Basic exercises: what and how
By “base,” as you understand, I mean basic exercises—multi-joint exercises that involve several muscle groups at once. For example, you are doing some exercise. Pay attention to how many joints are working.
If there is only one pair (elbows or knees), then this is an isolating exercise aimed at working individual muscles. If there are two pairs (elbows and shoulders or knees and hips), then this is already a basic exercise. But what’s interesting is that curling your arms with a barbell for biceps, although it actively uses only one pair of joints (elbows), is still considered a basic exercise - so to speak, an exception to the rule. I’ll explain why this is a little lower.
Actually, the simultaneous work of several muscle groups (for example, pectoral and triceps, as well as shoulders) is the main “trick” of basic exercises, due to which muscle growth, strength or endurance occurs. That is why novice athletes are recommended to use the basic ones for general development, since isolating ones perform completely different tasks.
"Base" for the whole body
Let's start from top to bottom and body parts.
Shoulder muscles (deltoid):
- bench press from the chest, from behind the head while sitting or standing (the trapezius muscles, triceps and upper chest are also pumped), also called the military press;
- Arnold press;
- dumbbell press sitting or standing;
- barbell pull to the chin;
- horizontal stretch to the shoulders (on the middle block).
The peculiarity of shoulder presses is the simultaneous work of not only the shoulder muscles, but also the upper part of the trapezius.
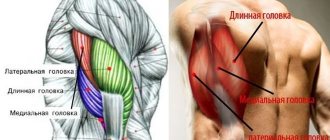
Chest and triceps muscles:
- bench press with a wide, narrow or medium grip, at a positive, negative angle or on a flat bench;
- dumbbell bench press at different angles or on a flat bench with different hand placements;
- push-ups from the floor with different widths of palms, from a hill;
- push-ups on parallel bars with your own weight, with additional weight, with the center of gravity shifted forward or backward, with different widths of the bars;
- pullover with a dumbbell (also uses the back muscles);
- reverse push-ups (rest your hands on the bench behind you).
Bench presses, with the correct technique, also use the back muscles and the front of the shoulders.
Back muscles and biceps:
- pull-ups on the bar to the chest, behind the head with a wide, narrow or medium grip;
- pull-ups on the bar with a reverse middle grip, parallel grip (palms in), extended grip (palms out);
- pulling the upper block to the chest and behind the head with different grips;
- traction of the lower block to the stomach;
- rowing a barbell or dumbbell in an inclined position towards the lower abdomen;
- one-arm dumbbell row;
- T-bar pull;
- barbell pull to the chin;
- curling arms with a barbell (curved bar) for biceps;
- curling arms with dumbbells with wrist rotation;
- Hammer exercise.
The trapezius muscles of the back deserve special attention, three sections of which are pumped on different days (usually in parallel with other main muscles): the upper section together with the shoulders during seated or standing presses, the middle and lower sections together with other back muscles when pulling weights towards oneself and shrugs.
The standing biceps curl (a single-joint exercise considered basic, which I promised to talk about) is considered basic because, although only one pair of joints works dynamically, the muscles of the back and shoulders work statically. But the same curls with a barbell on a Scott bench are already isolating, due to the exclusion of the back and shoulders from the work. Something like this.
Muscles of the abdomen and lower back:
- flexion-extension of the body with rotation of the body;
- flexion-extension of the torso on an inclined bench;
- bending to the sides with a dumbbell;
- hyperextension;
- deadlift with different leg positions, including in the Smith machine;
- deadlift (Romanian).
It is noteworthy, but exercises in the form of deadlifts of various modifications, in addition to pumping the lower back and the lower part of the rectus abdominis muscle (abs), are an excellent help for the development of legs, as described below.
Muscles of the legs and buttocks:
- deadlifts of various modifications;
- squats with a barbell, in a Smith machine, with dumbbells (Plie exercise, for example);
- leg press in a hack machine;
- lunges with weights of various modifications;
- jumping high from a place, “stepping” onto a bench with weights;
- lifting the pelvis while lying with your back on a bench (feet on the floor).
By the way, all exercises in which you straighten your legs at both the knee and hip joints can be considered basic. The main thing is to adapt them in such a way that you can use additional weight - your own body weight may not be enough.
As for the development of the calf muscles, if you want to develop them with basic exercises, and not with isolating exercises, calf raises while sitting or standing, then pay attention to standing jumping exercises (possibly with a weighted weight). Here you train your entire legs, including your calves, by straightening your legs at all joints and pushing off the floor with your toes.
I think the essence of the basic exercises is clear to you. We also met those in isolation in absentia. And do you think these are all types of exercises? No, there are still special ones. If you are interested, you can ask me about them in the comments. In the old fashioned way, I suggest sharing this article and subscribing to blog updates: I always have something else to surprise you with.
ADDITION:
Basic exercises are multi-joint movements that involve several muscle groups and joints at once. As a rule, it is thanks to basic exercises that athletes of varying degrees of training manage to build muscle mass to one degree or another. Yes, auxiliary movements in the form of isolation exercises also affect muscle growth, but only after work has been done with the basic ones, and not vice versa.
Among the basic ones there are simply basic exercises that work both medium and small muscle groups at the same time, as well as basic basic exercises that involve the muscles of almost the entire body (and this is not an exaggeration, but a scientifically proven fact).
Strength exercises for the whole body
Chest and triceps muscles
Basic:
- bench press on horizontal and inclined benches;
- dumbbell bench press on the same benches - can be done at home;
- horizontal bench press, with a positive and negative incline of the bench;
- Hammer press (simulates bench presses, but with free weight);
- push-ups with different hand positions - for home use;
- dips;
- reverse push-ups - suitable for home use.
Insulating:
- arm extensions in a block simulator;
- extension of arms from behind the head and in a bend over with dumbbells - for home;
- French press standing, sitting or lying with barbells or dumbbells - with dumbbells and kettlebells suitable for home use;
- lying dumbbell flyes - for home;
- bringing your arms together in a crossover (block frame).
Back muscles and biceps (biceps)
Basic:
- deadlifts in various ways - for home, if done with dumbbells or kettlebells;
- pull-ups on the bar with various grips (wide, medium, narrow, reverse, deployed) - for home use;
- barbell row or dumbbell bent over - with dumbbells for home;
- one-arm dumbbell row in an incline position - at home;
- traction of the upper block to the chest and behind the head in a block simulator;
- traction of the lower block to the stomach;
- deadlifts on lever machines.
Insulating:
- pullover with dumbbells - for home;
- hyperextension - for home;
- shrugs with a barbell or dumbbells - with dumbbells for home;
- arm curls with a barbell or dumbbells - for home, if with dumbbells;
- Scott Bench Curls;
- concentrated curls with dumbbells - for home.
Shoulder muscles
Basic:
- barbell or dumbbell presses from the chest or behind the head while standing or sitting - you can do it with dumbbells at home;
- presses in Hummer-type machines;
- Arnold bench press - at home;
- row of a barbell or dumbbell to the chin - with dumbbells at home;
- horizontal broach.
Insulating:
- lifting dumbbells to the sides, to the sides while bent over, in front of you (they are also called swings) - we do all this at home;
- lifting dumbbells to the sides while lying face down on a bench - at home;
- raising arms to the sides in block exercise machines.
Leg muscles
Basic:
- squats with a barbell on the shoulders, chest and arms;
- Smith machine squats;
- “plie” squats - for home;
- leg press in a machine or hack squats;
- “donkey” calf raises - at home;
- jumping out of place - for home;
- lunges with dumbbells or in a Smith machine - with dumbbells at home.
Insulating:
- leg extension in a block simulator;
- leg curls in a block simulator;
- raising your toes while sitting in a machine;
- leg extension and abduction in a block exercise machine;
- swing your legs in different directions in a simulator or in a “block”.
Abdominal muscles
Basic:
- flexion of the torso with a block simulator;
- bending the torso on a horizontal bench;
- bending the torso while lying on the floor - for home;
- bending the torso while lying on the floor on its side - for home use.
Insulating:
- bending the torso on an inclined bench;
- raising your hips to your chest while hanging on the bar - at home.
Most of the exercises presented are definitely suitable for a girl, especially squats in a Smith machine with legs forward, lunges with different leg positions. In addition, there are a lot of exercises where girls can do with their own weight or the weight of their own body parts. For example, lifting a bent leg while on all fours.
General or main "base"
Have you ever encountered such a sport as powerlifting? If yes, then you understand what I am leading to, and if not, then I will tell you briefly. In this sport, there are only three competitive exercises - the bench press, the squat with a barbell on the shoulders and the deadlift. These three exercises constitute the very foundation with which any guy needs to begin his sports activities.
Again, without exaggeration: the bench press (with the correct technique) loads the muscles of the chest, arms, back, buttocks, legs and torso. Quite a lot, right?
The deadlift is no less, although the working muscles are different. Their number is approximately the same, only the body zones are different. What can we say about squats with a barbell, where you have to control the barbell on your shoulders: here, in addition to the main (dynamically and statically working muscles), the work also includes stabilizer muscles, which are responsible for balancing the body with weights.
In short, by performing these three exercises, you are guaranteed to be able to hypertrophy your own muscle tissue. But let's not dwell on this and go through specific areas of the body. I propose to consider the exercises from top to bottom.
"Base" for the shoulders
Among the basic exercises for the deltoid muscles (shoulders), I most often came across the following exercises (by the way, they can be performed both in the gym with sports equipment, and at home with homemade ones, or with dumbbells, kettlebells, expanders - this applies not only shoulder exercises):
- bench press from the chest while standing or sitting (“military press”);
- overhead barbell press while standing or sitting;
- standing or sitting dumbbell press;
- Arnold press;
- horizontal broach (on the middle block);
- barbell pull to the chin.
By including these exercises in your training program, you will not be left behind in terms of broad shoulders.
I will say in advance that there are related exercises that simultaneously pump both some muscle groups and others. For example, dips: the pectorals, triceps, and anterior deltoids (shoulders) work here. Therefore, it is difficult to separate some muscles from others, and even impossible when it comes to basic exercises.
“Base” for the chest and triceps muscles of the arms
The chest and triceps are pumped with the help of:
- bench press on various benches (horizontal, negative or positive incline), as well as with different widths between the palms;
- dumbbell bench press (again, on different benches);
- dips (even with additional weight);
- reverse (back) push-ups;
- push-ups from the floor with different positions of the hands (great for home);
- pullover with dumbbells.
As I already said, there are exercises that involve completely different muscles. So, if you pump your chest and shoulders on different days (and usually this is the case, the chest is pumped together with the triceps), then take a break of two days between them - your shoulders need rested triceps.
“Base” for the back and biceps of the arms
You can develop your back and such popular muscles as biceps with the following exercises:
- deadlifts of various modifications;
- pull-ups on the crossbar (horizontal bar) in various ways and with different grips;
- traction of the upper and lower blocks;
- Bent over barbell and dumbbell rows;
- one-arm dumbbell row in a bent-over position;
- T-bar pull.
A wide back means your deadlifts. Do them, and you will certainly rock your own “frame”.
“Base” for legs and buttocks
You can pump up your legs and butt with the following basic exercises:
- squats with a barbell on the back, chest or arms, as well as similar movements in the Smith machine;
- leg press in appropriate machines (for example, a hack machine);
- lunges with weights of various designs - forward, backward, to the side;
- walking on a hill with weights.
The list of basic leg exercises can be safely supplemented with isolating exercises such as leg bending and extension in exercise machines - they perfectly complement this entire “base”.
FC. Exercises for all muscle groups
Exercises for all muscle groups: a complex for practicing at home
Home workouts are a great way to stay in good shape without spending extra money (on a gym membership or purchasing exercise equipment).
A competent selection of exercises allows you to work all the muscles of our body: tone them and lose extra pounds.
Let's look at effective exercises for all muscle groups at home, examples of training and nuances of training.
Training at home: basic rules and recommendations
Recommendations
Description
Choose a time convenient for you
There are a large number of myths regarding the best time for strength training: some people train only in the morning on an empty stomach, others try to exercise in the evening. In practice, it is best to simply choose a convenient period of time - when the body is full of strength and you are ready for a productive activity without haste. The final result does not depend on the time of day, but on the regularity and plan of your training.
Important! You should not exercise after a heavy meal (the best option is 1.5-2 hours after a meal) and a couple of hours before bedtime.
Training length – 40-60 minutes
The duration of the session is especially important if you are planning to lose weight. The structure of the training includes a warm-up (warm-up exercises: running, brisk walking, jumping rope) - 10 minutes, the main part and a cool-down (gymnastics for stretching the muscles of the whole body) - 10 minutes. For a set of basic exercises you have about 30-40 minutes left.
Note! You should not increase the duration of the training with the help of a warm-up or cool-down - these are only auxiliary elements for working on the body.
Train 3 times a week
This schedule is equally effective for both beginner and advanced levels: the muscles recover well between individual sessions, and the body is ready for a new load.
Alternating loads
Combine cardio and strength training for all muscle groups. A fairly effective option (especially when losing weight) is to alternate strength and cardio training every day.
Use furniture
A table, stable chair or stool can be useful for stretching and doing some exercises (eg leg swings, reverse push-ups, etc.).
Important! Using furniture as a support when training at home is only worth it if your weight does not exceed approximately 70 kg.
Exercise not only in the apartment, but also in the fresh air
Training (running in the park) or pull-ups on horizontal bars will be twice as useful. If it's a little cool outside, this is an additional plus; your body will then burn more calories (energy for heating).
Modify your training program every 4-6 weeks
The most correct and effective system of exercises gradually ceases to affect the body - the human body simply gets used to a certain type and sequence of physical activity. That is why you should periodically make changes to your plan. Such changes are stressful for the body, due to which the process of burning fat and increasing muscle mass will be enhanced.
Complete Full Body Workout
Pros and Cons
The benefits of a full body workout include:
- At each lesson, all muscle groups are involved in the work. This can help avoid atrophic processes (reduction of some areas of muscle tissue in volume).
- With such a load, the body produces an increased amount of testosterone, which is necessary for the growth and timely restoration of muscle tissue.
- With a fairly varied training plan (connect muscles to work from different angles, in different sequences), complete adaptation of muscle fibers to such a load is almost impossible (this contributes to constant progress).
- When performing the same exercises, positive muscle adaptation occurs, which slows down the process of muscle growth, but increases strength and endurance.
The disadvantages include the following:
- Risk of increased fatigue. Quite often, athletes may experience a state of overtraining (with a lack of proper rest).
- Monotonous workouts can reduce motivation for results and cause fatigue (to prevent this, try to make changes to the training plan).
What is included
Exercise
Description
Warm-up (necessary for a comprehensive warm-up of all muscles) – approximately 10 minutes
- Place your hands on your shoulders and rotate your arms back and forth. Perform 10 turns.
- Place your hands on your waist and bend your body to the sides.
- The starting position is similar to the previous one, but you need to rotate your pelvis clockwise/counterclockwise.
- Perform jumping rope for 2 minutes without a break.
For hands
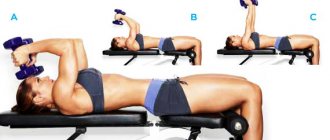
Your feet should be shoulder-width apart and hold weights (dumbbells or water bottles) in your hands. Perform curls, performing 20 repetitions for each arm (3 sets).
For the chest muscles (fitball or stable chair required)
Take a lying position (emphasis on the upper back), legs should be bent at the knees and left on the floor for a stable body position. Take the weight and gently lower it behind your head as you inhale. As you exhale, lift the weight. Perform 4 sets of 12 repetitions.
For the back
Take a classic position while lying down, palms at a medium distance. Next, smoothly lower your chest towards the floor surface. The back at this moment should be straight, the pelvis and lower back should be on the same line. Perform 3 sets of 10 reps.
For the press
Lie down on a special mat, bend your knees. Place your hands at the back of your head. As you exhale, begin to lift your body to your knees (while keeping your lower back firmly pressed to the floor surface), and then lower yourself back down. It is necessary to do 3-4 approaches of 15-20 times.
For the gluteal muscles
Sit on the floor (use a mat), keeping your back vertical without arching your lower back. Maintaining your posture, lift yourself up using your tense pelvic muscles (the position is similar to sitting in a chair). Stay at the top for 20-30 seconds and sit back down. Repeat the exercise 10-15 times.
For legs
Take a position lying on the floor, your arms should be located along your body. Next, the pelvis is up so that the shoulders and head remain pressed to the floor. Perform 3-4 sets of 12 lifts. You can use weights - place it just below the belt line.
Cool down (necessary for comprehensive muscle stretching and eliminating tension)
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, pull one knee toward your chest and hold for 20 seconds. Do a similar movement for the other leg.
- Raise your left arm up and reach your fingertips towards the ceiling for 10-20 seconds. Repeat the same movement for your right hand.
- Stand on your knees and, bending your lower back, lower your pelvis behind your heels. Stay in this position for 10 seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat the movements 3-4 times.
Training program
Important! The best option for beginners is 2 workouts for all muscles per week.
A sample lesson plan is structured as follows:
Day 1
- Warm-up: about 10 minutes.
- Push-ups: 3×10.
- Lifting weights up (use dumbbells or water bottles): 3x15.
- Bent-over weight row: 3×12.
- Squats: 3×20.
- Hip raises (one leg emphasis): 3×10.
- Lying body raises: 3×15.
- Plank: 3x30 seconds.
- Cool down: muscle stretching – 5 minutes. Day 2
- Warm up: approximately 10 minutes.
- Reverse push-ups: 3×12.
- Forward lunges: 3×12.
- Arm swings (using weights): 3×15.
- Hip raises: 3×12.
- Bent-over raises with weight: 3×15.
- Lying leg raises: 3×15.
- Side plank: 3x10 seconds (each side).
- Cool down: stretching elements.
If you are planning to get rid of excess weight, as well as increase the endurance of your own body, you should pay special attention to cardio exercises (running, jumping). The optimal length of such a load is more than 30 minutes. Only after half an hour does our body begin to burn fat at an average heart rate. For beginners, the best option would be a combination: 2 strength training + 2 cardio sessions per week. To get an effective load on all muscle groups, you need to learn how to perform all the basic exercises with the correct technique. Try to choose complex multi-joint exercises that use several muscles at the same time - push-ups, pull-ups, etc. As your muscles get used to regular exercise, use a variety of weights. The main point of any workout is concentration; try to monitor your breathing and muscle function in each exercise. With a thoughtful approach and dedication, home workouts can bring more benefits and results than a haphazard visit to even the most popular gym. Training for all muscle groups is a kind of construction kit - you can independently assemble different exercises, focusing on the target muscles. At the same time, any beginner is able to vary the load due to simple and complex versions, the use of various weighting materials, pieces of furniture, etc. During exercise, use minimal pauses - approximately 30-40 seconds (try to move all the time to maintain a fast pace of training). Also, do not forget about the water regime; as a rule, during one moderate-intensity workout you should drink at least 500 ml of still water (dehydration during physical activity significantly worsens your well-being and overall productivity).
Main conclusions
Proper training at home will help improve your fitness and pump up your muscles. To create a lesson plan you need:
- Choose a convenient time and a list of training exercises for each muscle group.
- Set the sequence, number of approaches and repetitions for each exercise, rest time.
- Adding stretches for warm-up and cool-down will help avoid sports injuries and discomfort during and after exercise.