Don't rush to the operating table!
First - the word, then - the medicine and only then the knife. This ancient canon of medical science could not be more applicable to the area of healing where the success of treatment depends on the independent efforts of the patient. And also from following our recommendations, aimed primarily at treatment with proper movement, physical exercise and cold.
A herniated disc, or spinal herniation, is the result of dehydration, or dehydration, of the disc. And not “prolapse of the nucleus pulposus,” which is what neurosurgeons are trying to convince us of. The disc is simply erased without receiving the nutrition provided by the muscles.
A hernia is not a splinter that can be removed. It is not the cause of pain. Athletes often ask me: “Where did I get a hernia, my muscles are good!” I answer: “Your muscles are overloaded, they have lost their trophic, that is, contractile-relaxation function.”
If a person has a pathology of the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine, then it is necessary to “address” the muscles that are responsible for feeding the intervertebral discs of this section. It is they who should be involved in the work regime through physical exercise, remembering that muscles can be restored.
In contrast to a dystrophically altered disc, which will never become normal in structure. It’s just that for the entire subsequent part of life, the movement of the spine of this section will be supported by the muscles responsible for its nutrition. And this is where physical exercise comes to the rescue. proper breathing and cryotherapy. I will name some exercises that you can perform successfully at home.
Every home should have a horizontal bar or some kind of device under the ceiling that replaces it. If you cannot do pull-ups due to age or excess weight, then attach one or two expanders to the horizontal bar. Sit on a chair or on the floor and perform various pulling movements. How many? At least 20 in one approach.
An exercise for the chest muscles is push-ups. Perform push-ups in series of 10 times. The more series, the higher the therapeutic effect. Try to keep your body straight.
Then we’ll complicate the task a little: we attach one end of the shock absorber to a fixed support and perform the following exercise:
- pull to the chin, bending your arms;
- Pull with straight arms up to a position above your head.
I advise you to perform all these exercises in blocks daily and alternately: one day - deadlifts, another day - push-ups, the third day - shock absorbers.
To complete the story about the treatment of intervertebral discs of the cervical spine, I will add that manual manipulation in this area can lead to injury to deep muscles and ligaments. And operations lead to tetraparesis - loss of sensitivity and, alas, to disability.
I will focus on controlling the mobility of the joints of the spine, which is associated with maintaining the elasticity of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus. I'm talking about flexibility exercises.
Among them there is such a thing as a “folding knife”. Sitting on the floor, try to clasp your toes with both hands. Mild soreness under the knee is essential! In this case, we achieve stretching of the lumbar muscles of the spine and the muscles of the back of the thigh. It is important to bend towards your feet as you exhale.
There is also the “plow” exercise: while lying on your back, lower your straight legs behind your head until they touch the floor. But this is, so to speak, for the advanced. There is no need to try to reach the floor in the first movement; you can immediately stretch the back muscles, and they will make themselves felt for a long time. As a preparatory exercise, I recommend lifting and lowering your legs 90 degrees with a gradual increase in the range of motion until your legs touch the floor behind your head.
How many times? It is advisable to do at least 20 repetitions in one approach.
These simple exercises will relieve physical inactivity and give the body flexibility and elasticity to the muscles, which is important in the presence of spinal hernias.
Pain in the cervical spine, headaches, tinnitus, dizziness, depression, vegetative-vascular distance - all these ailments are somehow related to the cervical spine. It contains seven vertebrae, of which C5-C6 are the main, or cult, since they bear the entire weight of the head. What happens in the cervical spine when a hernia occurs there?
The intervertebral disc is cartilage, 84% water. It serves as a shock absorber and a kind of bearing for the spine. Cartilage does not have its own vessels and receives all the water necessary for its existence through the pumping function of the muscles. If stagnation occurs in them, they stop working, become dehydrated, and the dry disk, like a “bearing without lubrication,” simply falls apart. Let me note that a disintegrated disc does not cause any physical damage, although neurosurgeons are trying to convince sick people of this.
A disc herniation is shavings from a disc worn out by movements of the neck, which has accumulated under the ligaments of the spine. These shavings must be “swept away.” Only muscles will help this, and not a knife or laser from a neurosurgeon.
The cervical region, apart from the weight of the head, does not bear any other load. But in its structure it is a transition zone from the central brain to the peripheral, to the spinal cord. The brain receives nutrition (blood) through vessels passing through the muscle layer of the so-called “collar zone”. If something slows down its movement, headaches occur.
Over the course of many years of practice, the following conclusions can be drawn: a collapsed disc cannot be “twisted”; surgical removal of the disc is pointless, because apart from new scar-adhesive changes, there is nothing to expect.
Typically, by the age of 60, our muscle tissue resource is exhausted. And if the muscles, which make up 40% of the body, are inactive, hypoxic, ischemic, vascular, dystrophic conditions of the whole organism arise. Therefore, for people who are full of pills and they no longer give any effect, and do not want to put up with headaches, often combined with pain in the shoulders, arms, and neck, I recommend exercises that restore blood flow through the vertebral arteries.
The neck muscles are supported by the back muscles, so all exercises related to the load on the back muscles affect the vessels that supply the brain. This is primarily various types of pull-ups.
Older people can replace pull-ups with deadlifts. In every home it is good to have a horizontal bar or some kind of device under the ceiling that replaces it. Even if you cannot pull yourself up due to age or excess weight, then use the horizontal bar for other purposes. For example, we attach expanders or rubber bandages to it. We sit on a chair or on the floor and perform traction movements to the chest and behind the head.
If you don’t have an expander or a rubber band, do push-ups from the floor in the classic version (resting on your palms and straight toes) or in a simple version - with emphasis on your knees. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the body is straight and touches the floor with the entire plane when doing push-ups. For weakened people, I offer 10 times five push-ups.
The back muscles work well in combination with the shoulder muscles in an exercise that I call “cutting wood.” We attach the same expander or rubber bandage to a fixed support.
The higher the support, the better the muscles of the cervical spine are worked. We must try to ensure that while moving back and forth, the back also works.
An expander can be replaced with dumbbells and a similar exercise can be performed. For the chest muscles, which affect the nutrition of the brain, there is a “pullover” exercise.
Lying on the floor, or better yet, on a bench or sitting, we pull the weight forward with straight arms from behind our heads, stopping it in front of our chest. We perform the exercise with dumbbells; they should have such a weight that a person can lower behind his head and lift with straight arms at least 12-15 times.
This means that today we do push-ups, tomorrow we “cut wood”, after tomorrow we pull dumbbells or an expander.
Every day in our program there is one exercise that we do for a long time, 15-20 minutes, increasing the mobility of movements. Then quantity will turn into quality.
And, of course, we finish the classes by dousing them with cold water. But if you suffer from headaches, then lifting the bucket and tipping it over yourself is quite difficult. Therefore, take a contrast shower, the finishing point of which will be standing under ice water for 3-5 seconds. This is enough to burn the body. And in a month or two or three you will feel like a completely different person.
Schmorl's hernia
A Schmorl hernia is a pressing of a disc into an underlying vertebra.
Dysplasia of the vertebral surface does not cause any pain and can only affect the flexibility of the part of the spine where this hernia is found.
This was an accidental finding by a radiologist, a congenital spinal defect. It does not cause pain, but the hernia area must be “treated” with physical exercise. Typically, Schmorl's hernia is found at the level of the thoracic spine. Much depends on the physical condition of a person. Call on the horizontal bar to help you - while hanging, exhale, raise and lower your legs.
This is the so-called “half-rivet”. At the first stage, you can raise your knees, but not to the level of the forehead, but to the level of the abdomen. For physically weaker people, I recommend doing the “plow” exercise while lying on your back. With each raising and lowering of your legs, they should go further and further behind your head until they touch the floor. Usually 20 times is enough, with touching the floor in the last five repetitions. When lowering your legs behind your head, exhale!
And, of course, take a cold bath. This is cryotherapy, cold treatment. It will only bring benefits!
Go to next page→
A little about the disease
A herniated disc is a complex disease, and doctors often recommend surgery. However, spinal surgery is also fraught with certain consequences.
A vertebral hernia occurs due to disruption of metabolic processes in the tissues of the discs, mechanical injuries, and heavy loads. This provokes protrusion of the nucleus pulposus and pinching of the nerve endings. Complications include paralysis of the legs and dysfunction of the hip organs. A hernia significantly impairs the quality of life, causing severe discomfort when sitting, moving, lifting something heavy, turning and bending.
Valentin Dikul’s technique deserves special attention in the treatment of hernia. He himself once suffered a serious injury, and specialists promised him either limited motor functions or complete immobility. However, he himself managed to develop an effective method for completely restoring the important functions of the spine, and, following it, he was able not only to recover, but also to return to the circus arena.
After finishing his work at the circus, Dikul seriously began studying medicine and received the title of academician. He approaches treatment issues very responsibly and competently. The specialist does not promise an instant recovery, since an improvement in the quality of life can only be achieved through close cooperation with the doctor and his compliance with all recommendations.
Exercises for spinal hernia: basic rules
The main principle of back exercises for Dikul hernia is the absence of haste. Many patients, having gotten rid of primary pain, immediately try to increase the load in order to achieve a quick recovery. But you can’t do that. It is important to increase the load gradually, first training the muscle corset, and then more seriously working out different muscle groups.
Exercises for intervertebral hernia are divided into three groups:
- Gentle course. Indicated in the initial period of treatment. Gentle exercises can be performed regardless of fitness level. It is important to avoid fatigue and overexertion. The purpose of the complex is to prepare the patient’s body for future recovery. Exercise helps restore lost nerve connections between muscle tissue and the spinal cord.
- Intermediate course. The second stage of treatment can take up to 20% of the total course duration. Its specific time is determined by the stage and complexity of the disease, the level of training, as well as a number of individual characteristics of the body.
- Difficult course. These exercises will be aimed at restoring muscle strength in the affected area of the spine and consolidating the results achieved. Only strong muscles can support the body in the correct position and relieve stress on the spinal discs. And these are the main conditions for consolidating positive changes for a long time.
Only after you have completed the previous course in full can you proceed to the next one. The specific timing of this can only be determined by a doctor, depending on a number of individual characteristics.
Gymnastics for vertebral hernia should be performed regularly. You need to exercise at least three times a week or every day, depending on the recommendations of a specialist.
If you feel a deterioration in your health, do not panic - reduce your load and continue exercising. It is important to take a break if you become ill with an infectious viral disease.
It is recommended to adhere to a clearly developed technique and not change it unless the doctor recommends it.
Exercises for the spine with a hernia should be based on the following rules:
- You cannot change the order of doing the exercises, or increase the number of repetitions and approaches on your own.
- The intensity of training should be determined by personal well-being. Accustom your body to stress gradually, without making sudden overloads or pauses. Monitor any changes in your health. If any negative manifestations appear, consult a specialist.
- Don't make sudden movements. The torso or limbs must be moved in all directions with the same rhythm. Inhale air when tense, exhale when relaxing. Breathe calmly, not too deeply, do not hold in the air.
- Hanging exercises should not be performed in the presence of acute pain, otherwise you may further injure your spine. To lighten the load, you can perform exercises while lying down. You can move on to the crossbar or wall bars after completing the first courses, when the muscular corset of the spine is already quite strong.
The benefits of an expander for the musculoskeletal system
It is quite natural that most physical activities have contraindications and health restrictions. Therefore, the desire for a perfect body is often accompanied by dislocations, sprains and other injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
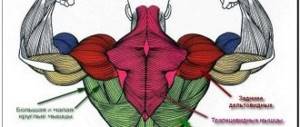
When exercising with an expander, you can use absolutely all the back muscles
However, exercises with an expander (with the right choice of load) only benefit the body. They:
- strengthen ligaments, improve joint mobility;
- stimulate blood circulation;
- prevent the development of joint diseases (including in elderly people);
- form correct posture;
- restore muscle activity during post-traumatic rehabilitation;
- burn calories, tone muscles;
- develop muscle strength and endurance, contribute to the formation of beautiful relief.
You can exercise with an expander at any age. The training will benefit both children and the elderly. The main thing is that the equipment corresponds to the age category. So, elastic rubber expanders are more suitable for children and teenagers, and spring metal exercise equipment is more suitable for adults.
Exercises for vertebral hernia
Exercises will help not only relieve pain, but also improve the muscle corset, restore connections between nerve endings and muscles. Exercises should be performed with spinal traction, which will make it possible to increase the interdisk space to the correct levels and relieve irritation of the nerve fibers in the spine.
For the exercise, you will need a rubber bandage (you can buy it at pharmacies or sporting goods stores) and loops that are attached to your legs and arms. Thanks to the latter, you can evenly distribute tensile forces and relieve discomfort. At the final stages, dumbbells, expanders and other weights can be used.
While lying on your stomach or back, perform the following exercises for intervertebral hernia of the spine (they are allowed if the acute forms of the disease have been removed):
- Lie on your back on the floor, attach loops to your legs and tie rubber bandages to them. The bandage must be at least 1.5 meters long. Extend your arms a little. Now slowly rotate your left hip to the right to the maximum angle, keeping the back of your head or shoulders still. Stay in this position for 2-3 seconds and smoothly return to the starting position. Do the same movement with the other thigh. One approach - 8 turns to the side. After each approach (there should be three in total), be sure to relax for 2-3 minutes.
- Spread your arms slightly to the sides, close your legs, and pull your toes towards you. Secure your legs with bandages. To prevent unnecessary body movements, hold on to the stretched bandages with your hands. Move both legs to the left, while letting your feet slide along the surface. Stay in this position for a few seconds, repeat the same in the other direction.
- The starting position is the same, but the hands are also secured with bandages. Feet are shoulder-width apart, arms crossed over chest. Rotate each shoulder one at a time, while being careful not to lift the rest of your body off the floor. Hold for a few seconds in the extreme position, then do the same with the other shoulder. Do three sets of eight reps each on each side.
- Rest a little and walk in a circle at a slow pace. Having restored your breathing and pulse, continue exercising. Lie on your stomach with your arms extended. To make the exercises easier, you can rest your heels on some piece of furniture. Raise your torso up to the maximum height so that your back bends. Hold the top position for a few seconds, then lower your torso.
- Lie on a hard surface with your back down, stretch your arms down, bend your knees at a right angle, place your feet on your toes. Perform an exercise to stretch the spinal discs by gently lifting your bent legs as close to your chest as possible. Hold for a couple of seconds and smoothly return to the starting position.
- The starting position is similar. At the same time as you tighten your legs, also raise your shoulders, try to pull them as close to your knees as possible.
The next complex is performed in a standing position. Keep your posture as straight as possible, do not bend your spine when performing power movements. Each exercise is repeated in three sets of 8 times in each direction. Perform the following exercises to treat a herniated disc:
- Stand up straight, straighten your back, take a stick with both hands and hold it horizontally at the bottom. Slowly lower yourself down, keeping your back straight and your knees slightly bent. The position should resemble that of an athlete lifting a barbell, and the stick in this case acts as a bar. Your knees should be bent, stay in this position for a couple of seconds. Look in front of you, watch your breathing.
- Step on the end of the bandage with your foot, hold the other end in the same hand, tighten the rubber, adjust the tension force taking into account your own physical capabilities. Place your other hand on the back of your head. Smoothly tilt the body to the side. The increasing tension of the rubber should create a clear counteraction. Then change the position of the bandage and repeat the movements. Hold the bend for a few seconds. The bandage can be replaced with an expander.
In the final stage of rehabilitation, it is permissible to perform exercises on the crossbar and wall bars. If you cannot hang by yourself, you can use loops to secure your arms and torso. Exercises for the back with a hernia are performed slowly and smoothly. They will be as follows:
- Hang on the bar and turn your pelvis to the sides, holding each turn for 2-3 seconds.
- While hanging on the bar, pull your knees towards your chest. Hold this position for a few seconds, then straighten up.
- In the same position, alternately move both legs to the right and left.
- Tie a towel under the muscles, on which your body weight will be concentrated. Perform backbends while simultaneously moving both legs behind your back.
Always follow the advice of a specialist. He may also prescribe exercises after hernia surgery, but usually not until 2-4 weeks after the procedure. In any case, it is important not to engage in amateur activities and listen to a professional.
We invite you to watch a video of performing exercises for the back with a hernia.
Effective exercises with a leg expander
To lose weight and strengthen muscles, you need to perform exercises with expanders for all muscle groups. You should select equipment based on your goals and level of physical fitness.
You can achieve results only if you practice regularly. To lose weight, you should train 3-4 times a week with high intensity and low resistance. To develop muscles, you will need to do 1-2 workouts per week for each muscle group.
List of exercises:
- Lying leg curl. It is necessary to attach the sports equipment to the barbell of the exercise machine and lie on your stomach. Hook your ankles onto the expander holder and lower and raise your legs. In this case, the legs should be carefully pressed to the floor. Perform 3 sets of 10 times, with a break of 2 minutes.
- Squats. You will need a rubber band-expander, fold it in half. Step on the edge with your feet and carefully press, and take the second edge of the expander in your hands. Slowly perform squats with a straight back. Do 2 sets of 15 exercises.
- Leg press. Tie a sports equipment ribbon to a barbell and secure your leg with an expander. Move away that there was a lot of tension on the tape, gradually pull your leg towards you and away from you. Perform the bench press 15 times for 3 sets, the interval between sets is 1-2 minutes.
- Tied legs. Fold the expander band in half and fasten the edges to both legs, so that the elastic band is stretched tightly. Lie on your back, lift your legs up, carefully spreading and bringing them together. Raise your legs in 2 sets of 20 times with a break of 2 minutes, perform exercises at least 3 times a week.
When choosing an expander, you must follow the recommendations of experts:
- The spring stiffness must be suitable, so before purchasing, test the model and do a few simple stretching and compression exercises.
- Choose a model with adjustable power and a set of springs.
- Compact models allow you to take the expander with you on the road, a business trip, and train at any time.
- Carefully visually examine the expander for defects; everything done must be properly secured. The handles must be free of chips and cracks, the rubber part must be free of stripes and tears.
- For tape models, choose a length of expanders of 1.2 meters or more; they stretch well and allow you to perform more exercises. The width of the tape should be at least 15-20 cm.
Safety when performing exercises is paramount:
- Carefully check the fastening of the expander to the horizontal bar or exercise machine.
- Before the exercise, visually inspect the equipment for cracks, breakages, and the strength of the handles and springs.
- When performing the complexes, make sure that your hands do not slip; use talc or powder.
An expander is a multifunctional, effective sports equipment; exercises with an expander help women acquire the desired shape at home in the shortest possible time.
Indications for use
It is recommended to perform exercises with an expander:
- schoolchildren (to strengthen muscles and form correct posture);
- beginner athletes;
- people with poor health;
- patients who have recently suffered musculoskeletal injuries.
The main thing is to choose the load based on your own capabilities.
Contraindications
An expander is a simulator on which it is simply impossible to get injured, so there are practically no contraindications to its use. Everyone can do back exercises, except people with acute joint diseases.
Exercises for the buttocks
Exercises with an expander for women are performed with a rubber band to tighten the shape and improve the appearance.
Exercises:
- “Sumo” means standing on an expander band, placing your feet shoulder-width apart, spreading your arms to the sides, and pulling the expander. Perform squats with a straight back 10 times, break for 3-4 minutes, repeat the exercise.
- "Stork". It is necessary to fix the expander on the floor with your foot, and firmly grasp the handles of the projectile in your hands. With your hands on opposite sides, pull the band tight and leave one leg back. Hold for 2 seconds, return to the original position, repeat for the other leg. Perform exercises 20 times for each leg.
- For pumping muscles. Tie the band expander to the exercise machine and take a horizontal position on the floor. Grasp the handle of the projectile and tie it to your legs. Gradually raise your legs and lower them one by one, straining your buttocks.
Video with exercises for the back with a hernia
Gymnastics must necessarily correspond to the patient’s condition. In case of acute inflammation, you should not perform exercises. But as soon as severe pain passes, you can begin to carry out exercise therapy training for a herniated cervical spine in order to cope with the disease as quickly as possible.
If the patient has pain, exercises should be gentle. It is best to perform all exercises in a special collar that fixes the position of the cervical vertebrae.
When performing exercises, you must lie on a flat, hard surface or sit on a stool, depending on the type of exercise.
You need to perform the following complex:
- While sitting, place your hands on your hips, palms down. Make circular movements forward and backward with your shoulders. As a result, blood circulation in the neck area improves and the mobility of the shoulder joint is restored.
- While sitting, lower your arms freely downwards. Straight arms are spread to the sides, then raised up, bringing the palms together, then again spread to the sides at shoulder level, and then returned to the starting position. The exercise brings the same effect as the previous one.
- While sitting, keep your arms along your body. With straight arms, swing your arms up through the sides and forward.
- Lying on your back, arms extended along the body. The fingers must be clenched and unclenched with force and at a fast pace. This exercise restores blood circulation in the hands and relieves paresthesia in them.
Regular, more intense exercise will help avoid flare-ups. Twisting and sudden movements are prohibited in any case, but the range of movements during the exercises may be greater.
An approximate complex could be like this:
- Sitting or standing, arms extended along the body. The head is tilted forward, with the chin toward the chest, backward as much as possible, to the right and left, trying to reach the ear with the shoulder. The shoulders should remain motionless - the tilts are performed exclusively by the head. As a result, blood circulation in the neck and brain improves, which eliminates tinnitus and headaches. The mobility of the spine is restored, muscle spasm is relieved.
- While sitting or standing, you need to turn your head to the right and left. At each extreme point, you need to fix the position for 2–5 seconds. As a result, the mobility of the cervical spine improves and blood circulation becomes more intense.
- Lying on your back, on a hard surface. The head is raised so that it forms an angle of 45 degrees with the floor. This position must be maintained for 2 to 10 seconds. As a result, the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle are strengthened and better support the spine.
- While standing, you need to perform circular movements with your arms back and forth. The muscles of the shoulder girdle will thus become stronger.
- Also while standing, pick up lightly weighted dumbbells. The arms are spread to the sides to shoulder level and held in this position for 2–10 seconds. The exercise eliminates paresthesia in the arms, improves mobility in the shoulders, and strengthens the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
- Standing on all fours, looking forward. The head is smoothly lowered down, trying to relax the muscles as much as possible. In this position, the spine should stretch itself under its own body weight. You need to maintain this position from a few seconds in the first workouts to a minute. As a result, the spine regains its flexibility and excessive stress is removed.
Some strength exercises can be performed both during remission of the disease and for its prevention. Any exercise that helps strengthen the muscles of the back and neck and ensures better blood circulation in these areas will be beneficial.
The training complex should include:
- Pull-ups. This exercise on the horizontal bar helps to gain strength in the muscles of the back and neck, and has a beneficial effect on the condition of the blood vessels in this area. You can replace pull-ups with rows with an expander if you can’t do pull-ups.
- Push ups. You can perform the exercise both in the classic starting position - with emphasis on the palms and toes, and in a simplified position - leaning on the palms and knees. During a workout, it is advisable to perform at least 50 push-ups, but they can be divided into sets - up to 10 sets of 5 repetitions.
- Pull the expander down. The expander must be secured to a fixed support. The higher this support is, the better. It is necessary to pull the free edge of the expander towards you, and then, loosening your grip, allow the expander to return to its original position.
- Exercise with dumbbells for the chest. Lying on the floor, you need to pick up dumbbells and lower them to the floor behind your head. With straight arms, you need to lift the dumbbells in front of you, and then smoothly lower them back. You must perform at least 12–15 repetitions.
Many patients do not take gymnastics seriously. This important component of complex treatment is often neglected, considering such an activity boring and not very effective. This opinion is erroneous, because exercise therapy provides a significant improvement in the patient’s condition. You can notice the first progress within a week, and after a month of regular training, the positive effect will be pronounced and lasting.
A video of exercises, which will be useful for cervical hernias, can help patients to perform the exercises most correctly.
Below are the most popular and effective exercises for men and women:
- Rowing to the waist while sitting. Starting position: sit on the floor, bring your legs together, straighten your knees and place them in front of you. Throw the expander over your feet and take the edges of the cord in your hands. As you inhale, straighten your back, move your elbows and shoulders back, trying to connect your shoulder blades. At the exit, return to the starting position. To feel all the back muscles without exception, you need to perform two or three sets of 12-15 repetitions. Rest between sets – 30 or 40 seconds.
- Standing back row. Starting position: stand up, place your feet shoulder-width apart, throw the ribbon over the horizontal bar, straighten your back, secure the ends of the cord in your hands. As you inhale, pull your elbows back, squeeze your shoulder blades together and move your pelvis back. Hold this position for 2-3 seconds. As you exhale, return to the original position.
- Bringing your hands together in front of you. Stand up, lean on your feet, place your legs exactly under your shoulders, straighten your back, tuck your pelvis forward, throw the elastic band over your back, and place its ends in your hands, with your arms lowered along the body and relaxed. As you inhale, forcefully bring your hands straight in front of you. If the length of the expander and your physical capabilities allow, try not just to stretch it out, but to cross your arms in front of you (this will increase the load significantly). Exhale and slowly return to the starting state.
- Raising your arms on a chair. Sit on a chair, rest your feet on the floor, straighten your back, throw the band over the seat of the chair, and take the ends of the expander in your hands. Taking a deep breath, pull the ends of the expander upward (to the level of the forehead or above), without straightening your elbows. Fix the load. As you exhale, return your hands to the starting position.
- Lunge arm stretch. Starting position: stand up, throw the expander over the horizontal bar, place your hands in front of you, hold both ends of the cord in your palms. Make a slight lunge forward with your right leg, also lean your body forward slightly, straighten your back, maintain a deflection, do not slouch. During the lunge, inhale and straighten your arms up. As you exhale, return to the starting point.
Pay attention to the technique of performing exercises with an expander
Exercises with an expander should be performed 10-12 times. After completing the exercises, rest and then do one or two more approaches.
You can also do Dr. Bubnovsky’s gymnastics with an expander. You can get acquainted with the list of exercises and the technique of performing them from your doctor.
Figure eight expander: complex for the whole body
Exercises “8” with an expander for women consist of the following actions:
- Lie on a horizontal surface, grip the expander with your shoulder blades and simultaneously raise your arms above your head, pulling on the machine. Repeat 4 sets of 15 exercises.
- In a horizontal position, squeeze the edges of the figure eight exercise machine in both hands and alternately lift the limbs. Perform 10 times for 5 approaches with an interval of 5 minutes.
- Insert your feet into 2 circles of the “8” expander and lie on the floor, fix your arms above your head. Raise your arms and legs at the same time, 15 times in 2 approaches per day. The interval between exercises is 1-2 minutes.
- Stand with a straight back, rest your hands on a chair, place each foot in a circle “8” and take your legs one by one, pressing them to the pelvis. Perform the method 10-12 times a day, daily.
Types of expanders and how to choose the right projectile
Based on the type of load, equipment is divided into compression expanders and tension expanders. In the first case, the projectile must be compressed, and in the second, it must be stretched.
Types of expanders
When choosing an expander, you need to pay attention to what muscles it is intended to train. Some products allow you to train a specific muscle group, while others are multifunctional and are used to develop different muscle groups. The rigidity (degree of resistance) of the expander is measured in kilograms.
Today, the following types of expanders are distinguished:
- carpal;
- shoulder (chest);
- rubber (tubular);
- latex tape;
- skier's expander;
- "butterfly";
- multifunctional.
Depending on the material, expanders are rubber, metal and plastic. Metal projectiles are intended for professional athletes, rubber ones for amateurs (including children and teenagers). As for plastic expanders, they can be both amateur and professional. However, they have a significant drawback - fragility.
Often there are products with anatomical loops for the legs or anatomical handles that follow the shape of the palm. The handles of the expander can be improved: have a massage effect or have ventilation holes.
When choosing the type and rigidity of the projectile, you need to start from what goal you are pursuing. Please note: the same muscle group can be trained using different expanders.
Your task is to choose the product that is right for you. To check how the projectile “behaves”, take it in your hands and do a few exercises. It is desirable that the resistance of the expander can be adjusted (this will allow you to gradually increase the load without risk to health).
Sports stores offer a wide selection of expanders: expensive and cheap, high quality and not so good. Experts recommend buying safe and reliable products from trusted manufacturers.
When choosing an expander, pay attention to its rigidity. Tips for choosing an expander:
- Choose the appropriate hardness. The equipment must match your build, level of training, and goals. Professional expanders can have a resistance of more than 50 and 100 kg, and the stiffness of amateur expanders rarely exceeds 25 kg. Information about the hardness of the product must be indicated on the label. You can also pay attention to the color of the projectile: yellow – low hardness, green – higher, red – medium, blue – high.
- Inspect the product before purchasing. When choosing an expander, pay attention to the quality of the material. There should be no defects or malfunctions on the surface of the apparatus that could reduce the quality of the exercises or cause injuries.
Types of posture correctors
Spinal supports are divided into different types depending on the source of pathology and the functionality of the product. The most common types are orthopedic reclinators, bandages in the form of a belt, magnetic and electronic devices. Reclinators are prescribed in the initial stages of the disease to correct mild skeletal deformities. Correctors in the form of a belt come in thoracic and thoracolumbar types and are produced in the form of wide belts with fasteners. These models relieve back strain and help with progressive pathologies or after operations. Electronic and magnetic devices give the user a signal in case of poor posture; they are suitable for those who lead an inactive lifestyle.
The device unloads the spine, promotes alignment of the upper part, is suitable for children and adults with weakened pectoral muscles, and is optimal for adjusting disorders in the initial stages. Models are divided into preventive and therapeutic. The first ones are distinguished by a slight degree of rigidity and are designed to develop the skill of keeping your back straight. The products are simple in design, made of cotton or sateen, and complemented with elastic pads. Therapeutic reclinators are prescribed for complex pathologies, severe stoop, scoliosis, and osteochondrosis. They have a rigid or semi-rigid body with metal or plastic ribs. Effectively fix the spine without restricting movements. The reclinator restores muscle tone and normal mobility of the vertebrae.
The belt helps with a weakened skeleton, straightens improperly formed back muscles, reduces stress, and helps you get used to an upright position. Waist correctors are either supportive or corrective. The first ones are elastic and do not contain rigid elements. They are worn if there are prerequisites for curvature. Such models are distinguished by a simple design consisting of shoulder straps and a corset. Corrective products are intended for the thoracic or thoracolumbar regions. The chest corrector is worn for kyphosis, stoop, scoliosis, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, during the recovery period after injuries or to prevent disorders. A thoracolumbar belt with a rigid back and metal ribs is chosen for severe disorders.
Magnetic corsets consist of a belt, straps that are fixed on the back and an elastic insert with magnets. Effectively improves posture, eliminates stoop and scoliosis. Can be worn to work or school. The design does not distract from everyday activities. Integrated magnets increase blood supply to muscles, relieve swelling, restore metabolism, improve well-being, and increase tone. The product is intended for people leading a sedentary lifestyle. Staying in the same position for a long time negatively affects the figure, displaces the vertebrae, and contributes to the occurrence of scoliosis and other orthopedic diseases.
The electronic corrector does not replace the orthopedic models described above, the wearing of which is prescribed by a doctor. The only task of this device is a reminder. If a person takes an incorrect position, the device reports this with a sound signal. The device helps you avoid slouching, maintains a healthy posture, minimizes the risk of spinal problems, and prevents fatigue and pain. The corrector is compact in size and can be attached to the body or clothing. For a child, you can buy children's models that are made in the form of a toy. The gadget does not require constant wearing.
General rules of use
Basic rules for using an expander:
- Exercises with an expander belong to the category of strength exercises, and to grow and strengthen muscles you should not perform many repetitions (multiple repetitions of exercises are appropriate for cardio training). The optimal number of repetitions in one approach varies from 12 to 15. If you feel that the exercises are becoming too easy, you can increase the rigidity of the apparatus (add resistance).
- Before any strength loads (including training with an expander), you need to do a warm-up. During it, you should warm up those muscle groups that will be worked out during the main part of the lesson. Every workout should end with stretching. It will prevent lactic acid stagnation and help avoid discomfort the next day after training.
- Exercises with an expander should be performed smoothly. The appearance of pain during exercise indicates the presence of health problems or that you are doing something wrong.
- When performing an effort, you need to “hang” in this position for a few seconds, and only then return to the starting position.
- Before you start training, you need to make sure that the expander is firmly attached to the wall or horizontal bar and is not damaged. The presence of microcracks, problems with fastening - all this can cause the cord to break at the most inopportune moment and lead to injury.
- It is advisable to exercise with an expander in shoes. If you catch a dense projectile on an unprotected foot, you can get calluses and cramps.
There are other exercise machines and sports equipment for strengthening the back, which you can familiarize yourself with in the following articles:
Kinesitherapy as an addition to medicine
You should not assume that when treating with movement you need to refuse standard medical care. The best option is combination with a gradual shift towards kinesitherapy.
Pharmacology is necessary as a supportive agent, without which the condition may worsen.
Treatment and prevention of diseases is divided into 2 types of therapy:
- Elimination of symptoms of the disease
. Sometimes the manifestation of symptoms provokes the development of the cause. Pills and standard drug treatment often eliminate the symptom. Treatment ends, but symptoms return. This benefits pharmaceutical companies. Investing money in developing drugs that will treat the cause (and sometimes this is simply impossible if the cause is an unhealthy lifestyle) is not a profitable endeavor. Billions are made from treating symptoms; - Elimination of the cause
. Few people think about why they developed this or that disease. But everything happens for a reason. And if you get to the bottom of it, you can not only get rid of painful symptoms, but also return health to the form it was 5, 10 or even 30 years ago. This is what kinesitherapy does. The doctor understands the causes of your diseases and prescribes treatment with movement. The “Home Doctor” expander is a tool for effective kinesitherapy.
Treatment of symptoms is ineffective and costly. But you need to approach your own health wisely. Movement therapy should not be perceived as a harsh alternative to modern medicine. We are talking about a supplement with a gradual transition to health.