Table of composition (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) and calorie content of foods
For reference. Calorie content is the amount of energy received by a person as a result of the absorption of a particular product. The number of calories a person needs depends on the work performed, physical activity, gender, age, latitude (cold or hot climate). Like any fuel, food products, when burned in the body's furnace, release energy. Therefore, food has a certain energy value that can be measured (for example, in kilocalories or joules). Therefore, another name for the energy value of food products is calorie content. Each of us has more than once seen on the factory packaging of store-bought products a number that corresponds to the energy value of 100 g of this product. Anyone can calculate how much energy their body will receive after consuming a certain amount of a product.
Knowing someone's daily diet, that is, the number of foods eaten per day, including drinks, and their energy value, it is easy to calculate the amount of energy received - the calorie content of the daily diet. Biochemists and nutritionists have long calculated the calorie content and composition of almost all food products.
It is simply impossible to provide for all the variety of food. However, taking into account the information on food labels, calculating the calorie content of the daily diet does not present serious difficulties.
All about proteins, fats and carbohydrates
Probably many of you have heard more than once about such a strange abbreviation as “BZHU”. If you decipher it literally, you get “Proteins Fats Carbohydrates”. In this article you will learn everything you need to know about proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and dietary fiber.
Proteins - represent “The physiological norm of protein for an adult healthy person who is not engaged in physical labor or sports is 80-100 g (including 50% animal and 50% plant)”; they are some building materials that are needed for bone tissue , muscles, skin, blood and lymph. Moreover, protein has many important and beneficial properties, including: strengthening immunity, absorption of fats, vitamins and minerals, helping to produce hormones necessary for the body, and also providing energy (1 gram of protein provides 4 kcal).
In some cases, the body needs an increased amount of protein - during exhaustion, during the recovery period, after infectious diseases, with chronic infections (tuberculosis), with anemia, with gastrointestinal diseases associated with impaired absorption of nutrients, with blood loss. Protein restriction in the diet is recommended for kidney diseases, gastrointestinal ulcers, and gout.
Fats (lipids) - they provide more than 30% of the daily energy value of our diet (one gram of fat contains 9 kcal). On average, an adult needs 80-100 g of fat, 30 of which should be vegetable. Fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins (for example, D, A, E, K) necessary for the body are introduced with fats.
Fats are divided into three types: those that increase cholesterol (meat, lard, butter, dairy products), those that practically do not contribute to the formation of cholesterol (oysters, eggs, skinless poultry), those that reduce cholesterol (fish oil , fatty fish, unrefined vegetable oils).
Carbohydrates are all foods that contain starch and glucose. They provide more than half the calorie content of the daily diet. The average daily intake of carbohydrates is 300-500 g, depending on gender, age and physical activity.
Carbohydrates are divided into “good” and “bad”. “Good” carbohydrates include: beans, coarse grains, lentils, most fruits, vegetables and herbs. They do not cause a large increase in blood sugar. “Bad” carbohydrates include: sugar and sugar-containing products, white bread, rice, alcohol, corn, potatoes.
Vegetables and fruits can be divided into three categories based on their carbohydrate content:
- A) up to 5 grams of carbohydrates per 100 g of product - cucumbers, tomatoes, cabbage, zucchini, pumpkin, eggplant, lettuce, sorrel, greens, chicory leaves, mushrooms.
- B) up to 10 g of carbohydrates per 100 g of product - carrots, onions, radishes, beets, beans, citrus fruits, berries, apricots, pears, melons.
- C) more than 10 g of carbohydrates per 100 g of product - potatoes, corn, peas, bananas, grapes, pineapples, apples, dates, figs.
The most useful vegetables and fruits are raw and steamed, because... they retain more vitamins and minerals.
Carbohydrates are contained in all bakery products (they are much more abundant where high-grade flour is used), in grain crops (they are mainly more abundant in starch-containing products - corn, rice, semolina, etc.).
Insufficient consumption of carbohydrates may lead to problems with metabolic disorders of fats and proteins, accumulation of harmful products in the blood, incomplete oxidation of fatty acids, and decreased blood sugar levels.
Excessive consumption of foods high in carbohydrates can cause problems with metabolic disorders, obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis, blood clots in blood vessels, caries, and disruption of the immune system.
Dietary fiber - has no energy benefit, but plays an important role in the process of digestion and removal of waste from the body, prevents the deposition of fat, and contains vitamins and minerals.
Sources: bran, fruit peels, vegetables, legumes, whole grain products and sprouted grains.
Vegetables
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Eggplant | 91,0 | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,5 | 24 |
| Swede | 87,5 | 1,2 | 0,1 | 8,1 | 37 |
| Green peas | 80,0 | 5,0 | 0,2 | 13,3 | 72 |
| Zucchini | 93,0 | 0,6 | 0,3 | 5,7 | 27 |
| White cabbage | 90,0 | 1,8 | — | 5,4 | 28 |
| Red cabbage | 90,0 | 1,8 | — | 6,1 | 31 |
| Cauliflower | 90,9 | 2,5 | — | 4,9 | 29 |
| Potato | 76,0 | 2,0 | 0,1 | 19,7 | 83 |
| Green onion (feather) | 92,5 | 1,3 | — | 4,3 | 22 |
| Leek | 87,0 | 3,0 | — | 7,3 | 40 |
| Bulb onions | 86,0 | 1,7 | — | 9,5 | 43 |
| Red carrots | 88,5 | 1,3 | 0,1 | 7,0 | 33 |
| Ground cucumbers | 95,0 | 0,8 | — | 3,0 | 15 |
| Greenhouse cucumbers | 96,5 | 0,7 | — | 1,8 | 10 |
| Sweet green pepper | 92,0 | 1,3 | — | 4,7 | 23 |
| Sweet red pepper | 91,0 | 1,3 | — | 5,7 | 27 |
| Parsley (greens) | 85,0 | 3,7 | — | 8,1 | 45 |
| Parsley (root) | 85,0 | 1,5 | — | 11,0 | 47 |
| Rhubarb (petiole) | 94,5 | 0,7 | — | 2,9 | 16 |
| Radish | 93,0 | 1,2 | — | 4,1 | 20 |
| Radish | 88,6 | 1,9 | — | 7,0 | 34 |
| Turnip | 90,5 | 1,5 | — | 5,9 | 28 |
| Salad | 95,0 | 1,5 | — | 2,2 | 14 |
| Beet | 86,5 | 1,7 | — | 10,8 | 48 |
| Tomatoes (ground) | 93,5 | 0,6 | — | 4,2 | 19 |
| Tomatoes (greenhouse) | 94,6 | 0,6 | — | 2,9 | 14 |
| Green beans (pod) | 90,0 | 4,0 | — | 4,3 | 32 |
| Horseradish | 77,0 | 2,5 | — | 16,3 | 71 |
| Cheremsha | 89,0 | 2,4 | — | 6,5 | 34 |
| Garlic | 70,0 | 6,5 | — | 21,2 | 106 |
| Spinach | 91,2 | 2,9 | — | 2,3 | 21 |
| Sorrel | 90,0 | 1,5 | — | 5,3 | 28 |
Vitamins: fruits and vegetables
Choose vitamins, minerals and fiber. It is believed that fruits are the richest in vitamins, but they are not.
The pantry of vitamins is vegetables.
Consider the content of vitamin C: pear -5 mg, apple -13 mg, currant 200 mg, rose hips -450 mg, potatoes -60 mg, bell pepper -250 mg.
Potassium (Ka) and magnesium (Mg) are necessary for muscle function.
Potassium content: grapes - 255 mg, beef -334 mg, parsley - 554 mg, spinach -774 mg
Athletes eat bananas to restore potassium - 358 mg. For comparison, parsley and spinach contain more of it than bananas. When eating bananas, you gain excess carbohydrates, sucrose and fructose; spinach does not have this.
The human body has 2 sources of energy: glucose and fructose.
Glucose is a universal source of energy for cells. When it enters the body, it can be converted into muscle glycogen, which then serves as energy for the activity of muscle fibers.
Fructose does not accumulate in the muscles, it can only be absorbed by liver cells, where it is converted into liver glycogen and serves to maintain blood sugar levels between meals. It is important to understand that liver glycogen cannot be converted into muscle glycogen and vice versa. The liver reserve is limited and when it is saturated with glycogen, it turns into fats.
The norm of fructose per day is 40 mg, optimal 20 mg.
You can't eat a lot of fruit. The daily diet is 3 apples. Not at once! And we stretch it out throughout the day. It is advisable to eat yellow-green apples, as they contain less fructose.
During a diet, taste preferences change. The body itself gives signals which elements are missing. Eat what you want, you don’t have enough protein, you don’t have enough omega 3 or fatty acids. Therefore, you go and buy, for example, fish or turkey, cheese (contains casein, i.e. fat) or fruit.
We buy
Greens: onion (green), dill, parsley, lettuce, spinach.
Berries: currants, rose hips.
Raw vegetables: tomatoes, eggplants, zucchini, zucchini, cucumbers, fresh and pickled cabbage, radishes, daikon, cabbage, carrots, sweet peppers, seaweed, turnips, etc.
Salads: with carrots and cabbage without brine.
Mushrooms (stewed): champignons, wild mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, etc.
Frozen foods: Cauliflower, broccoli, green beans, green peas, etc.
Don’t forget to buy lemons to alkalize the body to kill germs. During alkalization, the body's endurance increases. Lemon is cut into a mug into 2-3 pieces and filled with water, this drink is drunk throughout the day.
Fruits and berries
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Apricots | 86,0 | 0,9 | — | 10,5 | 46 |
| Quince | 87,5 | 0,6 | — | 8,9 | 38 |
| Cherry plum | 89,0 | 0,2 | — | 7,4 | 34 |
| A pineapple | 86,0 | 0,4 | — | 11,8 | 48 |
| Bananas | 74,0 | 1,5 | — | 22,4 | 91 |
| Cherry | 85,5 | 0,8 | — | 11,3 | 49 |
| Pomegranate | 85,0 | 0,9 | — | 11,8 | 52 |
| Pear | 87,5 | 0,4 | — | 10,7 | 42 |
| Figs | 83,0 | 0,7 | — | 13,9 | 56 |
| Dogwood | 85,0 | 1,0 | — | 9,7 | 45 |
| Peaches | 86,5 | 0,9 | — | 10,4 | 44 |
| Rowan garden | 81,0 | 1,4 | — | 12,5 | 58 |
| Rowan chokeberry | 80,5 | 1,5 | — | 12,0 | 54 |
| Garden plum | 87,0 | 0,8 | — | 9,9 | 43 |
| Dates | 20,0 | 2,5 | — | 72,1 | 281 |
| Persimmon | 81,5 | 0,5 | — | 15,9 | 62 |
| Cherries | 85,0 | 1,1 | — | 12,3 | 52 |
| Mulberry | 82,7 | 0,7 | — | 12,7 | 53 |
| Apples | 86,5 | 0,4 | — | 11,3 | 46 |
| Orange | 87,5 | 0,9 | — | 8,4 | 38 |
| Grapefruit | 89,0 | 0,9 | — | 7,3 | 35 |
| Lemon | 87,7 | 0,9 | — | 3,6 | 31 |
| Mandarin | 88,5 | 0,8 | — | 8,6 | 38 |
| Cowberry | 87,0 | 0,7 | — | 8,6 | 40 |
| Grape | 80,2 | 0,4 | — | 17,5 | 69 |
| Blueberry | 88,2 | 1,0 | — | 7,7 | 37 |
| Blackberry | 88,0 | 2,0 | — | 5,3 | 33 |
| Strawberries | 84,5 | 1,8 | — | 8,1 | 41 |
| Cranberry | 89,5 | 0,5 | — | 4,8 | 28 |
| Gooseberry | 85,0 | 0,7 | — | 9,9 | 44 |
| Raspberries | 87,0 | 0,8 | — | 9,0 | 41 |
| Cloudberry | 83,3 | 0,8 | — | 6,8 | 31 |
| Sea buckthorn | 75,0 | 0,9 | — | 5,5 | 30 |
| White currant | 86,0 | 0,3 | — | 8,7 | 39 |
| Red currants | 85,4 | 0,6 | — | 8,0 | 38 |
| Black currant | 85,0 | 1,0 | — | 8,0 | 40 |
| Blueberry | 86,5 | 1,1 | — | 8,6 | 40 |
| Fresh rosehip | 66,0 | 1,6 | — | 24,0 | 101 |
| Dried rose hips | 14,0 | 4,0 | — | 60,0 | 253 |
Dried fruits
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Dried apricots | 18,0 | 5,0 | — | 67,5 | 278 |
| Dried apricots | 20,2 | 5,2 | — | 65,9 | 272 |
| Raisins with pit | 19,0 | 1,8 | — | 70,9 | 276 |
| Raisins sultanas | 18,0 | 2,3 | — | 71,2 | 279 |
| Cherry | 18,0 | 1,5 | — | 73,0 | 292 |
| Pear | 24,0 | 2,3 | — | 62,1 | 246 |
| Peaches | 18,0 | 3,0 | — | 68,5 | 275 |
| Prunes | 25,0 | 2,3 | — | 65,6 | 264 |
| Apples | 20,0 | 3,2 | — | 68,0 | 273 |
Dairy products.
Dairy products, like cottage cheese, contain monosodium glutamate. Don't be scared! Cottage cheese contains 7 times more monosodium glutamate than the same amount of chips.
When buying cottage cheese, choose a minimum of fats and carbohydrates and a maximum of protein.
Cottage cheese on sale varies in fat content and comes from different manufacturers. If the amount of fats, proteins and carbohydrates is approximately the same from several manufacturers, choose the cottage cheese that you like best.
Cottage cheese with 2.5% fat content is quite suitable. Other milk: yogurt, kefir, bifidok, etc. are chosen based on the principle of more protein and less fat and carbohydrates.
Candy, sugar, chocolate
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Honey | 17,2 | 0,8 | 0 | 80,3 | 308 |
| Fruit dragee | 7 | 3,7 | 10,2 | 73,1 | 384 |
| Marshmallow | 20 | 0,8 | 0 | 78,3 | 299 |
| Iris | 6,5 | 3,3 | 7,5 | 81,8 | 387 |
| Marmalade | 21 | 0 | 0,1 | 77,7 | 296 |
| Caramel (average) | 4,4 | 0 | 0,1 | 77,7 | 296 |
| Chocolate coated candies | 7,9 | 2,9 | 10,7 | 76,6 | 396 |
| Paste | 18 | 0,5 | 0 | 80,4 | 305 |
| Sugar | 0,2 | 0,3 | 0 | 99,5 | 374 |
| Tahini halva | 3,9 | 12,7 | 29,9 | 50,6 | 510 |
| Sunflower halva | 2,9 | 11,6 | 29,7 | 54 | 516 |
| Dark chocolate | 0,8 | 5,4 | 35,3 | 52,6 | 540 |
| Milk chocolate | 0,9 | 6,9 | 35,7 | 52,4 | 547 |
Features of fats
Fats are the most important source of energy and the production of fat-soluble vitamin components (A, D, E). In addition, they provide the supply of unsaturated fatty acids, which are extremely important for lipid metabolism. Of the fats of animal origin, the most beneficial are fish or poultry fats.
Animal fats, in particular beef, lamb or pork, are predominantly refractory. They are much less digestible and contain cholesterol in larger quantities, which fully affects the formation of vascular sclerosis. Oils of vegetable origin (in particular, sunflower, corn or olive) are included in nuts and seeds. In addition, it is necessary to take into account that they are saturated with fatty acids and vitamin E.
Heat treatment provokes their partial loss, and therefore it will be much more useful to use vegetable oils in addition to salads. Milk fat is found in hard cheeses, sour cream, and the same applies to cream or butter. We should not forget that fats contain twice as many calories as proteins or carbohydrates.
Cakes and other confectionery products
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Waffles with fruit fillings | 12 | 3,2 | 2,8 | 80,1 | 342 |
| Waffles with fat-containing fillings | 1 | 3,4 | 30,2 | 64,7 | 530 |
| Puff pastry with cream | 9 | 5,4 | 38,6 | 46,4 | 544 |
| Puff pastry with apple | 13 | 5,7 | 25,6 | 52,7 | 454 |
| Sponge cake with fruit filling | 21 | 4,7 | 9,3 | 84,4 | 344 |
| Gingerbread | 14,5 | 4,8 | 2,8 | 77,7 | 336 |
| Sponge cake with fruit filling | 25 | 4,7 | 20 | 49,8 | 386 |
| Almond cake | 9,3 | 6,6 | 35,8 | 46,8 | 524 |
Food for weight loss: planning correctly
The very first thing you need to start with when planning a diet for weight loss is to understand what amount of food for you personally will contribute to safe weight loss.
In other words, it is necessary to determine the daily caloric intake for the period of weight loss, which, on the one hand, will create the necessary energy deficit, and on the other, will not lead to malnutrition, which can result in a slowdown in metabolism and constant hunger. Details on how to make such a calculation are written here. If something doesn't work out or you have questions, please consult me.
So, the total caloric content was determined. Now it is important to properly distribute it among meals. Ideally, the distribution should look like this:
- Breakfast – from 20 to 25%
- First snack – from 10 to 15%
- Lunch – from 30 to 35%
- Second snack – from 10 to 15%
- Dinner – from 15 to 20%
How to calculate these percentages? Let's assume that your daily caloric intake is 1200 kcal, which means that breakfast can account for from 240 (20%) to 300 (25%) kilocalories of your daily diet.
Please note that the first half of the day (breakfast, first snack and lunch) accounts for most of the total food intake for the day.
As a rule, before 15-16 hours our metabolism is set to expend energy coming from food, and after 16, on the contrary, to accumulate it. Therefore, try to adhere to the general rule - dinner should not be the largest meal. “Favorite harmful foods” - sweets, cakes and other delicacies, it is also better to eat before 16:00.
If you do not skip any meals (and this is highly undesirable), you will eat at intervals of 3-4 hours. This is a very good eating rhythm for weight loss. On the one hand, you maintain the rate of metabolic processes at a high level (accelerate metabolism), on the other hand, you prevent the development of strong hunger and appetite, which is often difficult to control.
This is fractional nutrition. As you can see, everything is quite simple. The main thing is to start, and soon this rhythm of eating will become a habit.
Bread, bakery products, flour
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Rye bread | 42,4 | 4,7 | 0,7 | 49,8 | 214 |
| Wheat bread from grade I flour | 34,3 | 7,7 | 2,4 | 53,4 | 254 |
| Butter pastries | 26,1 | 7,6 | 4,5 | 60,0 | 297 |
| Baranki | 17,0 | 10,4 | 1,3 | 68,7 | 312 |
| Drying | 12,0 | 11,0 | 1,3 | 73,0 | 330 |
| Wheat crackers | 12,0 | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,4 | 331 |
| Cream crackers | 8,0 | 8,5 | 10,6 | 71,3 | 397 |
| Premium wheat flour | 14,0 | 10,3 | 0,9 | 74,2 | 327 |
| Wheat flour, grade I | 14,0 | 10,6 | 1,3 | 73,2 | 329 |
| Wheat flour, grade II | 14,0 | 11,7 | 1,8 | 70,8 | 328 |
| Rye flour | 14,0 | 6,9 | 1,1 | 76,9 | 326 |
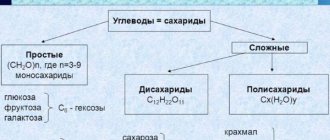
Types of carbohydrates
Depending on their size, carbohydrate molecules can be simple or complex.
- Simple carbohydrates: Various types of sugars, such as glucose and sucrose (table sugar), are simple carbohydrates. These are small molecules, so they are quickly absorbed by the body and are a quick source of energy. They quickly increase blood glucose (blood sugar) levels. Fruits, dairy products, honey and maple syrup contain large amounts of simple carbohydrates, which provide the sweet taste in most candies and cakes.
- Complex carbohydrates: These carbohydrates are made up of long strings of simple carbohydrates. Because complex carbohydrates are large molecules, they must be broken down into simple molecules before they can be absorbed. Thus, they tend to provide energy to the body more slowly than plain ones, but still faster than protein or fat. This is because they are digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates and are less likely to be converted into fat. They also raise blood sugar at a slower rate and at lower levels than plain ones, but for a longer period of time. Complex carbohydrates include starches and proteins, which are found in wheat products (bread and pasta), other grains (rye and corn), beans and root vegetables (potatoes).
Carbohydrates can be:
- refined
- unrefined
Refined – processed foods , the fibers and bran, as well as many of the vitamins and minerals they contain, have been removed. Thus, metabolism processes these carbohydrates quickly and provides little nutrition even though they contain about the same amount of calories. Refined foods are often fortified, meaning vitamins and minerals are added artificially to increase nutritional value. Diets high in simple or refined carbohydrates tend to increase the risk of obesity and diabetes.
Unrefined carbohydrates from plant foods. They contain carbohydrates in the form of starch and fiber. These are foods such as potatoes, whole grains, vegetables, fruits.
If people consume more carbohydrates than they need, the body stores some of these carbohydrates in cells (as glycogen) and converts the rest into fat. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that can be converted into energy and is stored in the liver and muscles. Muscles use glycogen energy during periods of intense exercise. The amount of carbohydrates stored as glycogen can provide calories for the day. Several other body tissues store complex carbohydrates that cannot be used as a source of energy for the body.
Most nutritionists recommend that about 50 – 55% of your total daily calories should come from carbohydrates.
Glycemic index of carbohydrates
The glycemic index of carbohydrates measures how quickly consuming them raises your blood sugar levels. Values range from 1 (slowest absorption) to 100 (fastest, pure glucose index). However, how quickly levels actually rise depends on the foods ingested.
The glycemic index is generally lower for complex carbohydrates than for simple carbohydrates, but there are exceptions. For example, fructose (the sugar in fruits) has little effect on blood sugar levels.
The glycemic index is influenced by food processing technology and composition:
- Processing: Processed, chopped or finely ground foods tend to have a high glycemic index
- type of starch: Different types of starch are absorbed differently. Potato starch is digested and relatively quickly absorbed into the blood. Barley is digested and absorbed much more slowly.
- Fiber Content: The more fiber a food has, the harder it is to digest. As a result, sugar is absorbed into the blood more slowly
- fruit ripeness: the ripe the fruit, the more sugar it contains and the higher its glycemic index
- fat or acid content: food contains more fat or acid, is slowly digested and its sugars are slowly absorbed into the blood
- Cooking: How food is prepared can affect how quickly it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Generally, cooking or grinding food increases its glycemic index because it is easier to digest and absorb after the cooking process.
- Other factors : The body's nutritional processes vary from person to person, how quickly carbohydrates are affected by conversion to sugar and absorption. How well the food is chewed and how quickly it is swallowed is important.
Glycemic index of some foods
| Products | Compound | Index |
| Beans | Bean seeds | 33 |
| Red lentils | 27 | |
| Soybeans | 14 | |
| Bread | Rye bread | 49 |
| White | 69 | |
| Whole wheat | 72 | |
| Cereals | All bran | 54 |
| Cornflakes | 83 | |
| Oatmeal | 53 | |
| Rice | 90 | |
| Shredded wheat | 70 | |
| Dairy | Milk, ice cream and yogurt | 34 – 38 |
| Fruits | Apple | 38 |
| Banana | 61 | |
| Mandarin | 43 | |
| Orange juice | 49 | |
| Strawberry | 32 | |
| Corn | Barley | 22 |
| Brown rice | 66 | |
| White rice | 72 | |
| Pasta | — | 38 |
| Potato | Instant puree (via blender) | 86 |
| Puree | 72 | |
| Sweet puree | 50 | |
| Snacks | Corn chips | 72 |
| Oatmeal cookies | 57 | |
| Potato chips | 56 | |
| Sugar | Fructose | 22 |
| Glucose | 100 | |
| Honey | 91 | |
| Rafinated sugar | 64 |
The glycemic index is an important parameter because carbohydrates increase blood sugar, if quickly (with a high glycemic index) then insulin levels increase. An increase in insulin can lead to low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and hunger, which tends to consume excess calories and gain weight.
Carbohydrates with a low glycemic index do not increase insulin levels much. As a result, people feel fuller longer after eating. Consuming carbohydrates with a low glycemic index also leads to healthier cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of obesity and diabetes in people with diabetes, the risk of complications due to diabetes.
Despite the link between low glycemic index foods and improved health, using the index to select foods does not automatically lead to healthy eating.
For example, high glycemic index potato chips and some candies are not healthy food choices, but some high glycemic index foods contain valuable vitamins and minerals.
Therefore, the glycemic index should only be used as a general guide for food selection.
Glycemic load of foods
The glycemic index shows how quickly carbohydrates in food are absorbed into the blood. It does not include the amount of carbohydrates in the food, which is important.
Glycemic load, a relatively new term, includes the glycemic index and the amount of carbohydrates in a food.
Foods such as carrots, bananas, watermelon or wholemeal bread may have a high glycemic index, but contain relatively few carbohydrates and thus have a low glycemic load of foods. Such foods have little effect on blood sugar levels.
Cereals
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Buckwheat core | 14,0 | 12,6 | 2,6 | 68,0 | 329 |
| Buckwheat done | 14,0 | 9,5 | 1,9 | 72,2 | 326 |
| Manna | 14,0 | 11,3 | 0,7 | 73,3 | 326 |
| Oatmeal | 12,0 | 11,9 | 5,8 | 65,4 | 345 |
| Pearl barley | 14,0 | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 324 |
| Millet | 14,0 | 12,0 | 2,9 | 69,3 | 334 |
| Rice | 14,0 | 7,0 | 0,6 | 73,7 | 323 |
| Wheat "Poltavskaya" | 14,0 | 12,7 | 1,1 | 70,6 | 325 |
| Oatmeal | 10,0 | 12,2 | 5,8 | 68,3 | 357 |
| Barley | 14,0 | 10,4 | 1,3 | 71,7 | 322 |
| Hercules | 12,0 | 13,1 | 6,2 | 65,7 | 355 |
| Corn | 14,0 | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 325 |
The ideal balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the diet
The combination of these power components may vary in some details. It is believed that the average person of normal build (who does not strive to lose weight or gain weight) needs to compose his diet in such a way that half of the components entering the body per day are represented by carbohydrates, a third by proteins, and a fifth by fats. Thus, a normal balanced diet is represented by the formula BZHU 30% -20% -50%. However, a wide variety of variations are possible, for example:
- low carbohydrate - 40% protein, 25% fat, 35% carbohydrates,
- drying - 80% proteins, 10% fats, 10% carbohydrates.
The simplest way to understand the formula of a balanced diet and its subsequent implementation is to conditionally divide the dish into 6 sectors, three of which must be allocated for carbohydrates, two for proteins and one for fats.
You can take a more complicated route - calculate the allowable amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates per day using the following formula. 1 gram of proteins and carbohydrates contains 4 kcal, 1 gram of fat contains 9 kcal. Per day, for example, to maintain weight, a person needs to consume 2000 kcal (for weight loss, 15-20% less is needed, and for weight gain, 15-20% less). Using the formula, you can calculate the number of individual components in grams:
- proteins: (2000*0.3)/4kcal=150 grams of protein;
- fats: (2000*0.2)/9 = 44 grams of fat;
- carbohydrates: (2000*0.5)/4 = 250 grams of carbohydrates.
This means that to maintain a weight that suits you, you need to consume 150 grams of protein, 44 grams of fat and 250 grams of carbohydrates per day. However, when calculating daily calorie intake, it is necessary to take into account the level of physical activity.
Legumes
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Beans | 83,0 | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,3 | 58 |
| Peas | 14,0 | 23,0 | 1,6 | 57,7 | 323 |
| Whole peas | 14,0 | 23,0 | 1,2 | 53,3 | 303 |
| Soybeans | 12,0 | 34,9 | 17,3 | 26,5 | 395 |
| Beans | 14,0 | 22,3 | 1,7 | 54,5 | 309 |
| Lentils | 14,0 | 24,8 | 1,1 | 53,7 | 310 |
Mushrooms
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| White fresh | 89,9 | 3,2 | 0,7 | 1,6 | 25 |
| White dried | 13,0 | 27,6 | 6,8 | 10,0 | 209 |
| Fresh boletus | 91,6 | 2,3 | 0,9 | 3,7 | 31 |
| Fresh boletuses | 91,1 | 3,3 | 0,5 | 3,4 | 31 |
| Fresh russula | 83,0 | 1,7 | 0,3 | 1,4 | 17 |
What should you eat for effective and safe weight loss?
Food for proper weight loss should provide the body with all the necessary micro and macro nutrients. In other words, consist of the correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Very few foods consist of proteins, fats or carbohydrates alone. So, for example, an exclusively protein product is squid and some other types of seafood; all types of vegetable oils and animal fats (lard, butter) consist exclusively of fats; only carbohydrates are included in sugar.
The composition of the overwhelming majority of products includes all of the specified nutritional components, therefore, the division of products into protein or carbohydrate is quite arbitrary and is based on the component that predominates in their composition. Thus, protein components include meat and fish, carbohydrates include cereals, vegetables, pasta, and bread, despite the fact that they contain both fats and proteins.
Meat, offal, poultry
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Mutton | 67,6 | 16,3 | 15,3 | 0,0 | 203 |
| Beef | 67,7 | 18,9 | 12,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| horsemeat | 72,5 | 20,2 | 7,0 | 0,0 | 143 |
| Rabbit | 65,3 | 20,7 | 12,9 | 0,0 | 199 |
| Pork lean | 54,8 | 16,4 | 27,8 | 0,0 | 316 |
| Pork is fatty | 38,7 | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| Veal | 78,0 | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| Lamb Kidneys | 79,7 | 13,6 | 2,5 | 0,0 | 77 |
| Lamb Liver | 71,2 | 18,7 | 2,9 | 0,0 | 101 |
| Lamb Heart | 78,5 | 13,5 | 2,5 | 0,0 | 82 |
| Beef Brains | 78,9 | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| Beef liver | 72,9 | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| Beef Kidneys | 82,7 | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| Beef Udder | 72,6 | 12,3 | 13,7 | 0,0 | 173 |
| Beef Heart | 79,0 | 15,0 | 3,0 | 0,0 | 87 |
| Beef Tongue | 71,2 | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| Pork kidneys | 80,1 | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| Pork liver | 71,4 | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| Pig heart | 78,0 | 15,1 | 3,2 | 0,0 | 89 |
| Pig tongue | 66,1 | 14,2 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 208 |
| Geese | 49,7 | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
| Turkey | 64,5 | 21,6 | 12,0 | 0,8 | 197 |
| Chickens | 68,9 | 20,8 | 8,8 | 0,6 | 165 |
| Chickens | 71,3 | 18,7 | 7,8 | 0,4 | 156 |
| Ducks | 51,5 | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
Sausage and sausage products
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Boiled sausage Diabetic | 62,4 | 12,1 | 22,8 | 0 | 254 |
| Boiled sausage Dietary | 71,6 | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0 | 170 |
| Boiled sausage Doctorskaya | 60,8 | 13,7 | 22,8 | 0 | 260 |
| Boiled sausage Lyubitelskaya | 57,0 | 12,2 | 28,0 | 0 | 301 |
| Boiled sausage Milk | 62,8 | 11,7 | 22,8 | 0 | 252 |
| Boiled sausage Separate | 64,8 | 10,1 | 20,1 | 1,8 | 228 |
| Boiled veal sausage | 55,0 | 12,5 | 29,6 | 0 | 316 |
| Pork sausages | 53,7 | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| Dairy sausages | 60,0 | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0 | 277 |
| Russian sausages | 66,2 | 12,0 | 19,1 | 0 | 220 |
| Pork sausages | 54,8 | 11,8 | 30,8 | 0 | 324 |
| Boiled-smoked Amateur | 39,1 | 17,3 | 39,0 | 0 | 420 |
| Boiled-smoked Cervelat | 39,6 | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0 | 360 |
| Semi-smoked Krakow | 34,6 | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0 | 466 |
| Semi-smoked Minsk | 52,0 | 23,0 | 17,4 | 2,7 | 259 |
| Semi-smoked Poltavskaya | 39,8 | 16,4 | 39,0 | 0 | 417 |
| Semi-smoked Ukrainian | 44,4 | 16,5 | 34,4 | 0 | 376 |
| Raw smoked Amateur | 25,2 | 20,9 | 47,8 | 0 | 514 |
| Raw smoked Moscow | 27,6 | 24,8 | 41,5 | 0 | 473 |
Canned meat and smoked meats
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Beef stew | 63,0 | 16,8 | 18,3 | 0 | 232 |
| Tourist breakfast (beef) | 66,9 | 20,5 | 10,4 | 0 | 176 |
| Tourist breakfast (pork) | 65,6 | 16,9 | 15,4 | 0 | 206 |
| Sausage mince | 63,2 | 15,2 | 15,7 | 2,8 | 213 |
| Pork stew | 51,1 | 14,9 | 32,2 | 0 | 349 |
| Raw smoked brisket | 21,0 | 7,6 | 66,8 | 0 | 632 |
| Raw smoked loin | 37,3 | 10,5 | 47,2 | 0 | 467 |
| Ham | 53,5 | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0 | 279 |
Fats, margarine, butter
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Rendered lamb or beef fat | 0,3 | 0 | 99,7 | 0 | 897 |
| Pork bacon (without skin) | 5,7 | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0 | 816 |
| Milk margarine | 15,9 | 0,3 | 82,3 | 1 | 746 |
| Sandwich margarine | 15,8 | 0,5 | 82 | 1,2 | 744 |
| Mayonnaise | 25 | 3,1 | 67 | 2,6 | 627 |
| Vegetable oil | 0,1 | 0 | 99,9 | 0 | 899 |
| Butter | 15,8 | 0,6 | 82,5 | 0,9 | 748 |
| Ghee | 1 | 0,3 | 98 | 0,6 | 887 |
Proteins fats carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, according to many well-known nutritionists, should make up at least half of the calorie content of the daily diet. They are found in foods in the form of simple sugars, starches or fiber. There are a lot of ordinary carbohydrates in honey, fresh fruits, natural milk, sugar, grains, complex carbohydrates - in potatoes, regular boiled rice, pasta, bread and legumes. It is better to consume foods that contain a lot of simple/regular carbohydrates (for example, a variety of sweets, cakes) as little as possible. Otherwise, proper nutrition will no longer be so correct, and the ideal figure may deviate slightly from the ideal. Read more on the website healthy-news.ru. Eat more fresh fruits and natural foods rich in starch and fiber, but slowly, at regular intervals, so as not to immediately increase the amount of glucose in your blood.
Proteins perform many different functions in the human body, they are involved in:
- in cell regeneration,
- in the creation of enzymes,
- in the production of hormones and other antibodies, etc.
In addition, proteins serve as the main source of energy if our body lacks it. The main source of proteins and amino acids necessary for humans are products of animal origin, that is, meat. Unlike plant foods, these foods contain all the amino acids.
True, it is possible to choose an exclusively plant-based diet that will reward a vegetarian with a complete set of all important proteins. Nutritionists believe that on the calorie scale, protein should make up 10-15% of the nutritious daily diet. Both lack and excess of protein are dangerous to health. Proper nutrition is based on the rational use of all products, on an optimal menu. Fats perform two important functions in our body; they take part in the construction of cell membranes and at the same time serve as the main energy reserve for the body's cells. In addition, they form vitamins and some important hormones.
Fats can be saturated as well as unsaturated. Saturated fats are solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fats are liquid. Please note that our smart body can synthesize saturated fats on its own, so it is not necessary to include them in your daily diet. The body needs unsaturated fats for the constant construction of new cells. In the daily diet, fish and vegetable fats are always more preferable and healthy; it is better to abstain as much as possible from animal fats. Remember that proper nutrition is the key to an ideal figure. Perhaps not all food is tasty, but it is healthy.
Milk and dairy products
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Cow's milk cheese | 52,0 | 17,9 | 20,1 | 0,0 | 260 |
| Natural yoghurt 1.5% fat | 88,0 | 5,0 | 1,5 | 3,5 | 51 |
| Low-fat kefir | 91,4 | 3,0 | 0,1 | 3,8 | 30 |
| Full fat kefir | 88,3 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,1 | 59 |
| Milk | 88,5 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,7 | 58 |
| Acidophilus milk | 81,7 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 10,8 | 83 |
| Whole milk powder | 4,0 | 25,6 | 25,0 | 39,4 | 475 |
| Condensed milk | 74,1 | 7,0 | 7,9 | 9,5 | 135 |
| Condensed milk with sugar | 26,5 | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 315 |
| Curdled milk | 88,4 | 2,8 | 3,2 | 4,1 | 58 |
| Ryazhenka | 85,3 | 3,0 | 6,0 | 4,1 | 85 |
| Cream 10% | 82,2 | 3,0 | 10,0 | 4,0 | 118 |
| Cream 20% | 72,9 | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,6 | 205 |
| Sour cream 10% | 82,7 | 3,0 | 10,0 | 2,9 | 116 |
| Sour cream 20% | 72,7 | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| Special cheeses and curd mass | 41,0 | 7,1 | 23,0 | 27,5 | 340 |
| Russian cheese | 40,0 | 23,4 | 30,0 | 0,0 | 371 |
| Dutch cheese | 38,8 | 26,8 | 27,3 | 0,0 | 361 |
| Swiss cheese | 36,4 | 24,9 | 31,8 | 0,0 | 396 |
| Poshekhonsky cheese | 41,0 | 26,0 | 26,5 | 0,0 | 334 |
| Processed cheese | 55,0 | 24,0 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 226 |
| Fat cottage cheese | 64,7 | 14,0 | 18,0 | 1,3 | 226 |
| Cottage cheese semi-fat | 71,0 | 16,7 | 9,0 | 1,3 | 156 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 77,7 | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,5 | 86 |
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in foods are the main source of energy. Their main task is to allow the brain and muscles to work normally and cope with the necessary loads and energy costs. They form important enzymes and hormones.
Carbohydrates are found in foods in the form of glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, fiber, pectin, starch and glycogen. They can be grouped into:
- simple – greatly raise blood sugar levels;
- complex – slightly raise blood sugar levels.
The glycemic index (GI) is responsible for the ability of food to raise blood sugar levels. This makes it the most important indicator of every carbohydrate product. To improve the quality of nutrition you need:
- choose foods with a lower GI content;
- eat foods with high GI in smaller quantities.
This will allow you to receive the microelements the body needs, reduce the risk of diseases and lead a full, active life.
The metabolism of carbohydrates is determined by the glucose content in the blood, i.e. on the time and nutritional composition of the last meal. The blood glucose level is minimal in the morning after sleep, during which its level was not maintained.
Once you wake up, the body is in the best condition to use stored fat as an energy source, so walking and aerobics before breakfast are important.
The formation of reserves of carbohydrates entering the body in the form of intramuscular glycogen is observed when they are taken in the first half of the day. This leads to the recommendation to consume the bulk of carbohydrates before evening. In addition to providing energy, carbohydrates help build muscle and burn fat.
To build 1 kg of muscle mass, a large amount of energy is expended - approximately 5000 kcal. After this, daily maintenance of a more energy-consuming body is required. Carbohydrates provide energy to cells most quickly and the body prefers them to fats and protein. This allows proteins to perform their main function - building and repairing body tissue, including muscle.
During weight loss, the body converts fat into energy inside its cells. This process depends on the lack of the required amount of energy, which requires the use of one’s own reserves. However, even in this case, a certain part of carbohydrates is necessary to maintain basic processes and break down fat.
Since excessive and low consumption of carbohydrates leads to negative consequences, it is important to find your optimal amount. Feeling good will be a sign of how correct the chosen diet is.
Foods containing carbohydrates
Foods containing complex carbohydrates and low GI include:
- various cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal);
- vegetables (green peas, cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, etc.);
- individual fruits (figs, oranges, grapefruit, etc.);
- some sweets (marshmallows, butter cookies, etc.).
Almost all sweets, fruits and berries are simple carbohydrates and have a high GI value.
Eggs
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Chicken egg | 74,0 | 12,7 | 11,5 | 0,7 | 157 |
| Egg powder | 6,8 | 45 | 37,3 | 7,1 | 542 |
| Protein powder | 12,1 | 73,3 | 1,8 | 7 | 336 |
| Dry yolk | 5,4 | 34,2 | 52,2 | 4,4 | 623 |
| Quail egg | 73,3 | 11,9 | 13,1 | 0,6 | 168 |
Fish and seafood
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Gobies | 70,8 | 12,8 | 8,1 | 5,2 | 145 |
| Pink salmon | 70,5 | 21 | 7 | 0 | 147 |
| Flounder | 79,5 | 16,1 | 2,6 | 0 | 88 |
| crucian carp | 78,9 | 17,7 | 1,8 | 0 | 87 |
| Carp | 79.1 | 16 | 3.6 | 0 | 96 |
| Chum salmon | 71.3 | 22 | 5.6 | 0 | 138 |
| Smelt | 79.8 | 15.5 | 3.2 | 0 | 91 |
| Icy | 81.8 | 15.5 | 1.4 | 0 | 75 |
| Bream | 77.7 | 17.1 | 4.1 | 0 | 105 |
| Salmon | 62.9 | 20.8 | 15.1 | 0 | 219 |
| Macrurus | 85 | 13.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 60 |
| Lamprey | 75 | 14.7 | 11.9 | 0 | 166 |
| Pollock | 80.1 | 15.9 | 0.7 | 0 | 70 |
| capelin | 75 | 13.4 | 11.5 | 0 | 157 |
| Navaga | 81.1 | 16.1 | 1 | 0 | 73 |
| Burbot | 79.3 | 18.8 | 0.6 | 0 | 81 |
| Marbled notothenia | 73.4 | 14.8 | 10.7 | 0 | 156 |
| Sea bass | 75.4 | 17.6 | 5.2 | 0 | 117 |
| River perch | 79.2 | 18.5 | 0.9 | 0 | 82 |
| Sturgeon | 71.4 | 16.4 | 10.9 | 0 | 164 |
| Halibut | 76.9 | 18.9 | 3 | 0 | 103 |
| Blue whiting | 81.3 | 16.1 | 0.9 | 0 | 72 |
| Saber fish | 75.2 | 20.3 | 3.2 | 0 | 110 |
| Caspian fisherman | 77 | 19.2 | 2.4 | 0 | 98 |
| Carp | 75.3 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 0 | 121 |
| Large saury | 59.8 | 18.6 | 20.8 | 0 | 262 |
| Small saury | 71.3 | 20.4 | 0.8 | 0 | 143 |
| Salaka | 75.4 | 17.3 | 5.6 | 0 | 121 |
| Herring | 62.7 | 17.7 | 19.5 | 0 | 242 |
| Whitefish | 72.3 | 19 | 7.5 | 0 | 144 |
| Mackerel | 71.8 | 18 | 9 | 0 | 153 |
| Som | 75 | 16.8 | 8.5 | 0 | 144 |
| Horse mackerel | 74.9 | 18.5 | 5 | 0 | 119 |
| Sterlet | 74.9 | 17 | 6.1 | 0 | 320 |
| Zander | 78.9 | 19 | 0.8 | 0 | 83 |
| Cod | 80.7 | 17.5 | 0.6 | 0 | 75 |
| Tuna | 74 | 22,7 | 0,7 | 0 | 96 |
| coal fish | 71.5 | 13.2 | 11.6 | 0 | 158 |
| Sea eel | 77.5 | 19.1 | 1.9 | 0 | 94 |
| Acne | 53.5 | 14.5 | 30.5 | 0 | 333 |
| Hake | 79.9 | 16.6 | 2.2 | 0 | 86 |
| Pike | 70.4 | 18.8 | 0.7 | 0 | 82 |
| Ide | 80.1 | 18.2 | 0.3 | 0 | 117 |
| Far Eastern shrimp | 64,8 | 28,7 | 1,2 | 0 | 134 |
| Cod liver | 26,4 | 4,2 | 65,7 | 0 | 613 |
| Squid | 80,3 | 18 | 0,3 | 0 | 75 |
| Crab | 81,5 | 16 | 0,5 | 0 | 69 |
| Shrimp | 77,5 | 18 | 0,8 | 0 | 83 |
| Sea kale | 88 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 3,0 | 5 |
| Pasta "Ocean" | 72,2 | 18,9 | 6,8 | 0 | 137 |
| Trepang | 89,4 | 7,3 | 0,6 | 0 | 35 |
Caviar
| Product | Water, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | kcal |
| Chum salmon granular | 46,9 | 31,6 | 13,8 | 0 | 251 |
| Bream punch | 58 | 24,7 | 4,8 | 0 | 142 |
| Pollock punch | 63,2 | 28,4 | 1,9 | 0 | 131 |
| Sturgeon granular | 58 | 28,9 | 9,7 | 0 | 203 |
| Sturgeon punch | 39,5 | 36 | 10,2 | 0 | 123 |
Principles of nutrition
The diet should be complete, namely balanced in the number of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It is also equally important that the menu for diabetes contains a sufficient number of vitamin components and microelements.
The next principle is that the caloric content of food consumed must correspond to energy expenditure. This is what will make it possible to ensure an optimal degree of performance and maintain optimal body weight, which is also very important for any diabetic.
The diet over a 24-hour period is strongly recommended to be distributed taking into account the duration of action and the total period of time to achieve the maximum possible hypoglycemic effect of insulin. The same applies to tablet medications, which are aimed at ensuring optimal blood sugar levels. And, of course, we should not forget that food should be as varied as possible, nutritious and simply enjoyable - all this affects the digestion process.
The food each of us eats includes proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as vitamins, minerals and water. In the process of assimilation of food, the amount of energy necessary for the optimal functioning of the body is released. We are talking, in particular, about maintaining optimal body temperature, breathing, and blood circulation.
No less important is the replenishment of energy costs that are associated with the implementation of any work.
Experts point out that:
- the energy contained in food is expressed in kilocalories, which are designated as kcal;
- in the process of breaking down 1 g of carbohydrate and 1 g of protein, 4 kcal are released. While 1 g of fat can provide a person with 9 kcal of energy, which is very important for diabetes;
- the combination and total amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the diet for a given disease should meet all the needs of even a healthy person.
How is parsley used for type 2 diabetes?
As part of the compensation, 50 or 60% of daily calorie needs are met from carbohydrate foods. From 15 to 20% - from protein foods and no more than 25, but not less than 30% - from fats. At the same time, if overweight is identified, it is strongly recommended to reduce the daily calorie ratio by minimizing fat intake.