Training programsMiscellaneous
Think you need the entire gym for a killer workout? But no. A pair of dumbbells and a barbell are all you need for Craig Capurso's high-volume fullbody workout for maximum reps!
Author:
Heather Eastman, personal trainer, certified by the National Strength and Functional Training Association (USA)
IFBB Pro Craig Capurso is an expert in high-intensity AMRAP workouts, designed to hit as many muscle groups as possible in 30 minutes or less. For the uninitiated, AMRAP stands for “as many reps as possible,” that is, as many repetitions as possible. Typically, these workouts require a time limit—say, you have to do as many reps as possible in 60 seconds.
In this AMRAP circuit workout, Capurso suggests doing 6 sets of max reps with 20-second work intervals followed by 30-second rest periods. All six exercises are performed one after another, the sequence is repeated for six rounds. If you use every second of each rest period, your workout should take you 29 minutes and 30 seconds.
Because there's limited time between exercises, Capurso uses the same weights for all exercises to make it easier to switch from one movement to the next. This is a great plan, especially if you don't have enough space in the gym, if you're running out of exercise equipment, or if you just want to get a full-body workout done in just 30 minutes.
Maximum reps workout
Goblet Squats Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
Close-grip bench press Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
Standing Alternating Dumbbell Overhead Press Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
Bent-over barbell rows Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
Dumbbell Curls Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
French Bench Press with Dumbbells Maximum reps for 20 seconds, then 30 seconds rest
1
set
max.
repetitions
Repeat the workout six times
Goblet Squats
Capurso opens the workout with dumbbell goblet squats, spending 20 seconds doing as many reps as possible. By holding dumbbells in front of you, you will not only work your legs, but also your core muscles.
Craig advises placing dumbbells on your shoulders. “You don’t actually have to hold the dumbbells,” he says. “Use your shoulders to help distribute your weight.”
When performing squats, lower yourself as deeply as possible while maintaining the natural curve in your lower back. You should not lean forward. You can use a mirror as a technical advisor. Make sure the dumbbells move up and down in a straight, vertical line.
After 20 seconds, you will have 30 seconds to rest and prepare for the next exercise. In this vein, you will have to complete all six exercises, after which you will return to the beginning and go through the entire circle again.
Rest between sets and workouts
How long you'll have to rest between sets usually depends on your goals. This can be either mass gain or strength gain.
It will not be possible to place an exclusive emphasis on strength when training with dumbbells, since for this you need a lot of dumbbells of different weights so that you can slowly overcome larger and larger weights. Typically a barbell is used for these purposes.
Therefore, our goal now is a gradual increase in muscle mass and, as a result, their strength. The optimal rest between approaches in this case would be 1-2 minutes.
If you want to increase the intensity of the training, that is, make it more difficult, then you can reduce this time, but the minimum that you must adhere to is 30 seconds.
This way, by the way, you can solve the problem if your dumbbells do not have enough weight to constantly increase your training load. Just start reducing the rest time between sets and you will see how the previous weights that were previously quite easy for you will become much heavier.
As for the rest time between the workouts themselves, this is understandable based on the training program. You work out every other day, that is, a training day alternates with a rest day. On Saturday and Sunday you should have two days of rest in a row, since a fairly strong general muscle fatigue will accumulate over the week and you will not be able to recover with one day of rest.
Standing Alternating Dumbbell Overhead Press
For the third exercise, take the same dumbbells you used for goblet squats. Keep your core and legs tight as you alternate lifting one dumbbell and then the other.
You may be working at a fast pace, but this is not a reason to forget about proper technique.
“Build yourself a strong foundation from the floor up,” Capurso instructs. “Engage your legs, engage your core, keep your back perfectly straight, shoulders back a little, and get to work.”
As with any dumbbell exercise, you must learn to perform the movement technically and maintain proper form throughout the entire set.
“When the technique starts to falter, injuries happen,” warns Capurso, “and you definitely don’t want that.”
Workouts with dumbbells at home for beginners
Training for beginners at home should not be difficult, since the body is not yet prepared, and there is no one to monitor the technique. Therefore, the exercises will be simple in technique and will involve only one muscle.
Standing biceps curl
- We place our feet pelvis-width apart, knees slightly bent, arms with dumbbells along the body;
- Without turning the wrist, as you exhale, raise the dumbbells to your shoulders, bending your elbows, contracting your biceps. Do not rock the body;
- As you inhale, lower and relax your arms. To simplify the load, you can raise your arms one by one.
We perform 15-20 repetitions, three approaches.
Lifting dumbbells from behind your head
- Standing or sitting on a chair, keep your body straight;
- Take one dumbbell in both hands and extend your arms straight above your head, elbows pressed to your head;
- As you inhale, place dumbbells or a light weight behind your head, leaving your elbows motionless;
- On the way out, we straighten our elbows from behind our heads, including our triceps.
To make it more difficult, you can take two dumbbells at the same time. Perform 15-20 times in three approaches.
Standing Dumbbell Press
- Keep your body straight, knees slightly bent, hold dumbbells above your shoulders at chin level;
- As you exhale, press the dumbbells up using the shoulder muscles, straightening your elbows above your head;
- As you inhale, relax your shoulders and lower the dumbbells to the starting position.
Bent-over barbell row
Here you work with the same barbell that you used for the close grip bench press. There's no time to add or remove weights, so choose a weight that's heavy enough for both exercises.
The bent-over row is a technically challenging exercise, so Capurso makes a few recommendations. Allow your arms to relax a little at the bottom of the movement. Maintain a natural arch in your lower back. Rest on your heels. Don't forget to breathe.
You can hold the barbell with a pronated or supinated grip - whichever is more convenient for you. Just be consistent. A supinated (underhand) grip allows you to stretch the lats slightly more at the bottom of the movement and work them more actively, while a pronated (overhead) grip allows you to increase the load on the front deltoids.
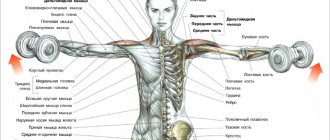
Shoulder exercises
A beautiful pumped up body also means a sculpted shoulder girdle.
. So warm up and get started with the most effective exercises for strong and expressive couch potato shoulders.
| Seated dumbbell press. We train the lateral parts of the deltoid muscles. Doing this exercise regularly will make your shoulders wider. Sit on a bench/chair/stool and press against the back/wall. Keep your body straight throughout the exercise. Hold dumbbells in your hands so that your forearms point straight up. Without jerking, but with a powerful movement, press the dumbbells. Try not to point your elbows forward. At the top point, wait for a momentary pause and gradually return to the starting position. There's no point in stopping here, so start climbing again. |
| Arnold press. The Arnold Press exercise works well on the deltoid, as well as the trapezius and a little triceps. Sit down. Keep your body straight, keep your back straight. Hold the dumbbells in front of you with your palms facing you. Press your elbows towards your body. Begin to smoothly squeeze the dumbbells upward, while simultaneously turning your hands with your palms facing forward. After lifting the dumbbells and extending your arms almost completely (do not straighten them all the way), return by turning your hands in the opposite direction. This placement of the arms and the changed trajectory of movement help to increase the load on the anterior deltoids. The Arnold Press engages those muscle fibers that are not used in the classic dumbbell press. |
| Dumbbell raises to the sides. Dumbbell swings load the lateral (middle) parts and work the deltoids more deeply. For this exercise, choose a light weight. Take dumbbells, stand straight and slightly bend your elbows (this position should be maintained throughout the entire approach). Raise the dumbbells vigorously to the sides until they reach head level. Hold on for a second. Now slowly lower your arms and raise them again. Repeat the required number of times. The exercise can be performed in a sitting position. |
Dumbbell biceps curl
Use the same pair of dumbbells you used throughout the entire workout. Just stand straight - without swinging your body - and lift both dumbbells at the same time.
The dumbbell lift is the last exercise in the circuit. When the 20 seconds are up, rest and return to the beginning of the workout, which is goblet squats. You need to do six laps in total. Record the number of reps you complete so you can tally your points after your workout.
As with many of his workouts, Craig Capurso uses a scoring system to measure the total amount of work done. This is why 30 seconds between exercises is a recommended rest period, but not required.
You can shorten your rest periods by adding the time you save to your points. Either way, you'll get more work done in less time than someone who always rests 30 seconds between sets.
“Let's say you completed all 6 laps in 28 minutes and 30 seconds,” says Capurso. - Sixty seconds left. Add them to the final score."
This scoring system allows you to track the dynamics of changes in strength indicators, as well as aerobic and anaerobic endurance, because you can score points not only due to the total number of repetitions, but also due to faster recovery.
“Among other things, you also have an indicator of willpower - this is the amount of work that you are able to do in a specific workout over a certain period of time,” says Capurso.
The proposed complex is quite heavy, but the load volume here is still smaller. There will be no severe depletion of the central nervous system, which means that you can do the AMRAP circuit program at least every week.
A set of exercises with a barbell for the gym and at home
The best option is three times a week. Moreover, during training, different muscle groups should be used. For example, I work separately on the abs, arms, chest, and a second time on the legs, and the like. It is optimal when two groups are worked out in one workout. It is necessary to take into account the fact that the recovery time for each group is different.
This deadlift variation is great for targeting the hamstrings. Starting position: legs shoulder-width apart, feet facing forward, dumbbells at your sides. Move your hips back slightly and bend your knees. Slowly lower your body towards the floor until you feel tension in the muscles of the back of your thighs (while holding dumbbells on the sides of your hips).
This exercise is more difficult than it looks, but it's worth it. Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, dumbbells at sides. Shift your weight to one leg and bend your knee slightly. Lean forward, lifting your other leg up behind you. Move the dumbbells forward as you bend over. Return to the starting position by slowly lowering your raised leg. The dumbbells should again be on the sides of the hips.
Before you begin the exercise, make sure the ceilings are high enough! Sit as if you were doing a classic squat, holding dumbbells at your sides. Your shins should be at right angles and remember to watch your posture. Come out of the squat by standing completely straight and lifting the dumbbells up.
Place your feet wider than your shoulders and bend them slightly at the knees, holding a dumbbell in your right hand in front of your knees. Pull the weight up, holding the dumbbell close to your body, while throwing your hips forward. When the dumbbell is at chest level, straighten your legs completely. Then squat down again to feel the weight.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, a dumbbell in each hand. Hold dumbbells in front of you. Bend your knees and move the dumbbells back between your legs. Then, with a quick movement, straighten your legs, while throwing the dumbbells up and forward to shoulder level. Keep your arms straight. Swings work great on your hips and buttocks.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Dumbbells in front of your knees, palms facing your body, chest forward, back straight. Keeping your arms straight, lift your shoulders, engaging your entire body: straighten your knees, twist your hips. Then bend your elbows and, holding them as close to your body as possible, pull the dumbbells to chest level. Keep your elbows slightly higher than your wrists.
Lack of free time to go to the gym is not a reason to give up playing sports. If you want to give your body beautiful shapes and build muscle mass, you can get by with a barbell and practice at home. When working with large weights, the help of an assistant will be useful.
Below are basic and isolation exercises with a barbell at home; choose and include suitable techniques in your program.
exercises with a barbell are performed at the beginning of the training after a thorough warm-up.
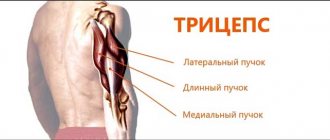
An effective exercise for triceps relief and developing endurance (5 doubles with heavy weights in 3 sets), increasing mass (10-12 times in 3-4 sets). Works: pectoralis major, deltoids, 3 triceps bundles.
We perform it on a bench or lying on the floor. If the volume of the discs does not allow you to lie under the bar, we place the plates on a support.
With the feet of our bent legs resting on the floor, we lean our chest slightly forward:
- take a narrow grip;
- press up with the force of the triceps;
- lower, touching the chest area with the bar.
The lowering phase is 2 times longer.
Isolation exercise for triceps and shoulders. If you work with an EZ bar, it is possible to relieve tension from the forearms and, by reducing muscle resistance, ensure comfortable movements:
- grab the bar with an overhand grip;
- as you inhale, lower the projectile behind your head, trying not to touch the floor;
- As you exhale, with a jerking movement of your hands, we return the projectile to the IP.
We monitor the position of the elbows - they should not go too far to the sides.
Standing Press Variation
For relief and mass. Active: triceps, frontal delta:
- we lift the projectile from the classic rack;
- We take hold of the bar with our palms forward, placing our hands shoulder-width apart;
- squeeze over the top of the head;
- during the lifting phase, we do not place our elbows, we direct our joints towards the body;
- lower the load along the arc path until the forearms touch the upper chest;
- By tensioning the triceps, we return the bar to the IP position.
As an option - seated press. The technique is similar, only performed from a different position.
Practices should not be abused. The load on the elbow area can result in tendon strain.
Recommended:
- for men beginners: 16 x 3 with a load of 10 - 15 kg;
- girls: 13 x 3 6-10 kg each.
Shrugs behind your back
A modeling exercise for the volume of the trapezius and pumping of the neck muscles. The emphasis is on the trapezius, with a little less load on the rhomboid, levator scapulae, and forearms.
Unlike dumbbells, which provide an optimal range of motion and give roundness to the muscles, the barbell aligns the spinal column and forms a pronounced relief.
- The body is straight, the knees are bent;
- The goal is to grab the barbell with an overhand grip and wide-set hands. It's better if it's served by a partner. The projectile is located below the gluteal muscles.
- We stick out our chest, push our shoulders back, pull our stomach in, direct our gaze to a point, and squeeze up.
- When we reach the top point, we strain the trapezius as much as possible.
- As you exhale, lower the projectile and shoulders.
We do not bend our elbows in the positive and negative phases. This will reduce the amplitude of the lift and eliminate the load on the trapezius (12 x 4).
The trick of the exercise is the widest possible stance. In this position, tension is relieved from the lower back, hamstrings, and buttocks, and the quadriceps and hip adductors are optimally worked out. Since the inner thigh area is thoroughly involved, the practice is often included in girls’ programs.
- We squat to the level to take the bar without bending the body.
- On a deep inhalation, lift the projectile with your leg muscles. Exhale at the midpoint of the trajectory.
An important condition is to maintain a stably straight back position.
- Men: 12-15 x 4 with a weight of 25-30 kg;
- girls do the same, but with 10 kg discs.
Deadlift
One of the main exercises for working out all the muscles. The work involves the main groups and small muscles. In the positive phase, the quadriceps, buttocks, and quadriceps contract to a greater extent. Stability is provided by the gastrocnemius and soleus.
Strength exercise requires careful adherence to technique.
- IP - projectile in front of you, knees touching the classic bar;
- lower the pelvis as if doing a deep squat;
- the hands are spaced wider than the shoulder line, we hold with an overhand grip;
- we move our body forward, consciously tense our muscles and lift the barbell without jerking movements;
- pull up close to the shins;
- after passing the midpoint, exhale;
- lower under control;
- continue after a second pause.
Lifts with a contour bar are relevant for weak shoulders and undeveloped coordination. The quadriceps will receive the main load. The principle is the same. Training once a week - 6-10 takes in 3-4 approaches for all types of practices.
The exercise tightens the hips and buttocks. Unlike the classic version, the knees are absolutely straight.
- We pull the projectile using the muscles of the body.
- The muscles of the lower extremities are isometrically tense.
The Romanian version of the deadlift is a favorite exercise for weightlifters to develop power in the hips and buttocks. The technique is similar, but the projectile rises to the middle of the thigh.
The main exercise for pumping the lower part of the body. Works: quadriceps, lumbar region. The gluteus maximus, obliques and rectus abdominis are less heavily loaded.
The practice requires flexibility in the wrists and strength in the shoulders and ankles. The position of the lower extremities determines the focus of the load.
- With narrow feet, the emphasis shifts to the frontal area of the thigh;
- with a wide one - to the inner one.
With crossed arms, we raise the bar to the chest. This grip is convenient when working with light weights.
Weightlifting is caused by lifting the barbell with the forearms turning towards you and is used in working with heavy discs.
- In the basic position, the bar rests on the shoulders.
- We move our buttocks back, imitating an attempt to sit on a bench.
- We return to the IP.
- We take the bar with a comfortable grip, although a narrow position helps control the position of the bar.
- The depth of squats is variable: to horizontal with the floor or lower.
In the latter case, the gluteus maximus muscles are activated. - Slowly and smoothly we lower ourselves with a deep breath and quickly get up. Exhale after passing the midline.
Exercises with a barbell at home for legs in video format:
- Leave your knees bent at the top.
- Below we avoid pauses.
- When lifting, we do not move the body forward.
- Carefully removes the bar from his shoulders.
- To stabilize the body, it is better to cross your feet.
To get powerful results, powerlifters and bodybuilders lower their buttocks almost to the floor. A deep squat increases leg mass and develops explosive strength. The quadriceps, calves and dorsum of the thigh receive the maximum load.
- Regardless of the type of squats, men perform from 12 to 16 repetitions in 3 sets.
- For an experienced athlete, it is better to work with heavy weights and perform up to 6 repetitions. The program is built on the principle of gradual loading.
- For girls, practice with a barbell is recommended as lower body training from 10 x 3.
Advanced athletes are encouraged to diversify the complex with weighted jumps:
- We hold a barbell with a light weight with an overhand grip on the trapezius.
- We go down and take a jumping pose.
- With a jolting movement of the feet, we jump up.
- We land smoothly on our toes, then distribute the weight along the foot.
Complex techniques are performed 6-8 x 3. At each training, we pump 2 muscle groups once a week.
Exercising with a barbell at home is an alternative to regular trips to the gym; in order to pump up, use the above practices and the result will be no worse than after going to the gym.
Squats
4 sets of 15-20 repetitions (perform the first 10 repetitions slowly, controlling the 2-second negatives, and pause. Then finish the exercise with fast repetitions) |
4 sets of 8-12 reps (2-4 second negatives, 1-2 second positives) |
4 sets of 20 reps (2-4 second negatives and positives) |
4 sets of 15-20 reps (squeeze dumbbells instead of placing hands on the floor, performing 4-second negatives and positives) |
4 sets of 30 seconds each (holding dumbbells with a goblet grip) |
4 sets of 10-15 reps |
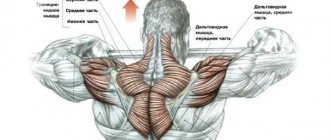
Exercises to train your back muscles
Basic exercises with dumbbells to train your back muscles at home.
| Shrugs (trapeze) with dumbbells. “Shrugs” are a simple, but the most successful exercise for developing the upper trapezius. Take dumbbells in your hands. Feet shoulder-width apart, stomach tucked in, shoulders turned, chin pressed to chest. Smoothly lift the dumbbells, trying to (figuratively) connect your shoulders at the back of your head, slightly moving them back and up. Then slowly lower your arms back. It is advisable to do the exercise in two or three sets of 15-20 repetitions, starting with a heavier weight and ending with a lighter one. |
| Bent-over dumbbell rows. The exercise is aimed at developing the latissimus dorsi muscles using the biceps. Bend over. The back should be almost parallel to the floor. Look forward, keep your back straight. Bend your legs slightly at the knees. There is no need to stick your hands with dumbbells forward. Pull the dumbbells towards you, approximately to the middle of your abdomen. Watch your elbows - they should look up, not to the sides. Return to the starting position and repeat immediately. |
The bench press works the top, middle, and bottom of the chest. The best basic exercise for increasing muscle size and chest power.
Execution technique
- Lie down on a horizontal bench so that the barbell is directly above your head. The back of the head, buttocks and shoulders are pressed against the bench, the back is slightly arched (rounded) in the lumbar region, the legs are wider than the shoulders and rest on the floor.
- Grab the barbell with a wide overhand grip (palms up), with the space between your hands wider than your shoulders.
- Release the bar from the supports and press it up. At the top, the arms are straight (but not locked at the elbows), and the bar of the bar is located exactly above the middle of the chest. This is the starting position. If you have a huge barbell weight, remove it from the supports only with the support of an assistant (partner).
- Taking a deep breath, lower the bar to your lower chest. As soon as the bar touches your chest, stop breathing and strongly press the barbell up (and not just up, but slightly diagonally, in line with the racks, so that at the top point the barbell is strictly above the middle of the chest).
- Exhale only after you have completed the hardest part of the bench press
. At the top (arms straight), stop and tighten your chest even more. - Lower the bar smoothly and at a moderate pace; press the barbell from the chest at a normal or accelerated pace.
- Don’t stop at the bottom point: the bar barely touches your chest, immediately press it up.
- Don't pause at the bottom. As soon as the barbell touches your chest, do not relax your muscles and, using the energy available in them, press the barbell up. By stopping, you reflexively worsen muscle contraction and, in order to squeeze the barbell, you will need to “gather all your strength into a fist” again, spending additional energy on this. In addition, with each new repetition it will become more and more difficult to do this. Ultimately, you may not complete the intended number of repetitions.
- Stopping your breathing during the bench press
is extremely important for keeping your torso in a safe, stable position and helps you develop a significantly stronger load. Do not forget, the more stable the position of the torso, the more intense the work of the muscles and the less pressure on the joints. - Don't stop breathing for too long. When performing the exercise at an average pace, holding your breath should last about 2-3 seconds.
- After going through the most difficult part of the movement while lifting the bar, finish the repetition with a deep exhalation. If you feel a lack of strength, ask your partner for help. Never stop halfway! The barbell must be in motion all the time.
- The heavier the barbell, the more tense the muscles are and the more you have to exhale as you go through the toughest part of the barbell lift.
- When pressing the barbell, press your feet into the floor with all your might, hold the bar as tightly as possible, and do not lift your shoulders and hips off the bench. This will stabilize the torso and allow you to achieve maximum contraction of the chest muscles.
- At the bottom, do not squeeze the barbell with your chest, bending your whole body upward. This can cause injury!
Application
Intended for:
Everyone, from beginner to professional.
When:
At the beginning of training the pectoral muscles. In the middle of the workout, perform fly-ups with dumbbells on a lying bench.
How many:
3-4 sets of 8-12 times.
Sports instruction:
No exercise comes close to
the bench press
in solving the problem of dramatically increasing the volume of muscle mass and power of the chest muscles. And although the center of the load here is directed to the middle of the chest, its lower and upper parts work at full strength. But know that this load distribution is good when you hold the bar with a wide grip. If the grip is strictly shoulder width, then the center of the load moves towards the top of the chest.
Muscles involved in the bench press
, are of great importance for many sports that are characterized by hand push-ups, pushes, hits and throws: boxing (lateral and direct blows to the body), tennis (hitting the ball with an open racket), discus throwing and shot put.