs after a workout will add fat to their body , but post-workout is about the only time of day when you can be sure that carbs aren't being converted into body fat. carbohydrates immediately after training.
If you are on a diet to reduce your body fat percentage, but you consume carbohydrates at all meals, then you should not avoid eating carbohydrates after a workout. It's best to cut back on carbohydrates at other meals and save them for the period immediately after exercise.
Maybe you're afraid to eat carbs after exercise because you've heard that eating carbs immediately after exercise can lower your growth hormone and testosterone levels. However, this is not true. Why? Because growth hormone and testosterone levels peak during the training period, and when the training is completed, they plummet, regardless of whether you ate anything or not. So, eat after your workout and stop worrying about your already plummeting hormone levels. [8]
Complex or simple?
A traditional question for novice athletes: what carbohydrates to eat after strength training – complex or simple? There are several opposing views on this matter. Let's look at what they are based on:
- If you close the carbohydrate window with sugar, you will almost immediately stop catabolism. However, due to the high glycemic index, the liver will not be able to convert all incoming carbohydrates into glycogen. Therefore, some of them will participate in the processes of lipid formation. The result is more mass, but also a slight increase in the percentage of body fat.
- Using slow carbohydrates, you will reduce the rate of muscle gain, because... catabolic processes will not be stopped immediately, which means that a certain amount of muscle mass will burn in the process of optimizing the body’s resources. In return, you will get higher quality muscle mass with a lower percentage of body fat.
- Don't close the carbohydrate window. In this case, you risk causing muscle hyperplasia, but the price that athletes have to pay for such frivolous treatment of the body is often measured in health.
- Close only the white window. This is the wrong approach. If the body experiences an energy shortage, it will simply use proteins as an energy source. It's like fueling a fire with dollar bills (source: PubMed).
Let's start with protein (protein) before training.
I have repeatedly written about the fact that protein is the main building material for muscle growth, and that it is the lack of protein in the body that can significantly reduce your results and success in the gym. It may seem that the definitively correct answer would be: “Always eat protein and always before training.” However, there are people who cite certain studies that prove that this is not a prerequisite for successful training. However, both points of view can be correct. The answer to this oddity lies in the fact that all people are different, and they go to workouts at different times of the day and the amount of protein consumed is different for everyone. And also different times for the breakdown of eaten food into microelements, protein in particular. On average, splitting can take from 2 to 6 hours. That is, if you ate a large amount of protein (more than 20 grams) an hour or two before working out in the gym, then by the time you approach the exercise equipment, the amount of amino acids in the blood plasma will be optimal and high enough for a successful workout. Under these conditions, consuming additional protein immediately before a training session will not have any positive effect and you can skip the pre-workout protein and not lose any muscle fiber growth potential.
But if the last food intake before the gym was more than two hours ago, and the amount of protein was less than 20 grams, then I strongly recommend adding 20-40 grams of protein to the body’s firebox half an hour before entering the gym, otherwise the training session may result in the opposite effect. Case studies suggest that pre-workout protein will help increase blood amino acid levels and therefore the synthesis of new protein and new muscle fibers.
When the need arises to consume pre-workout protein, the question immediately arises, which one is better to use for the purpose of quickly saturating the blood with amino acids, which protein will be the best fuel for the body during training. Pre-workout protein should have high levels of leucine (an amino acid that stimulates protein synthesis). In fact, any type of pre-workout protein will increase your amino acid levels to a certain extent, but the best option is to use a fast-absorbing form of it - whey protein, which is also very rich in leucine. Research also shows that this same type of protein is great for post-workout nutrition for the same reasons.
Previously, it was difficult to choose a good whey protein that would suit me in terms of composition: that is, without artificial sweeteners, colors, monosodium glutamate, etc. But now sports nutrition manufacturers allow you to choose a decent whey protein based on price-quality ratio and composition, which will contain only whey protein isolate. Yes, this is just a dream! It is called WHEY plus and here are its advantages, which will seem like an argument for any athlete not only chasing a quick improvement in performance, but also avoiding contamination of the body with artificial components:
- Consists of 100% whey protein isolate, not a mixture of isolate and cheap forms of protein;
- Made from cow's milk, which is not injected with hormones;
- Consists of undenatured protein produced using cold micro- and ultra-filtration technologies;
- Naturally sweetened with stevia and naturally flavored;
- Contains no artificial junk like MSG or artificial food coloring.
What is?
Closing the carbohydrate and protein windows are the athlete’s primary tasks. Let's consider what is the best way to close the energy deficit after training:
| Product | Primary Nutrient | For what | When |
| Gainer with maltodextrin | Slow carbohydrates + fast proteins | Gainers based on maltodextrin, although considered the cheapest, are an ideal solution for closing the carbohydrate window due to their extremely high glycemic index. They almost completely restore glycogen reserves and help stop catabolic processes. | On intensive mass gain. |
| Gainer based on starch | Slow carbohydrates + complex proteins | Slow carbohydrates in combination with complex protein not only immediately close the carbohydrate and protein windows, but also slow down the process of increasing fat mass due to excess calories. Such a gainer will allow you to stay full longer, and the mass will be better and drier. | With dry mass gain. |
| BCAAs | Broken Amino Acids | BCAA is a serious anti-catabolic, which is used if you are on intense cutting and you need to stop catabolic processes without slowing down background fat burning. | Drying. |
| Whey Protein | Fast squirrels | Protein is included in most mass gainers and helps stop catabolic processes, which tips the anabolic scale towards muscle building. | Always. |
| Vitamins | – | Used to maintain the balance of minerals washed out during exercise. | Always. |
| Adaptogens | – | Adaptogens are used to speed up recovery and are used in both bulking and cutting, but are not considered essential. | Optional. |
How many calories can you burn in an hour?
The average person contains about 100 grams of carbohydrates in the liver and about 400 grams in the muscles. Studies have shown that the same person, even after a hard workout, burns only about twenty-five percent of muscle glycogen. Similar studies in two training areas (heavy lifting and high-intensity interval training) showed similar levels of exhaustion.
You might think that about five sets of front and back squats, leg presses, and leg extensions to muscle failure would force you to eat simple carbohydrates after your workout. But 10 grams of carbohydrates on a stick will not replace the 100 grams you burned during your workout.
Proteins as an alternative
We mentioned earlier that it is not recommended to close the carbohydrate window with proteins, since the body will burn proteins for energy. However, this method will be effective in the case of extremely intense drying (source - PubMed).
Be sure to take several factors into account:
- When burning proteins, the body spends more energy (for conditional digestion and breakdown).
- It will burn the minimum required amount of energy to stop catabolism, while the rest of the proteins will still be spent on its target task (formation of amino acid chains and accelerated restoration of muscle tissue).
What about pre-workout carbohydrates and how do they affect performance?
Fortunately, the answer to this question is more clear. Research agrees that they prolong the period of increased productivity. In particular, consuming carbohydrates half an hour before training provides muscles with additional fuel for training, while they do not directly stimulate additional muscle growth.
I say “won't stimulate directly” because eating carbohydrates before exercise does not speed up protein synthesis. They can help you work with heavier-than-usual weights and more repetitions than you would in classes without pre-eating carbohydrates. So, pre-workout carbohydrates can indirectly help you build more muscle over a period of time (but only if your training and diet are correct).
So, if you are going to consume carbohydrates before the gym, which ones are best?
When it comes to carbohydrates, the research is again fairly clear. For long-term endurance training (2 hours), carbohydrates with a low glycemic index are suitable, and for short, high-intensity training (45-60 minutes) - with a high one.
I am not a fan of purchasing and consuming carbohydrate supplements. To me, these are simply bloated, overpriced jars of monosaccharides (simple sugars) like dextrose and maltodextrin. Don't fall for the marketing hype - there's really nothing special about these types of supplements.
Instead, I prefer to get my pre-workout carbohydrates from food. My favorite sources: bananas, instant oats, white potatoes, white rice, cantaloupe (when in season), dates, figs, raisins and assorted dried fruits.
It seems like you have decided what to eat, but what about the volume of consumption of pre-workout carbohydrates?
Eat 25-50 grams of carbohydrates 30 minutes before starting your workout and you will notice an improvement in your performance.
Grocery list
Surely you would like to see a list of foods that are rich in fast carbohydrates, but the fact is that even protein (sports supplement) contains a certain amount of carbohydrates. What I mean is that the nutrients that interest us are found in many products that cannot be listed. But I will still give a short list of the most common ones.
Generally speaking, the products look like this:
- starchy vegetables;
- sugar;
- bakery products (all except black bread);
- sweet drinks.
If you want specifics, here it is:
- potatoes in any form (fried, boiled, fried, stewed, etc.)
- instant soups and potatoes;
- fruit juices, sweet carbonated and non-carbonated drinks;
- sweet fruits (banana, watermelon, although it is a berry, grapes);
- honey;
- vegetables (turnips, carrots, corn flakes, celery root);
- baked goods and cookies (bagels, sweet buns, white or gray bread, rice biscuits, biscuit sweets, donuts, etc.);
- various syrups.
By the way, the glycemic index of the above foods does not fall below 69. That is, this level is quite high, which affects the level of blood sugar or glucose. Say what is more convenient, although it is the same thing.
All slow carbohydrates have an index below this level, indicating that they do not have too much of an impact on blood sugar. But it is worth understanding that this level is also different for different foods rich in fast carbohydrates. For example, fried potatoes have a level of 95, but white bread is only 70.
I would also like to say something about alcohol: it also belongs to fast carbohydrates. Beer, for example, has a glycemic index of 110 units.
Table
General table to lose weight (Product name - GI (glycemic index)).
- Potatoes in any form – 80–95
- Fruits – 63–100
- Honey - 89
- Juices and drinks – 65–75
- Bread and derivatives – 67–95
- Cookies, waffles and more - 72–80
- Vegetables – 65–100
- Fast food - 66–93
This table will help you navigate when choosing certain products. Just know that if the product you choose falls into one of the categories, then it will definitely be within the given figures.
Therefore, I advise you to use fast carbohydrates less and resort to them only when necessary (after training). In any other situations, a large number of foods containing a lot of fast carbohydrates will affect the gain of extra pounds. And I'm not talking about muscles now.
So, you have seen what fast carbohydrates are, a list of products and a table for weight loss. Enjoy it for your health, and if you want to thank me for such valuable information, then you can just share this article with your friends on social networks. Write what you think about the product list, and don’t forget to subscribe to my blog updates. Good luck in the rocking chair.
Conclusion on pre-workout nutrition
The timing of nutrient intake is much less important than that they (translated from English as “If It Fits Your Macros”) i.e. fit into or match your macros and ensure you stick to your meal plan.
Although, once you've already taken care of these things, optimizing when you eat can be what can help you build muscle even faster.
Luckily, it's not very difficult, either.
- Eat some protein and carbohydrates every few hours.
- Eat before your workout if you haven't eaten a little beforehand.
- Eat after a workout, and it's better to eat sooner rather than later.
- Eat enough fat every day.
- And get most of your calories from a nutritious diet.
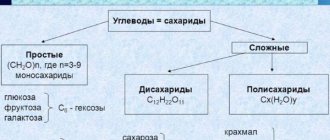
Simple
We are talking about sugar, mainly found in fruits, milk and other products. Simple sugars are divided into:
- monosaccharides consisting of one molecule.
- disaccharides consisting of 2 molecules;
The following are the most commonly found sugars.
Monosaccharides The most famous include fructose and dextrose.
Fructose (fruit sugar) is rarely included in post-workout shakes. Many people believe that fruits are a good source of carbohydrates, and they are wrong. A 25 gram serving has a GI of 11, which is not enough for post-workout recovery.
Dextrose or glucose is found in many foods. A 50-gram serving has a GI of 96, which is why dextrose is often included in various post-workout supplements. But you need to take it with caution, because... the body may react unpredictably. Thus, overweight people may experience the deposition of carbohydrates in fatty tissues. Those who have just started taking dextrose should carefully monitor the condition of their body and immediately respond to any alarming symptoms.
Disaccharides The most popular include:
- Lactose or milk sugar. A 25-gram serving of lactose has a GI of 48.
- Sucrose. This regular table sugar contains two molecules: fructose and glucose. A 25 g serving has a GI of 60.
From the above, we can draw the following conclusion: a suitable ingredient for a post-workout shake is dextrose. The rest have an insufficiently high GI.
And finally, let's talk about pre-workout fats.
There is an interesting opinion that by increasing fat consumption before going to the gym, carbohydrate consumption will decrease, which will increase the body's performance.
- However, research proves the opposite. Increased fat intake in the 24 hours before exercise (cycling in this case) reduces race performance time compared to a high carbohydrate diet.
- Another study proved that when the body has already “adapted to fat,” the body’s consumption of carbohydrates decreases, but this does not affect performance in any way.