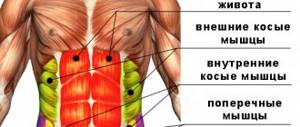
Before you start training hard, you need to get acquainted with the theory. More specifically, to work on specific areas you should know the structure of the frame. For example, to properly train the abdominal area, you need to know the abdominal muscles. This will help you choose the right individual set of exercises for the rectus, oblique, internal and external abdominal muscles.
Mandatory study of the theory of the anatomical structure of the muscular frame makes it possible to see the work of specific muscle groups, as well as methods of influencing them. This approach determines which movements will pump up the indicated areas. It will also be possible to find out where the main processes will take place during the work process. In this way, tension in a specific part of the abs is controlled and a training process is created that you control. So that all the work on the body does not go in vain, and also in order to correctly shape your figure, you need to find out which areas should be worked on especially carefully and how to do it.
Abdominal muscle anatomy
Although the abdominal muscles are deep and cannot be seen (unlike abs), let's still go to the mirror and carefully look at our stomach.
Upper muscles
These are the abdominal muscles located in the front of the abdomen. They consist of three layers: a deep layer, an intermediate layer and a superficial layer.
Deep layer
These three muscles always work together. Due to this, the internal relief of the muscles is built. Thanks to the deep muscles, we can do deadlifts, squats and dumbbell presses.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is not involved when performing strength exercises, but this does not detract from its advantages. It is very important for breathing. The diaphragm begins at the front of the chest, encircles it, and converges at the lower back.
Pelvic floor
The pelvic floor consists of the muscles located below the level of the pelvis. When you take a deep breath, the diaphragm lowers and the pelvic floor holds the breath. The diaphragm and pelvic floor are the main parts of the body that stabilize the spine.
Transverse abdominis muscles
The transverse muscles are located slightly below the oblique muscles. They provide stability to the pelvic floor, keeping it immobile. The transverse muscles are located directly on the linea alba - the connective tissue that runs exactly down the middle of the torso and adjacent to the lower back.
Intermediate layer
The intermediate layer is located between the deep and superficial layers. It is made up of several muscles, but the most important is the internal oblique.
Internal oblique muscles
These muscles originate from the linea alba, a vertical line in the middle of the torso, and attach to the femur. They run perpendicular to the external oblique muscles. The main functions of the internal oblique muscles are to regulate breathing and rotate the torso.
Surface layer
These muscles are familiar to everyone. If you are thin enough, you do not have large reserves of subcutaneous fat - you can even see it. These are the so-called “abs cubes”.
External oblique muscles
The external obliques run from the chest to the hips. Many of us believe that thanks to these muscles we can turn and tilt our body, this is a true statement, but not entirely complete. Also, the external obliques are muscles of stability and balance.
The external oblique muscles help stabilize the pelvis. Some people have a tendency to push their hip bones too far forward, thereby arching their lower back. This is very harmful: it creates strong pressure on the spine. Thanks to the external oblique muscles, the pelvis restores balance by tilting back and returning to a neutral position.
Rectus muscles
The rectus muscles originate from the pubic bone. Further, their locations are the 5th, 6th, 7th vertebrae and the lower part of the chest. These areas are separated vertically by the linea alba and 3-4 layers of connective tissue horizontally. These divisions create 6 or 8 separate abdominal muscles, which we call “abs.”
Posterior muscles
The core muscles are not only the front muscles, but also the back ones. It's important to know what's going on on our backs. We'll focus on three specific muscle groups in this section: multifidus, quadratus lumborum, and erector spinae.
Multifidus muscle
The multifidus muscle is a group of small muscles that span 2-4 parts of the back. You may never see them, but they are important because they provide feedback to your brain about where your body is in space. These muscles also help control the position of the spine.
Quadratus lumborum muscle
This large muscle runs from the upper thigh to the lower back. It is responsible for lateral tilts of the body, as well as for preventing these very tilts. The quadratus muscle is essential for controlling body movements.
Erector spinae muscle
This group of muscles starts from the sacrum and upper thigh and connects to the rib cage, upper neck, and even the base of the skull. Muscles are important for regulating movement during squats and deadlifts.
Types of bellies in women and men
Exercises for a flat stomach
There are different types of bellies. To determine your type, you need to stand in front of the mirror so that you can see yourself in full height and carefully examine your figure. In this case, you need to take a natural pose, do not try to suck in your stomach and straighten your back. Having determined the type of belly, it will be easier to find a way to solve the problem of losing weight.
Pregnant
Pregnant belly
This abdominal structure occurs in 40% of young mothers. After childbirth, the uterus increases in size and descends even lower into the pelvis, since during pregnancy the ligaments lose their elasticity. As a result, a rounded female tummy is formed, as if its owner has not yet experienced the joy of motherhood.
Short
This type of belly appears, oddly enough, from training. Hypertrophied muscles cannot withstand the load and bulge forward.
"Apple"
One of the main types of belly in women at any age. It is characterized by bloating in the afternoon. Why does my belly get bigger in the evening? There is only one reason, including for men, – poor nutrition.
"Lifebuoy"
It is considered a variation of the previous form. Clothing that compresses the waist and sedentary work contribute to the appearance of a double belly.
Bloating is caused by poor nutrition
Stressful
Characterized by the deposition of fat around the navel.
Skeletal structure in the abdominal area
Often we don't even think about the importance of bones in our body, focusing all our attention on the muscles. But bones and cartilaginous joints are of great importance for the development of muscle tissue.
Pelvis
The pelvis has two main movements: a forward tilt, in which the hips move back, and a posterior tilt.
Lumbar
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae located between the rib cage and pelvis. It affects the lumbar curve (movement forward, backward, lateral bending, rotation of the torso).
You can feel how important all these movements are during training: the resistance force holds the spine in place and prevents the vertebrae from bending. The lumbar region is not particularly flexible except for forward and backward bending, so the more you can control or resist the movement, the healthier and stronger your back will be. And this is the first and, perhaps, main condition for strength exercises.
The benefits of abdominal training
Speaking about the anatomy of the abdominal muscles, as a rule, the first thing that comes to mind is a peculiar aesthetic image: convex raised cubes and a flat stomach, on which there is no hint of fat deposits. Perhaps this information may surprise some, but Mother Nature did not give us these muscles for beauty.
Every aspiring athlete interested in the anatomy of the human abs should know that the abdominal muscles are responsible for vital functions that ensure movement and health. Therefore, it is necessary to train them not only in order to achieve a beautiful relief, but also for a number of other important reasons:
- Muscle relaxation. When we sleep, our lumbar muscles tend to remain tense, which does not allow the spine to fully recover. Because of this, people wake up tired and with back pain. Abdominal muscle training allows you to relax the lumbar muscles and relieve tension from the spine.
- Spine protection. You may not know, but the spine is responsible not only for supporting the back muscles, but also for supporting the abdominal muscles. If the abdominal muscles are not sufficiently trained, this increases the load in the intervertebral discs of the spine, which several times increases the risk of destruction of the lumbar spine.
- Reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This disease develops with age, usually as a result of the accumulation of excess fat deposits in the abdominal area.
- Positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Abdominal muscle training improves digestion and also prevents constipation and bloating.
- Positive effect on the cardiovascular system. Intense abdominal muscle training works well on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Another advantage is that the hip and knee joints do not receive excessive load.
- Improving sports performance. The abdominal muscles play an important role in everyday life, as well as in sports where you need to frequently turn your body and run quickly. Studies show that athletes with weak abdominal muscles are more likely to have colic in their sides. To get rid of this problem, you need to strengthen the abdominal wall.
Functions of the abdominal muscles
Below are the functions performed by the core muscles. Some of them are probably already familiar to you: squats, body bends. It turns out that the task of muscles is not only to flex and extend parts of the body. Here are the main five functions of the abdominal muscles:
Intrathoracic pressure
Take a deep breath and hold your breath. In this case, the diaphragm begins to put pressure on the pelvic floor and the transverse abdominal muscles. It is this process that is so important for maintaining the strength of the spine, and also allows us to perform exercises such as squats, deadlifts and various presses.
Anti-extension
Most people, especially those who have just begun their acquaintance with fitness, believe that the abdominal muscles, like the spine and back, are given to us only for bending the torso. Now try leaning back? Does not work? This is because our spine is securely secured by the rectus abdominis and oblique (external and internal) muscles to prevent sagging and curvature.
Lateral flexion and anti-lateral flexion
The internal and external oblique muscles help us bend in different directions. This is lateral bending. In addition, it is the oblique muscles, as well as the quadratus lumborum muscle, that perform the function of anti-lateral flexion. This is necessary to maintain the spine in a neutral position and maintain balance. Imagine you are carrying a heavy bag. One side of the body takes on the entire load and makes further movement possible, while the other has to maintain balance so that you do not fall on your side.
Anti-rotate
The rectus abdominis, transverse and oblique (external and internal) muscles are responsible for turning the body to the sides. They not only help rotate the body, but also prevent uncontrolled movements and keep the torso in a straight position. This muscle function is very important, especially when lifting weights with one arm.
Anti-bending
Abdominal exercises are a prime example of flexion. We can all bend forward – it’s natural. But if you're doing barbell squats or deadlifts, it can be difficult to keep your balance without falling on your face. Thanks to the abdominal muscles, our torso is able to maintain position without loading the spine.
How to solve a problem
After establishing the type and reasons, the question arises of how to start removing the belly:
- To eliminate the “apple” and the “lifebuoy” you will have to reconsider your diet. Foods high in sugar and flour products should be excluded from the diet. You need to add fresh vegetables and bran: they contain fiber. It is better to have dairy products for breakfast to normalize digestion. It is recommended to increase physical activity. You can sign up for dancing, ride a bike in the park;
- The stress belly, by its very name, hints that it’s time to calm down. You need to stop refueling with two cups of coffee before your workday and replace them with healthy green tea or uplifting cocoa with marshmallows. The diet should be enriched with nuts and herbs, drink mineral water, and sleep at least 8 hours. For sports activities, you can choose yoga or Pilates;
- To get rid of a low belly, you should ask your trainer to change your training program, reduce the weight you lift, and try different types of lunges instead of squats. You must first develop the entire muscle corset and only then return to intensive pumping of the abs;
- when solving the problem of how to get rid of mommy belly, you should try to include fatty fish and avocado in your diet, and also wait until the body recovers after childbirth and start training your abs;
Abdominal muscles
Important! The “vacuum” exercise, which is a retraction of the abdomen, is very popular now. When performing this exercise, the transverse muscle is activated, due to which a muscle belt is formed around the waist. According to reviews, the “vacuum” helps reduce the waist by 1-3 cm.
Basic abdominal exercises
Now that we have studied the structure of the skeletal skeleton and muscles, and also understood the biomechanical processes of the core muscles, it’s time to apply all this knowledge experimentally. Here are a few basic exercises that require no special training and will allow you to get the most out of it.
Exercise #1 – TRX loops
The TRX is a very effective machine that can give you rock-hard 6-pack abs and improve your balance. Many people have completely untrained lower backs, as this is a rather difficult place to work the muscles. Therefore, they need additional measures to compensate for the tension and create the best balance of the anterior and posterior muscle groups.
Starting position – stand up straight, fasten the loops on your hands. Exhale, tense your body muscles.
Then bring your arms together vigorously in front of you. Watch your back - it must be straight!
This exercise works the rectus abdominis, internal and external abdominal muscles. The spine, neck and upper back are actively trained. You can control the strength and intensity of the movements yourself, which is very convenient.
Exercise No. 2 – dead beetle
The exercise perfectly works the abdominal muscles without putting unnecessary stress on the lower back.
Lie on your back, raise your arms up. Then lift your leg at a 90-degree angle and, at the same time, lift your opposite arm. Hold the top position for a bit and return to the starting position. Please note: your back should be pressed tightly to the floor, no need to rise. Try to touch your heel, stretch the muscles.
Exercise No. 3 – Pallof press
This is a great exercise to strengthen your oblique abdominal muscles. Allows you to control the rotation of the body to the sides.
To perform this you will need an expander with a handle for your hands. The challenge is to do a forward press with a pulley at your side. Take the handle in your hands and begin to pull forcefully towards yourself. This is not easy, the force of resistance will actively hinder you. The quadratus lumborum muscle, transverse, internal and external oblique abdominal muscles are well worked out. Hold the handle against your chest for 20-30 seconds, then return to the starting position.
Exercise #4 – One Arm Deadlift
The one-arm deadlift is a very useful exercise for improving balance. Take one dumbbell and stand straight. Bend forward, holding a dumbbell in one hand and squeezing your abs. Then return to the starting position. Gradually make the exercise more difficult by bending down as low as possible.
Since the weight is on one side, you will have to make every effort to maintain balance. This exercise is also great for increasing your strength and developing endurance. The oblique muscles and quadratus lumborum muscles are involved.
Combine exercises
It is unlikely that you will be able to pump up a beautiful abs with the help of just bending the body on the floor or on an abdominal bench. Experts advise combining exercises. The optimal workout for getting a six-pack may include, for example, low-range isolated crunches, abdominal crunches, or hanging or incline leg or knee raises. To train the oblique abdominal muscles, crunches from a lying position, which can be done with weights, will also be effective.
Tips and tricks
We have already figured out the female and male anatomy of the abdominal muscles, now we would like to give some advice to those who are planning to train this muscle group.
- If you are a girl and you do not have excess fat, this does not mean that you should neglect training your abdominal muscles. It is important to understand that weak abdominal muscles can cause your stomach to sag. By regularly training these muscles for several weeks, you can not only tighten your stomach, but also make it flat.
- Don't forget to warm up! This applies not only to abdominal training, but to all training in general. A good warm-up prepares your body for more challenging activities and prevents future injuries.
- Pump up more than just your abdominal muscles! We address this advice to all “green” beginners. Remember once and for all: to get a beautiful and aesthetic physique, you need to train all the muscles of the body.
Where are the abdominal muscles located? What areas do they consist of? How should they be trained? What is the difference between male and female abs? We hope that we were able to provide complete and detailed answers to these questions. We wish you success in your training!
Source