Publication date: December 24, 2021.
Sumo squats are squats with a wide stance and toes turned outwards, which allow you to load the muscles of the buttocks and inner thighs.
They are very similar to plie squats. Many people do not distinguish between these two exercises at all.
We will consider sumo squats to be squats in which the legs are located at the maximum distance from each other, and the toes point forward and to the sides.
Accordingly, plie squats are an exercise that involves a less wide stance of the legs.
Contraindications to squats
Such exercises are contraindicated for problems with the lower back, spine and knees.
You also don’t need to do it if you have weak core muscles. In any case, the load on such areas should increase over time. There are a number of common mistakes that some people make with plie squats. This includes straightening the legs at the top, strongly arching the back, looking down or looking down, knees going beyond the toes, and the use of weights that are too heavy. To prevent such mistakes from happening and make the exercise safer and more correct, you need to follow some recommendations from experts:
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/Bjr2soKbtgw
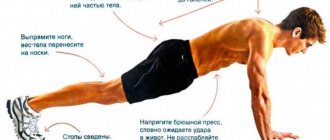
When rising from a squat position, you should try not to straighten your legs completely, as this will put a lot of stress on the knee and reduce overall tension in the muscles. When performing squats, it is very important to pay special attention to the correct technique. It is better to take less weight, but from a technical point of view, do everything correctly. The knee joint should move in the direction of the toe of the foot, without being limited by its general plane. It will be easy to avoid such a mistake - move your pelvis back, as the technique of this exercise suggests. When doing squats, look straight or slightly up
This will help control the load in your hands. If the general position of the back is incorrect, there is a risk of injury to the lower area. To prevent this, you need to constantly keep your spine straight. The vertical position of the spine is typical when squatting. The correct exercise technique involves moving your pelvis as far back as possible, as if you were trying to sit down on an imaginary chair, while tilting your body slightly forward.
Also during squats you need:
The amplitude range is considered an individual parameter for everyone. Squats can be deep, as well as with a reduced range of motion. The main tactics in this case are given to the training goal. If you want to work the muscles of the buttocks, then you need to squat low and deep. If you move more than parallel, then it is the quadriceps muscles that will be worked. Also, the muscles that will take part in the exercise directly depend on the rotation of the feet and knees. The external orientation pumps up the adductor muscles more, and when the toes are brought together, the load goes to the quadriceps, which is why the exercise loses its effectiveness. You need to turn your toes at an angle of 45 degrees. But with the correct squatting technique, this can be noticeably corrected. As with other squats, the sumo technique greatly affects the lumbar region of the back, which is why if you perform the exercise, you need to further strengthen this area using hyperextension. There is no need to use too heavy loads. You can understand that you have overdone it this way: if during the normal course of the exercise you make an involuntary jerk with your pelvis, then the weight is too heavy for you. At the lowest point, it is best to stop for 2-3 seconds, and then rise sharply and quickly to the starting position. To prevent knee injuries from occurring, you need to carefully ensure that your knees are parallel to your feet. The weight during squats should be transferred to the heels. This will help to optimally stimulate the gluteal muscles, it will also be rational in terms of biomechanics. At this time, you need to keep your back in a level position, arching at the lower back. Before performing the exercise, you need to do a little warm-up and stretching.
It is important to pay more attention to stretching the inner thigh area. Watch your breathing, and perform the main effort during exhalation.
Adviсe
- Choose the appropriate type of apparatus - it can be a dumbbell, a kettlebell or a barbell.
- When performing a squat, move your pelvis back, do not bring your knees forward so that they protrude beyond your toes.
- Maintain a slight arch in your lower back and keep your back straight.
- To achieve rapid muscle growth, use heavy weights, but be careful: if you cannot do the exercise with the selected weight with the correct technique, reduce the load.
- If you want to achieve maximum muscle gains, do 6 to 15 repetitions per set.
Analysis of the exercise
It is generally accepted that the dumbbell squat is one movement. There are actually two variations. Everything that is performed with a significant abduction of the pelvis back is not a squat, but a deadlift, that is, a movement that assumes the pelvic-dominant nature of the exercise.
What muscles work
Therefore, muscle activation will be different in both versions of the dumbbell squat:
- If we are talking about a vertical back and a squat “with extension and bending of the knees,” then the movement will be exclusively knee-dominant, and the quadriceps, hamstrings, buttocks, and calves will work to a greater extent;
- If we have a squat with the pelvis abducted backwards, and perhaps not into a corner, then this is to a greater extent the dominance of the femoral biceps, and partly the buttocks. However, the opinion that only the buttocks work only in a squat with a tilted back and abduction of the pelvis is erroneous. In the case of such a squat, the quadriceps is still involved, but to a lesser extent. From a positional point of view, stretching the glutes is more promising in a high back position, since the compression in this position is deeper.
The distribution of the load among the muscles will be as follows:
- The quadriceps is involved as a hip extensor, to a greater extent – the vastus lateralis and rectus head;
- The buttocks (maximus and gluteus medius) are included in the work at the lower part of the amplitude and, as it were, “push” the body from below;
- The abs and spinal extensors help keep your torso level and stabilized during movement.
Some fitness enthusiasts consider the squat with dumbbells in their hands a movement for women's training. The main reason is that this exercise does not allow you to lift as much weight as the barbell exercise. But in fact, the squat does not have any “gender”, and it can be a beneficial solution for developing thigh muscles for both boys and girls.
Changing up their routine allows athletes to engage their muscles in a different way and work different muscle groups more actively. In fact, this version of the squat is more suitable for the so-called “spine sufferers,” that is, people with spinal injuries. Many athletes perform it not with dumbbells in their hands, but with one load suspended from the belt.
The classic squat with dumbbells is holding the equipment in straight arms extended along the body. You need to prepare for this squat in the same way as for a regular barbell squat. The beginning of the workout is an aerobic warm-up, then some strength work with lighter weight dumbbells, and finally, performing an exercise with a working weight for the number of repetitions specified in the plan. Even if the weights are still small, it is not recommended to skip joint warm-up and mobility work.
How to squat with dumbbells correctly
The squat with dumbbells and the barbell are similar to each other in terms of working the back and knees:
- A rigid hold of the back is required so that the athlete does not lose the vertical position of the spine. In the version with a barbell, it is psychologically easier to contract and lower the shoulder blades, since in this case the athlete will not perform a movement that stabilizes the dumbbells themselves. Anthropometry hinders many people; due to the position of the body and arms, they do not receive sufficient rigidity, and dumbbells interfere with them, touching their hips. Here you can work out the muscles only if you select equipment with an adequate disc diameter;
- The start of a squat is always with the knees raised, and not with the pelvis abducted. During work, the knees tend to the sides and move in the same direction as the fingers, and not inward or forward;
- You should not allow you to stand on your toes and shift the load forward. The athlete cannot perform the exercise completely, he is not able to consistently regulate the load and is not ready to align the body in the exercises;
- Technically correct execution of the movement means the position of the knees in the projection of the foot;
- The theory that you should exhale while lowering into a squat is not correct. You need to breathe here the same way as in a squat with a barbell. At the start, take a deep breath and lower yourself into a squat position without breathing. Start to stand up, and only then, in the second third of standing up, exhale sharply. Otherwise, the stability of the center of the body will be lost and you will not be able to stand up technically.
Errors
- Bringing the knees inward with X's;
- Exit on the toes, edge of the foot or heel;
- Tilt of the body forward;
- Pelvic peck;
- Round back
Performance Recommendations
- Select the working weight according to your fitness level. Basic exercises for beginners should not be a battlefield for the ego;
- The depth of the gray is selected individually. Talk that there is some kind of “female” or “male” version of the squat is not entirely true. Doing squats is more promising for both the development of the quadriceps and the development of the buttocks.
Inclusion in the program
The exercise is included first in the programs of non-professional athletes. The squat will be more effective if performed exclusively after a good warm-up. It should include rolling out your hamstrings, buttocks, and calves on a roller, light cardio for no more than 5 minutes on an exercise bike or elliptical, and then several approaches to light weights, after which work according to plan. Some athletes may require special preparation of the hip joints - a “crab walk” with a shock absorber, as well as pelvic lifts in the gluteal bridge without weights.
Seto-repetition schemes depend on the training goals:
- Beginners should not train to failure;
- Even experienced athletes should always use the help of spotters.
Sample training program
Most weight lifting exercises are included in the training process either for the purpose of gaining additional volume or to increase strength indicators. Beginners should not immediately lift heavy weights. You should start small. Even experienced lifters are also not recommended to lift the usual weight, since changing emphasis requires adaptation.
If your goal is strength, do 3 sets of 4 reps. This is due to the fact that sumo is not the only pulling exercise, so there is no particular point in striving to give it your all. If the deadlift is done last during training, then you can perform four approaches, but for the final one, take lighter weights and bring it up to twelve repetitions. This loads the muscles to capacity and allows you to completely burn all the remaining energy during the workout.
Those who want to increase muscle size, but not increase strength, should do from eight to twelve repetitions. When the maximum number of repetitions is given without any difficulty, then the weight lifted should be increased. In this case, the number of repetitions is reduced to nine to ten. You need to do three approaches. The sumo deadlift brings maximum benefit only when, after the last repetition, you no longer have the strength to lift the apparatus again. Otherwise, either the weights are too light or the number of repetitions needs to be increased.
Execution options
There are several variations of the wide-foot squat:
- Plie pulse when squatting with a small amplitude. Lower your hips to the horizontal, lift them up quite a bit and repeat again. In this way, the result is consolidated, that is, the target muscles are refined.
- Plie with emphasis on one leg, allowing you to redistribute the load. One leg is placed on the toe, and the other on the foot. This option is ideal for diversifying training and pumping up a specific leg.
- The toe plie is a variation of the exercise for well-coordinated and fit people. Only socks touch the floor. Not only the inner thigh muscles are involved in the work, but also the calves.
- On the calf muscles, when only the heel is lifted alternately from the lowest point. This exercise gives the calves a beautiful and well-developed relief.
- With a jump, when they jump at the top point. This variation has an aerobic component and trains the heart muscle well.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/fXBFeSY5mpc
Rules for performing squats
In order for the exercises to have the desired effect and not harm the ligaments and joints, you need to follow several recommendations:
- The squat should be performed while inhaling, and returning to the starting position while exhaling. Breathing during training is extremely important - if you do not take a good breath during a squat, your blood pressure will increase and the muscle fibers will not receive enough oxygen, as a result of which your training will not bring results.
- You cannot bend your neck and back, you only need to look forward. Avoiding deformation of the neck and spine is also very important for effective use of the back of the body. A straight back will help avoid discomfort during exercise and stretching. In order to control your posture, you should first perform squats in front of a mirror and observe yourself.
- The body weight should not be transferred to the toes. In this case, the position of the center of gravity shifts and creates extra stress on the joints.
- You can't spread your knees.
If the exercise is performed correctly, then after the fifth squat a noticeable tension will appear in the muscles.
Japanese squats are a universal way not only to tone muscles, but also to solve the problem of swelling of the lower body, cope with cellulite, and also tighten the skin.
Daily squats will help you gain slender legs and beautiful buttocks within a few months.
Types of squats
These variations are performed to work the muscles more deeply, or to work on the weak points of the power movement in powerlifting.
Simulates a stance in a sumo deadlift. Develops hips, buttocks and hip adductors.
The barbell is held on the chest, a clear approach is required. The body cannot tilt forward.
Zerchera
The barbell is held by bending the elbow, at waist level. The movement serves to correct excessive forward lean in the classic barbell squat.
The barbell is grasped with a straight grip behind the back. Some believe that this works the hamstrings and buttocks better.
Lunge Squat
One of the scissoring movements that corrects leg imbalances is essentially one foot placed slightly back on the toes and the athlete simply lowers into a squat from that position.
One leg squat
The athlete stands on the box, stretches forward or simply lowers the non-supporting leg and performs the movement first with one leg, then with the other. This is necessary to correct the “difference in strength” of the legs.
Varieties of deadlift
There are 3 main ways to perform deadlifts: classic, Romanian and sumo. The differences between these movements lie in the different starting positions of the athlete and the different muscle groups working. Romanian deadlift, sumo or classic: which is better? We hope that our article today will help you find answers to these and other questions that interest you.
Classic deadlift
In the classic version of the deadlift, the athlete’s legs are positioned shoulder-width apart, the feet look parallel to each other, the gaze is directed forward, and the movement itself is carried out by the force of the back and hip muscles. The main load is taken on by the spinal extensors; it is through their work that most of the amplitude is passed, while with our legs we only “tear” the bar off the floor and set powerful inertia.
Romanian deadlift
The fundamental difference between the Romanian deadlift and the classical deadlift is the deadlift process itself. It involves minimal leg work and distribution of the main load on the back muscles. The exercises are performed with straight legs throughout its entire amplitude.
Sumo deadlift
When doing sumo-style deadlifts, the legs are positioned wider than the shoulders (in some cases they practically rest against the plates), we hold the bar slightly narrower than shoulder width and lift using the force of the quadriceps, adductor muscles and buttocks. The back movement here is much shorter than in the classic version.
The amplitude of the sumo deadlift is somewhat smaller than that of the classic deadlift, so powerlifters, whose goal is to lift the greatest weight, resort to sumo more often. But CrossFit athletes also do not disdain this exercise, although weight is a secondary factor for them. Some people's anatomy is simply better suited to sumo, other people's anatomy is better suited to classics, which can only be determined through trial and error.
The sumo deadlift requires a good stretch in the hip adductors, this will help you feel more comfortable lifting heavier weights and also minimize the risk of injury.
For many athletes, the question arises: which deadlift is better, sumo or classic? The answer is simple - to each his own, it all depends on your physical and genetic data. If you have long legs and short arms, then it would be more rational to perform a sumo deadlift, if on the contrary, then a classic one.
If your back muscles are more developed, do classic deadlifts, but if your leg muscles dominate in their development, do sumo. Try both options and choose which one is easier for you to maintain the correct technique. Although, on the other hand, why do you need to stop? For comprehensive development, a CrossFit athlete needs to perform both versions of the deadlift, because only an integrated approach and proper distribution of the load lies the path to high athletic achievements and truly impressive performance.
Execution technique
Starting position:
Place a kettlebell on the floor between your legs. Place your legs in a wide sumo position (wider than the shoulder girdle). Turn your feet 30-45°. Grasp the projectile with both hands by the handle. Keep the body in an upright position. Your arms should be straight - do not squat down deeper than necessary. You will lower yourself down 4 counts, pause for 3 seconds at the bottom point and return to the starting position.
Basic movement:
- Press your heels into the floor. Slowly bend your knees and lower yourself into a squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Lower your hips down and back a little, and place the weight on the floor between your legs.
- Place the weight on the heels of your feet to push off and return your body to an upright position.
- Smoothly straighten your knees as your hips move upward. As with all squats, the buttocks should not rise before the shoulders.
- Repeat as many times as necessary. It is recommended to perform 3 sets of 5-6 repetitions.
Sumo squat (easy version)
If you find the kettlebell technique too difficult, there are two things you can do. The first is to do squats without weight. The second is to decrease the range of motion with the weight (just a quarter of the way down).
"Sumo" (difficult version)
Since the depth of the squat is limited, you can increase the load on the target muscles by adding a 5-second pause at the bottom of each repetition.
Sumo squats: technique of execution
First you need to stand up straight, maintaining a natural arch in your lower back. Spread your legs to the sides, turn your feet outward. The width of the legs and the angle of rotation are selected individually, but try to spread your legs as far apart as you can and turn your toes out 45 degrees. Sit down like this several times without weight. If you manage to bring your thighs parallel to the floor and you do not feel any discomfort, you can use this position.
The sumo squat technique involves the following sequence :
- Take the starting position with your legs wide apart and your toes turned out to the sides. If you are doing sumo squats with a barbell, pay attention to the placement of the bar. It should lie slightly below the neck, on the back muscles. If you are using dumbbells, you can lower them in front of your body with your arms outstretched so that during the squat the weight passes between your legs, or you can take one dumbbell by the disc and also lower it in front of your body. The second option is considered more convenient.
- As you inhale, try not to lean forward too much. Squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor. The knees should be in the same plane as the toes and not move inward - this is very important. Try to move your pelvis back as far as possible with your flexibility.
- Exhaling, slowly rise from the lowest point.
The exercise is recommended to be performed in 3-4 sets of 10-15 times .
If you squat below parallel to the floor, you can better work your gluteal muscles. But keep in mind that this seriously increases the load on your knees, so perform moderately deep sumo squats.
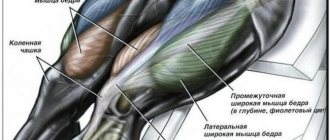
What muscles work when squats
There are many types of squats that can work different muscles to varying degrees. But basically, in the question of which muscle groups work when squatting, the following are distinguished:
- Quadriceps or quadriceps femoris muscle. Squats are the best way to work this muscle, which is responsible for straightening the legs at the knee.
- Calf muscle. Helps maintain the body in balance, maintain an upright position, and avoid falling forward and backward.
- Popliteus and gluteus maximus muscles. Responsible for straightening the legs.
- Back muscles. Also partially responsible for squatting. They help maintain a straight body position.
- Abdominal muscles. Allows you to maintain balance. When squats, the middle and lower abs swing.
- Thigh biceps.
Now it’s clear which muscles swing when squatting. This exercise uses important muscle groups, so it is considered equally useful for both men and women. Women especially love it, since squats perfectly help them tighten their buttocks and legs, and additionally work their back muscles.
This is a basic exercise, and if performed correctly, it can replace a whole set of exercises on simulators.
Squats are also considered beneficial for health. We invite you to see which muscles work when squatting in the photo, where everything is presented in detail and clearly.
Before you start doing squats, you already know which muscles are pumped, be sure to warm up the muscles and prepare them. Light jogging, brisk walking, jumping, and so on can serve as a warm-up. Warming up significantly reduces the risk of injury. We also prepare muscle tissue and limbs, improve blood circulation and give ourselves the opportunity to better perceive the loads that are placed on us.
Plie execution scheme
- You will need to start with a minimum of 3 sets of 10 classic pliés 3 times a day.
- Then gradually increase the number of repetitions, adding 1-2 repetitions per approach.
- With good execution technique and complete mastery of the deep squat, you can add weights starting from the minimum. Let your body get used to the changes.
- Increase the weight gradually: first, increase the number of repetitions with the existing weight, and then ask for “addition” and repeat this over and over again - the exercises will be the most effective, and you can not only pump up your buttocks, but also increase their size.
- If you work without weight and want to increase the effectiveness of your workout, then “step out” from the squat into a jump or rise onto your toes after each repetition.
- If you do squats with a barbell, then you need to increase the weights as follows: take a weight of 10 kg, the first week - 6 repetitions, the second - 10, and the third - 12. Then increase the weight by a couple of kg, and also the first week 6 repetitions, the second – 10, the third – 12. This is the sequence of progression.
Increased efficiency
- Increasing weights is provided by programs with periodization, when they begin to perform the exercise with small weights and high-repetition schemes, gradually reducing the number of repetitions and increasing the weight;
- The more the athlete works on joint mobility, the more effective the exercise will be;
- If the goal is strength results, you should abandon a large number of “auxiliary” exercises
Pancakes under the heels
You probably paid attention to some super mega online trainers and part-time fitness bikini trainers - how they place small discs (“pancakes”) weighing up to 1.25-2.5 kg under the heels before squats. Beginners often copy such habits of their more “wise and sophisticated” owners of gorgeous asses, without even asking themselves why this is necessary
It is believed that this is better, just better, without details.
“The exercise is more effective, it seems that the gluteal muscles feel better, but I don’t know…”
It seems very similar to the opinion that small, frequent meals speed up metabolism. If you still believe in this, you are welcome: “Dear, I accelerated my metabolism or myths about “promoted” metabolism”
In fact, there is a logical explanation for such actions. Even two at once: a higher heel position is needed either to isolate the quadriceps (quadriceps muscles of the thigh), or to neutralize the lack of stretch development.
In the first case, simultaneously with the lining of the discs, the width of the stance changes: the legs are placed narrower, the toes point straight forward or at a slight angle to the sides (less than 45 degrees). The technique of squats is also changing: they are moving away from deep squats to half-squats. The grip width of the barbell with your hands increases, up to extreme marks, and the pace slows down to medium or even slow. The back is held vertically, and the bar is held somewhere at the level of the spine of the scapula or even higher. All this allows you to isolate the quadriceps femoris muscle.
In the second case, pancakes are placed under the heels to compensate for insufficient stretch development. You need to understand that this is a necessary measure, and you need to correct your physical imperfections: develop and improve your stretching.
WHAT ARE THE DANGEROUS OF PANCAKES UNDER THE HEELS:
If your heel is raised, the load on the knee joint noticeably increases, and therefore it is easy to get injured. This load leads to increased wear and tear on the knees. So adding pancakes is a short-term, dangerous and, in our opinion, rather pointless measure. And the gluteal muscle is actively and fully worked out only in the case of squats without pancakes.
Bone Wide does not recommend placing boards, plates or blocks under your heels when squatting. If you can’t do it without them, it means only one thing: you don’t have enough stretching and your inflexible muscles don’t allow your body to take the desired position. First of all, you should stretch the Achilles tendons, hamstrings, hip adductors and buttocks
In addition, you will need to pay attention to stretching the muscles of the shoulder girdle and pectoral muscles - otherwise you simply will not be able to hold the barbell in the desired position
If stretching is really difficult, take at least 6 weeks to gradually and carefully improve the stretchability of your muscles, and only then think about starting to learn the squat technique. Of course, just doing squats will help improve the stretch, but during this “learning” period you will not be able to squat with good form.
For this reason, you run the risk of “learning” a bad technique, which you then have to “unlearn”
Of course, just doing squats will help improve the stretch, but during this “learning” period you will not be able to squat with good form. For this reason, you run the risk of “learning” a bad technique, which you then have to “unlearn.”
No matter how good or bad your leverage (i.e. limb length and limb ratio) is, good stretching will help you squat more technically than any heel pads.
Interesting Facts
As you might guess, this exercise got its name due to the fact that the pose of the athlete performing it is similar to the stance of a sumo wrestler in the arena.
Despite the fact that sumo wrestlers look very clumsy, they are in good physical shape - the norm for them is several hours of grueling training a day. Among other things, they do stretching and strength training.
By the way, sumo wrestlers also do those same squats that we call sumo squats. Traditionally they are performed with a large stone held at chest level.
Thanks to regular exercises to stretch muscles and ligaments, those who engage in this unique sport can squat very low. All athletes should take note of this point: good stretching is never too much.
Benefits of plie squats (sumo)
Squats (plie) are used to warm up and strengthen the core muscles of the lower extremities. With multiple repetitions, they make the muscles more resilient and stronger. But that is not all. Sumo squats increase the functionality of the leg joints and make the ligaments and tendons more elastic. The Achilles tendon is actively stretched, in the area of which a so-called “heel spur” can form with age. Plie serves as a preventative measure for this very unpleasant disease.
Plie squats help you quickly and effectively form beautiful legs and firm, pumped buttocks. Proven effectiveness and simplicity have made the exercise incredibly popular. It is performed in the gym, as part of fitness training and at home.
Sumo or plie squats are the best exercise for the legs and buttocks
And of course, like any other types of squats, sumo helps to increase the speed of metabolic processes, energy consumption, and burn fat deposits. Therefore, they are often included in training complexes aimed at weight loss.
Recommendations
- Barbells help to avoid falling on your toes due to falling on your toes; they are recommended for use in squats and lunges for all beginners who have problems with sitting up;
- For those who do not have the ability to hold dumbbells with a direct grip, there are wrist straps;
- The grip develops perfectly when using dumbbells, and this does not depend on the presence or absence of straps, even with them it can develop and strengthen gradually. The straps only prevent the dumbbells from falling;
- The gaze in this exercise should be directed forward, so that the head does not tilt and the athlete does not fall on the toe or heel;
- It is worth choosing dumbbells of adequate weight so as not to get injured, and so that their weight does not “pull” the body forward or backward due to inertia;
- At first, while there are no weightlifting weights and proper mobility, you can put weight plates under your heels;
- Grip problems can be solved by developing the forearms with regular exercises, such as kettlebell lifts.
Common Mistakes
Not only beginners, but also people who have been regularly visiting the gym for a long time can make technical errors when performing exercises, especially basic ones. The most common ones for sumo are:
- placing your legs too wide, which increases the risk of muscle strain;
- arching your back is very dangerous, it should always remain straight;
- a large distance between the shin and the barbell in the classic version of the exercise, so the load on the forearms, shoulders, triceps increases significantly, and it is also much more difficult to maintain balance;
- using equipment when working with light weights interferes with the development of correct technique;
- push when lifting up with your toes, not your heels - in this case, the load shifts from the buttocks and legs to the back and calves and the exercise becomes ineffective;
- sharp angles in the knees and their extension beyond the toes are very traumatic for the joints;
- jerking while lifting can lead to back problems;
- lowering the head down - promotes arching of the back and in this position it is difficult to maintain balance and not lean forward;
- in pursuit of quick results, using a projectile that is too heavy for the current physical form - for beginners it is better not to use weights until the technique is perfect;
- Full straightening of the legs at the knees increases the load on the knee joints.
Technique for performing sumo squats
We all know this exercise, SAT and STANDED, SAT and STANDED. What is difficult, many will ask... Alas, it would all be so simple)) + judging by what I see in my fitness club, there are still difficulties (to put it mildly), and there are a lot of them. My task is to tell you about each component of the squat, as well as all the subtleties and secrets of this exercise, so that you don’t do nonsense, but know everything from A to Z and purposefully target the desired area (butt).
The photo below demonstrates an incorrect squat:
Ps her legs are set too narrow, this is not sumo style (but this is not a mistake, just a word).
But it is incorrect due to the fact that the girl began to squat by bending her knees, and not by moving her pelvis (butt) back, as a result of which her knees go very far beyond her toes, and this is an unacceptable mistake that many girls make