What are proteins?
Protein is our building material due to which tissues and cells in the body are renewed. It contains 20 types of amino acids, 9 of which are essential (not synthesized in the body) and the remaining 11 are replaceable. Essential amino acids must come to us with food from outside. They are found in large quantities in products of animal origin (meat, eggs, fish, cheese, cottage cheese) and are almost completely absent or contained in minimal doses in plant proteins.
The best protein foods are foods of animal origin, as they contain more nutrients and amino acids. But you don’t need to neglect plant proteins either.
Their ratio should look something like this: 70-80% proteins of animal origin, 20-30% proteins of plant origin.
Basics of proper nutrition
Fats, carbohydrates, and proteins are necessary for the full functioning of all vital systems of the body. Summarizing the above and adding a little new information, we invite you to familiarize yourself with the recommendations that will allow you to ensure the right approach to nutrition:
- Study the daily intake of BJU and try not to exceed it; an excess (as well as a deficiency) of substances will negatively affect your health.
- When calculating the norm, take into account your weight, lifestyle and physical activity.
- Not all proteins, fats and carbohydrates are beneficial: give preference to foods containing complex carbohydrates and unsaturated fats.
- Consume fats and complex carbohydrates in the morning, and proteins in the evening.
- Products containing proteins, fats and complex carbohydrates should be heat treated only in the form of steaming, stewing or baking, but never frying in oil.
- Drink more water and eat small meals, as this diet can ensure better absorption of substances.
Knowledge about proteins, fats and carbohydrates will help you create a correct and balanced menu for every day. A properly selected diet is the key to health and well-being, productive working time and proper rest.
Based on the degree of digestibility, proteins can be divided into 2 categories.
- Fast. Their breakdown occurs very quickly (fish, eggs, chicken, seafood).
- Slow. Accordingly, their breakdown occurs very slowly (cottage cheese and proteins of plant origin).
Fast proteins are preferably taken when we need to quickly replenish its reserves. This is usually when we just woke up, the time before and after our workout.
Slow proteins satisfy the feeling of hunger for a longer time and enrich us with amino acids for a longer time, thereby protecting our muscles from destruction. They are best consumed before bed. Overnight they have time to be completely digested and absorbed. It is not recommended to eat slow, vegetable proteins (legumes, seeds, nuts) before going to bed, let it be cottage cheese or casein protein.
For people leading a normal, inactive lifestyle, the protein norm is 1-1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight. For those training, this will be approximately 2 grams per 1 kilogram of our body weight. All this protein must be distributed among all main meals, since it is difficult for the body to absorb more than 30-50 grams of protein at one time.
CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates, synthesized from carbon dioxide and water, are the most abundant organic molecules on earth. Carbohydrates include sugar and starch, which are the main sources of energy for the human body. Dairy products contain large amounts of less sweet milk sugar - lactose.
Carbohydrates are essential due to the high energy requirements of the central nervous system (i.e., brain) of mammals. The brain has a limited ability to use non-carbohydrate energy sources. In humans, the estimated brain requirement is 100 g of glucose per day.
Despite the fact that a person consumes significantly more carbohydrates than fats and proteins, their reserves in the body are small. This means that the body must be supplied with them regularly. The need for carbohydrates depends to a very large extent on the body's energy expenditure. It is significantly higher among manual workers and athletes. Unlike proteins, and to a certain extent, fats, the amount of carbohydrates in diets can be reduced without harm to health.
The most important sources of carbohydrates: bread, buckwheat, semolina, rice, sugar, potatoes, watermelon, carrots, beets, grapes, apples.
Sweets, pastries, cakes, jam, ice cream and other sweets are the most attractive sources of carbohydrates and pose an undoubted danger to people who are gaining weight. A distinctive feature of these products, the number of which has been growing rapidly in recent decades, is their high calorie content and low content of essential nutritional factors.
What is the maximum amount of carbohydrates that can be tolerated?
The maximum rate of carbohydrate utilization is 4 mg/kg per minute, which corresponds to approximately 400 g per day (1500 kcal/day) for the average person.
What level of sugar consumption can be normal?
It depends on age, nature of work, active recreation. Consuming 80-100 grams of sugar per day for a healthy young person can generally only be beneficial. For athletes and people involved in intense physical labor, these standards may be slightly increased. In adulthood and old age, as well as people leading a sedentary lifestyle, it is recommended to reduce sugar consumption.
Fats are divided into 3 types
- Cholesterol (cholesterol).
- Triglycerides.
- Phospholipids.
Cholesterol is a natural lipophilic alcohol, that is, an organic compound that is present in the cells of living organisms. It is the source of our sex hormones. Without cholesterol, our reproductive system will not be able to function normally. He can be good and bad. Cholesterol is found in animal products: meat, poultry, fish, seafood and dairy products.
Triglycerides are a mixture of fatty acids and glycerol, which are the main fatty components of blood. The body primarily uses triglycerides as energy for thermoregulation.
Phospholipids are almost the same as triglyceride, but they do not play any significant role in providing us with energy. Their main role is structural. Phospholipids are the material for our membranes, which rushes to where the damage occurred, after which the cell is restored, as if after restoration. Their deficiency stops the restoration work, which leads to various disorders at the level of cell membranes.
Phospholipids are found in chicken eggs, unrefined vegetable oils, and slightly less in chicken, beef, liver, cheese and fish.
Fats
Fats are a source of energy. In addition, they are necessary for the successful absorption of a number of vitamins by the body and serve as a supplier of essential fatty acids.
There are two types of fats: saturated and unsaturated. Saturated fats contribute to the accumulation of cholesterol and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Unsaturated fats, when consumed in moderation, can burn fat and prevent blood clots.
Unsaturated fatty acids are found in fats of plant origin; they do not contain cholesterol, but on the contrary, help cleanse the body of it, preventing thrombosis and atherosclerosis, promote the separation of bile and normalize intestinal function. This type of fat is easily absorbed and digested fairly quickly.
Unsaturated fats are found in the following plant foods:
- sunflower, olive, flaxseed and corn oil;
- nuts and seeds;
- olives and black olives.
Fats are necessary for the body. If they are completely excluded from the diet, a number of negative consequences may occur:
- dry skin;
- bad mood and depression;
- chronic fatigue and drowsiness;
- constant feeling of cold;
- inability to concentrate.
It should also be mentioned that the absence of fat in the diet will not lead to weight loss, but on the contrary, it may result in the appearance of extra pounds. The fact is that the body will compensate for the lack of fats using proteins and carbohydrates. And by consuming fats and simple carbohydrates in large quantities, you equally risk becoming overweight.
Excessive fat consumption impairs the absorption of protein, magnesium and calcium, and problems arise with the digestive system. Proper fat metabolism will ensure the consumption of vitamins contained in vegetables and fruits.
Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids (exchange and comparison)
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates serve as building materials and a source of energy for the body.
Proteins, polysugars and nucleic acids are polymers, consisting of monomers (amino acids, monosaccharides and nucleotides, respectively).
PROTEINS
- the main building material, make up 50% of the dry mass of the body, are part of the organelles, membranes and cytoplasm of cells. Functions: catalytic (accelerate reactions), transport, propulsion, protective, etc.
Proteins are not stored in the body; excess proteins are converted into fats or carbohydrates. Proteins themselves cannot be synthesized from carbohydrates and fats, because fats and carbohydrates do not contain nitrogen. Lack of protein in food is dangerous, especially for children and adolescents.
The oxidation of proteins produces carbon dioxide, water and ammonia. Ammonia travels through the bloodstream to the liver and is converted into urea, which is excreted in urine and sweat.
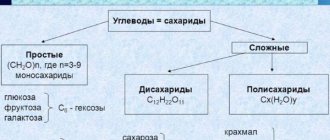
CARBOHYDRATES
are divided into monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysugars.
Monosaccharides (dissolve in water and have a sweet taste):
- ribose (part of ATP, RNA),
- deoxyribose (part of DNA),
- glucose (the main source of energy, formed during photosynthesis, oxidized to water and carbon dioxide during respiration).
The reserve by which the concentration of glucose in the blood is maintained at a constant level is the glycogen reserve in the liver. Excess carbohydrates in the body are converted into fats.
Polysugars (do not dissolve in water, have no taste). Perform construction and storage functions:
- starch is a storage carbohydrate in plants,
- glycogen is a storage carbohydrate in animals and fungi,
- Cellulose is a component of plant cell walls.
LIPIDS
- This is a group of substances that do not dissolve in water. These include fats, phospholipids (part of the plasma membrane - construction function) and steroids (sex and cortical hormones - regulatory function).
FATS – consist of glycerol and fatty acids. Function – energy reserve. The oxidation of fat releases twice as much energy as the oxidation of a gram of protein or carbohydrate, as well as water and carbon dioxide.
Fats are stored in subcutaneous fatty tissue and in the linings between organs. In addition to storing energy, adipose tissue functions as thermal insulation, water storage and mechanical protection.
Fats in the body can be formed from proteins and carbohydrates.
NUCLEIC ACIDS
participate in the storage and implementation of hereditary information.
- DNA is part of chromosomes
- mRNA carries information from the nucleus to the ribosome,
- tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome
- rRNA is part of ribosomes.
You can also read
DETAILED NOTES: Lipids, Enzymatic (catalytic) function of proteins, Functions of proteins with examples, Carbohydrates
ASSIGNMENTS OF PART 2 OF THE USE ON THIS TOPIC
Part 1 tasks
Choose one, the most correct option. Fiber contained in raw vegetables and fruits eaten by humans improves
1) digestion in the stomach 2) breakdown of carbohydrates 3) intestinal motor function 4) absorption of nutrients into the blood
Answer
3
Choose one, the most correct option. No transformation occurs in the human body
1) proteins into fats 2) carbohydrates into proteins 3) carbohydrates into fats 4) organic substances into inorganic
Answer
2
Choose one, the most correct option. Only proteins perform the function
1) protective 2) energy 3) storage 4) motor
Answer
4
PROTEINS Choose three options. What foods are high in protein?
1) sour cream 2) cottage cheese 3) cheese 4) potatoes 5) bread 6) fish
Answer
236
PROTEIN EXCHANGE 1. Establish the sequence of protein metabolism in the human body, starting with their intake from food. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) oxidation with the formation of ATP, carbon dioxide, water, urea 2) formation of peptides under the action of pepsin 3) synthesis of myosin, casein 4) food proteins 5) formation of amino acids under the action of trypsin
Answer
42531
2. Establish the correct sequence of protein digestion, starting with their entry into the oral cavity with food. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) mechanical grinding and wetting 2) entry of amino acids into the blood 3) breakdown into peptides in an acidic environment 4) breakdown of peptides into amino acids using trypsin 5) entry of the bolus into the duodenum
Answer
13542
PROTEINS - LIPIDS 1. Establish a correspondence between the characteristic and the substance to which it belongs: 1) proteins, 2) fats. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) consist of molecules of fatty acids and glycerol B) consist of residues of amino acid molecules C) protect the body from hypothermia D) protect the body from bacteria and viruses E) are polymers E) when oxidized, 1 gram gives 38.9 kJ
Answer
212112
2. Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and organic substances of the cell: 1) proteins, 2) lipids. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) consist of amino acid residues B) are part of chromosomes C) form a bilayer in the cell membrane D) have a high calorie content (about 9 kcal/g) E) are enzymes E) have a tertiary and quaternary structure
Answer
112211
PROTEINS - CARBOHYDRATES Establish a correspondence between the functions and properties of organic substances in the cell and their types: 1) carbohydrates, 2) proteins. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) perform a transport function B) are a reserve substance in the cell C) consist of glucose monomers D) perform an enzymatic function E) provide active transport through membranes E) form a cell wall
Answer
211221
Establish a correspondence between the structure and function of a substance and its type: 1) Hemoglobin, 2) Glycogen. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) The molecule is highly branched B) It has a quaternary structure C) It is stored in the liver D) The monomers are amino acids E) It is used to maintain oxygen levels
Answer
21211
Establish a correspondence between nutrients and the food products in which they are contained: 1) proteins, 2) carbohydrates. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) bread B) meat C) potatoes D) cottage cheese E) cheese E) sugar
Answer
212112
PROTEINS - NC Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and organic substances: 1) proteins; 2) nucleic acids. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) are represented by a globule B) have peptide bonds C) are synthesized in the nucleus D) serve as biocatalysts E) include a polynucleotide chain E) are capable of replication
Answer
112122
PROTEINS VERSUS NC Select three options. Proteins, unlike nucleic acids,
1) participate in the formation of the plasma membrane 2) are part of chromosomes 3) perform humoral regulation 4) perform a transport function 5) perform a protective function 6) transfer hereditary information from the nucleus to the ribosome
Answer
135
PROTEINS - LIPIDS - CARBOHYDRATES Establish a correspondence between the structural features and properties of a substance and a substance that has these features: 1) Proteins, 2) Carbohydrates, 3) Lipids, write down the numbers 1, 2 and 3 in the correct order.
A) Non-polar, insoluble in water B) Contains a glycerol residue C) The monomer is glucose D) The monomers are linked by a peptide bond E) They have enzymatic functions E) They are part of the cell walls of plant cells
Answer
332112
LIPIDS FUNCTIONS 1. Select three options. What functions do lipids perform in the body?
1) energy 2) propulsion 3) information 4) construction 5) protective 6) transport
Answer
145
2. Choose three correct answers out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated. The functions of lipids in the human body are:
1) catalytic 2) energy 3) construction 4) propulsion 5) transport 6) regulatory
Answer
236
LIPIDS EXAMPLES Choose three correct answers out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated. Which of the following substances are classified as lipids?
1) insulin 2) glycogen 3) triglycerides 4) cholesterol 5) testosterone 6) collagen
Answer
345
LIPIDS EXCEPT All but two of the following features can be used to determine the functions of lipids in a cell. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) storage 2) regulatory 3) transport 4) enzymatic 5) construction
Answer
34
LIPIDS METABOLISM Establish the correct sequence of fat metabolism in the human body, starting with their intake from food. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) formation of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids 2) synthesis of lipoids in body cells 3) processing of food fats by the enzyme lipase in the duodenum 4) generation of energy during the oxidation of substances to carbon dioxide and water 5) absorption of breakdown products into the lymphatic capillaries of the small intestine
Answer
31524
LIPIDS - CARBOHYDRATES 1. Establish a correspondence between the functions and substances: 1) carbohydrates, 2) lipids. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) ensure recognition of tissue cells of their own type B) form a double layer of membrane C) participate in hormonal regulation D) form the walls of plant cells E) protect the body from heat loss
Answer
12212
2. Establish a correspondence between the property or function of organic substances and their type: 1) lipids, 2) monosaccharides. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) soluble in water B) hydrophobic C) form the basis of cell membranes D) consist of glycerol and fatty acid residues E) are formed as a result of the breakdown of starch
Answer
21112
3. Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and groups of substances: 1) lipids, 2) carbohydrates. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) form glycocalyx B) create thermal insulation covers of the body C) non-polar hydrophobic substances D) colorless crystalline substances E) form the basis of cell membranes E) consist of residues of higher carboxylic acids and glycerol
Answer
211211
CARBOHYDRATES Choose three correct answers out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated. The functions of carbohydrates in the human body are
1) regulatory 2) energy 3) storage 4) construction 5) storage of genetic information 6) enzymatic
Answer
234
Choose three options. What carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides?
1) ribose 2) glucose 3) cellulose 4) fructose 5) starch 6) glycogen
Answer
124
MONOSUGAR - POLYSUGAR 1. Establish a correspondence between the characteristics of a carbohydrate and its group: 1) monosaccharide, 2) polysaccharide
A) is a biopolymer B) is hydrophobic C) is hydrophilic D) serves as a reserve nutrient in animal cells E) is formed as a result of photosynthesis E) is oxidized during glycolysis
Answer
221211
2. Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and groups of substances: 1) monosaccharides, 2) polysaccharides. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) participate in the synthesis of nucleic acids B) form a glycocalyx C) have molecules from three to seven carbon atoms D) form glucose during hydrolysis E) are a reserve substance in the cell E) have a sweet taste
Answer
121221
Establish a correspondence between the characteristics of carbohydrate molecules and their types: 1) cellulose, 2) glucose. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) monomer B) polymer C) soluble in water D) insoluble in water E) part of plant cell walls E) part of plant cell sap
Answer
212112
CARBOHYDRATES EXCEPT 1. All of the following characteristics, except two, can be used to determine the properties, structure and functions of polysaccharides in a cell. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) perform a storage function 2) perform catalytic and transport functions 3) consist of residues of amino acid molecules 4) perform an energy function 5) are part of cell walls
Answer
23
2. All of the characteristics listed below, except two, are used to describe the characteristics of polysaccharides. Identify two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) perform structural and storage functions 2) consist of amino acid residues 3) are hydrophobic 4) serve as enzymes 5) are part of the cell wall
Answer
24
3. All of the characteristics listed below are used to describe the functions of carbohydrates. Identify two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) form the cell walls of plants and fungi 2) accelerate metabolic processes 3) are stored in cells 4) serve as coenzymes 5) are part of nucleotides
Answer
24
STARCH EXCEPT 1. All but two of the following characteristics can be used to describe the starch molecule. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) consists of a single chain 2) is highly soluble in water 3) in combination with proteins forms a cell wall 4) undergoes hydrolysis 5) is a reserve substance in plant cells
Answer
23
2. All of the listed features, except two, can be used to describe a starch molecule. Identify two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) highly soluble in water 2) consists of glucose residues 3) has both branched and unbranched molecules 4) has a sweet taste 5) is a reserve substance in plants
Answer
14
CARBOHYDRATES METABOLISM Choose three correct answers out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated. What processes occur during the digestion of carbohydrates in the human digestive canal?
1) breakdown of monosaccharides with the formation of lactic acid 2) breakdown of monosaccharides to CO2 and H2O 3) breakdown of polysaccharides to disaccharides 4) formation of glycogen from glucose 5) conversion of disaccharides into monosaccharides 6) breakdown of fiber by microorganisms
Answer
356
CARBOHYDRATES METABOLISM SEQUENCE 1. Establish the sequence of processes of carbohydrate metabolism in the human body. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) absorption of monosaccharides into the intestinal villi 2) entry of monosaccharides into the body’s cells 3) synthesis of the body’s own polysaccharides 4) breakdown of polysaccharides in the digestive canal 5) entry of monosaccharides into the blood
Answer
41523
2. Establish the sequence of processes of carbohydrate metabolism in the human body. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) the entry of glucose into the cells of the body and a decrease in its concentration in the blood 2) the breakdown of starch by enzymes of digestive juices to glucose 3) increased secretion of insulin by the pancreas 4) the entry of starch into the body with food 5) the absorption of glucose and an increase in its concentration in the blood
Answer
42531
3. Determine the correct sequence of events that occur during the metabolism of carbohydrates in the human body, starting with the entry of food into the oral cavity. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) Oxidation of sugars in cells to carbon dioxide and water 2) Receipt of sugars into tissues 3) Absorption of sugars in the small intestine and their entry into the blood 4) Beginning of the breakdown of polysaccharides in the oral cavity 5) Final breakdown of carbohydrates into monosaccharides in the duodenum 6) Excretion from the body water and carbon dioxide
Answer
453216
CARBOHYDRATES - NC 1. Establish a correspondence between the features and types of molecules: 1) DNA, 2) polysaccharide. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) has the ability to replicate B) can form a branched structure C) consists of nucleotides D) is formed by combining simple carbohydrate molecules E) performs protective and energetic functions E) provides template synthesis of ribonucleic acids
Answer
121221
2. Establish a correspondence between the types of organic substances: 1) carbohydrates, 2) nucleic acids - and the functions they perform in the cell. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) energy storage B) signaling C) storage of genetic information D) energy transfer E) part of cell walls and membranes E) implementation of genetic information (protein synthesis)
Answer
112112
Analyze the table "Organic substances". For each cell indicated by a letter, select the corresponding term from the list provided and write down the selected numbers in the order corresponding to the letters.
1) acceleration of chemical reactions 2) chloroplasts 3) proteins 4) hormones 5) fats 6) nucleus 7) transmission of hereditary information vitamins
vitamins
Answer
357
Analyze the table “Major Organic Compounds”. For each cell indicated by a letter, select the corresponding term from the list provided.
1) Nucleic acids 2) 5-10% 3) Plastic, storage, protective 4) 0.2-2% 5) Proteins 6) Energy, plastic, storage, protective, regulatory
Answer
526
Analyze the table “Nutrient Requirements of the Body.” For each letter, select the corresponding term from the list provided.
1) carbohydrates 2) vitamins 3) tea, juices, soups 4) cereals, cereals, root vegetables 5) oils, eggs, dairy products 6) for tissue growth and regeneration 7) the main source of fast energy for transmitting nerve impulses and maintaining homeostasis
transmitting nerve impulses and maintaining homeostasis
Answer
256
Analyze the table "Organic substances". For each cell indicated by a letter, select the corresponding term from the list provided. Write down the selected numbers in the order corresponding to the letters.
1) energy, protective, construction 2) polysaccharides 3) replication 4) monosaccharides 5) structural, storage, transport 6) energy, storage, regulatory 7) regeneration denaturation
denaturation
Answer
481
Analyze the table “Organic substances of the cell.” For each cell indicated by a letter, select the corresponding term or concept from the list provided.
1) proteins 2) lipid 3) glycerol 4) fatty acids 5) nucleotide 6) storage and enzymatic 7) transport and protective energy
energy
Answer
158
Analyze the table “Cell Substances”. For each cell indicated by a letter, select the corresponding term from the list provided.
1) Nucleic acids 2) Energy, structural, regulatory and protective 3) Contains ribose 4) Water 5) Storage and transmission of hereditary information 6) Contains deoxyribose 7) High molecular weight nitrogen-containing biopolymers, the monomer of which are amino acids
Answer
472
All of the characteristics listed below, except two, are used to describe the molecules shown in the figure. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) serve as a structural component of membranes 2) accelerate chemical reactions 3) transmit signals in the body 4) hydrophilic 5) can serve as a supply of nutrients
Answer
24
Match the chemical compounds shown in the figure with their characteristics. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) amino acid B) nitrogenous base C) glycine D) adenine E) part of proteins E) part of nucleic acids
Answer
121212
Choose three options. What substances are classified as biopolymers?
1) starch 2) glycerol 3) glucose 4) proteins 5) DNA 6) fructose
Answer
145
Choose three options. What functions do carbohydrate and lipid molecules perform in a cell?
1) information 2) catalytic 3) construction 4) energy 5) storage 6) propulsion
Answer
345
What transformations of substances can occur in the human body? Choose three correct answers out of six. Write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) glycogen into glucose 2) fats into proteins 3) hormones into enzymes 4) fats into carbohydrates 5) hormones into vitamins 6) carbohydrates into fats
Answer
146
All of the following organic substances, except two, can perform an energy function. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list, and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in your answer.
1) glycogen 2) glucose 3) lipid 4) vitamin A 5) hemoglobin
Answer
45
© D.V. Pozdnyakov, 2009-2020