How to effectively pump up your quadriceps?
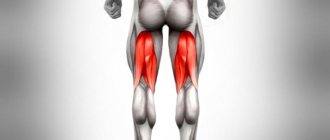
The leg muscles are the largest in the human body. Quadriceps exercises are performed by representatives of almost all sports disciplines. Without these exercises, you cannot achieve strength, mass, or endurance in your legs and body as a whole. The article discusses the best basic and isolated movements for the quadriceps for men and women, and presents training programs for boys and girls.
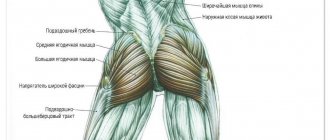
Anatomy of the quadriceps
The quadriceps (quadriceps femoris muscle) includes four muscle bundles:
- the vastus lateralis muscle is the largest bundle, participating in all movements associated with extension of the knee, and forming the lateral region of the thigh;
- vastus medialis (“droplet”) – also involved in movements associated with extension of the knee joint and is responsible for the formation of a rounded, full frontal surface of the knee;
- vastus intermedius muscle - located between the two previous bundles, actively involved in the work during extensions, squats, jumping, running;
- The rectus muscle is the longest bundle that gives the thigh a rounded shape, it is used not only in extension, but also in flexion, the only area of the quadriceps that is not directly attached to the femur.
© HANK GREBE — stock.adobe.com
Muscles of the back of the thigh
They originate on the tibial tuberosity, lie under the gluteus maximus muscle, and connect with the adductor muscle in the lower part. Then they are further separated.
Biceps femoris
Starts from the ischial tuberosity. At the back it extends along the entire length of the area under consideration and has the appearance of a spindle. Consists of two heads:
- long - connects at the top with the ischial tuberosity,
- short - attached to the lower leg.
The biceps muscle makes it possible to flex the limb at the knee joint and helps maintain balance.
Semitendinosus muscle
It extends down to the knee, narrows at the end, and is shifted towards the middle. Helps to straighten the inclined element and abduct the leg at the hip.
Semimembranosus muscle
Long and flat, runs along the back of the inner thigh, its initial end is connected to the pelvic bone, and ends on various fascia of the muscle tissue of the lower leg. Performs the same functions as the previous one.
Features of working with quadriceps
Correct technique plays a huge role in the work of the quadriceps. The health and condition of the knees and lower back depends on it. By sinning with the technique of performing exercises, the athlete transfers the main load to other muscle groups.
Like all large muscles, the quadriceps muscle takes a long time to recover. In most cases, there is no point in training it more than once a week . An option with two leg workouts is allowed, but then they are separated: the first one works the quadriceps, the second one works the back of the thigh.
The basis of the training program should be basic (multi-joint) exercises. They are designed for mass and strength, as they load the legs and body in a complex manner. Isolated movements help to detail the muscles, give them a “cut,” and can also be used to warm up before heavy compound exercises.
For this reason, in the first few years of systematic training, you need to focus on the “base”. And only then, having gained mass and strength, you can start polishing your legs. This doesn't mean that beginners should ignore single-joint movements. They are also needed, but priority is given to the basic ones. This also applies to women seeking to lose weight and have a striking silhouette. Basic movements performed in a high-repetition style are the main secret to success.
Strengthening
As already mentioned, depending on how developed the fiber groups in question will be, the physical abilities of each person will depend. In order to thoroughly work out each area, it is enough to regularly perform three simple but quite effective exercises. What is typical is that even training at home will not keep you waiting long for results.
You need to start with squats. Starting position: your feet are shoulder-width apart, your back is always straight, your arms can be put forward to help you maintain balance. You need to lower slowly while exhaling, until your thighs are parallel to the floor, rising slowly, while inhaling. Two sets of 15 squats are recommended.
The “push” exercise also works well on all groups of the lower extremities. You need to kneel down and place your hands on the floor. It is important to correctly distribute the weight. After this, you need to bend your knee and pull it towards the chest, and straighten it back. The back should be straight. We recommend 2 sets of 15 times on each leg.
And the last thing they do is lunge backwards. You need to stand straight, place your feet hip-width apart, and place your hands on your waist. The body weight is transferred to the leg being worked on. Then they take a breath, and the limb on which they were leaning is put back. The body remains straight. As you exhale, you need to push off the floor with your working leg and lift your extended limb up. 20 such repetitions are done for each leg and in 2 approaches.
Quadriceps exercises
There are hundreds of leg exercises. There is no point in listing everything: those described in the article are more than enough. Moreover, most movements are variations of the basic ones.
Basic
This section describes the main exercises for the quadriceps. Beginners often try to stay away from them, but without a “base” they are nowhere.
Squats
The main and most “scary” exercise for beginners. Barbell squats work most of the muscles in the body—the legs, buttocks, back, and abs. Even the arms and shoulders can be used - without strong ligaments in the arms it is difficult to hold a heavy barbell.
At the very beginning, focus on execution technique. Squatting incorrectly can cause problems with your knees, lower back and neck. To put more stress on the quadriceps, train with relatively light weights. By going too far with the plates, the athlete will not be able to avoid the powerful engagement of the buttocks and back.
Squat pattern:
- Starting position (IP) – the bar lies on the trapezius (in no case on the neck), hands hold the bar with a narrow grip (as far as flexibility allows), chest forward, back straight. It is strictly forbidden to hunch over during the entire movement. Feet stand shoulder-width apart, toes slightly pointed to the sides. To get into IP, you need to sit under the bar lying on the racks, remove it and step back.
- You need to start a squat by moving your pelvis back. The knees are in line with the feet - you cannot turn your knees inward. Also try not to bring them forward with your feet.
- Lower yourself to a position where your thighs are parallel to the floor. By undersquatting, you don't do enough work; by squatting deeper, you take the load off your quadriceps and put more stress on your gluteal muscles.
- Smoothly but powerfully, as you exhale, return to IP. The knees should remain slightly bent at the top - this is a prerequisite for reducing the risk of injury from the exercise.
At home, the barbell can be replaced with dumbbells. In this case, the hands with the shells are lowered down.
Front squats with barbell
Front squats are a similar exercise in which the barbell is placed in front rather than behind. Thanks to this, the load on the quadriceps becomes more targeted - the buttocks are used much less.
- Approach the bar lying on the racks and fix it on the front delts. The hands are placed crosswise, helping to hold the barbell - this is IP.
- Keeping your back absolutely straight, squat down to parallel.
- Return to IP.
The position of the hands may be different. Trained lifters often secure the bar with their hands positioned in the style of a weightlifter performing a clean and jerk. To do this you need to have a certain flexibility, strong ligaments and a powerful grip.
Leg press
The leg press eliminates the work of the back and buttocks as much as possible. At the same time, the simulator makes it possible to work with much more weight than in squats. To place the load on the quadriceps, you need to press with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- IP - the back and head are tightly pressed to the back of the simulator, the legs are almost completely straightened and rest against the bed, the hands firmly hold the handles.
- Bend your knees until a right angle is formed between your thighs and shins.
- Return your legs to IP.
A variation of this exercise is the single leg press. In this case, the weight is taken significantly less.
How to pump up the lateral thigh muscle
Place your feet approximately shoulder-width apart. As you inhale, moving your pelvis back, bend your knees to a right angle.
Training the vast lateralis quadriceps muscle - “breeches”
As you exhale, rise to the starting position. When performing the exercise, you need to fulfill several important conditions: Engage your abdominal muscles, this will ease the load on your back 2. Try to keep your back as straight as possible 3.
Try to keep your heels on the floor all the time 4. Don’t hold your breath It is noted that a slightly wider stance of the legs allows you to better work the lateral thigh muscle.
It is great for working on the outer thighs. Set a comfortable weight, stand under the supports and place your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly lower yourself as far as possible and return to the starting position.
It is important!
Avoid sudden movements and do not straighten your knees completely. Pain on the outer part of how to write with a tampon is usually associated with soft tissues: The vastus lateralis muscle hurts mainly due to injuries or unusually strong loads, for example, climbing a mountain, a long ski trip, etc.
How to pump up your hamstrings? Anatoly Smirnov
Treatment in this case is standard: There are other causes of pain in the area of the outer thigh.
Actually, this was all the structural and anatomical information on the leg muscles, now we move directly to the pumping-theoretical side of the issue.
This subchapter will provide information regarding the features of leg pumping. So let's look at each one.
The influence of genetics or legs are laid from youth. There is a theory that a certain type of physical activity in a child's early puberty affects the genetic type of muscle tissue fibers.
Exercises for the vastus lateralis muscle
Thus, if you are young from 7 years old and want to connect your life with bodybuilding in the future or simply be massive, especially in the legs, then you need to pay attention to sports such as: These are active in
As practice shows, people who preferred them in their youth, after puberty, had legs with good growth potential.
In these young athletes, white fast muscle fibers became the dominant muscle fibers in the legs. Subsequently engaged in bodybuilding, they have large volumes.
Helpful advice!
When it comes to proper leg training, understanding the fiber types is paramount.
In this regard, it will be useful to have the following information:. The main task in women's leg training is to correct problem areas and local increase in volume, such as how to pump up the lateral thigh muscle of the buttocks, without swinging the front thigh.
The main correction zones are:. In addition, any young lady wants rounded and voluminous buttocks without enlarging her hips. All these issues can be resolved by fine-tuning leg training.
Despite the fact that the muscle groups are the same for everyone, male and female legs have the following structural and visual differences.
Uff-ff, well, it seems like you’ve given it all away..., now you have a theory for creating legged legs: So far they’ve answered only in theory, yes there’s a lot of it, yes it’s tedious, but not everything is Maslenitsa for the cat, sometimes you have to force it.
Basic exercises for training quadriceps
Here you will find the best exercises with descriptions and photo demonstrations for high-quality training of the quadriceps muscles (quadriceps).
Published:
Author:
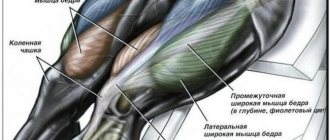
It is known that the large, powerful quadriceps, one of the strongest muscles in humans, consists of several elements that must be developed proportionally. The muscle consists of four heads: the rectus femoris, vastus internus, vastus externus, and vastus medialis. Having different starting points far apart from each other, all the heads converge in the lower part of the thigh and form a common tendon.
Functions and properties
The quadriceps femoris muscle, the photo and description of which allows you to appreciate the scale of the occupied area, completely covers the front and partially the lateral parts of the thigh. It has 4 main thin muscle processes on top, which occupy different locations in the upper thigh.
Toward the bottom, the muscle fibers join together to form a single large muscle and tendon that provide movement to the knee joint. The tendon of this muscle, due to its dense structure, completely covers the patella and blocks it from possible friction and injury.
The quadriceps femoris muscle has several main functions and is responsible for:
- extension of the lower leg in any position of the body, including when weighted and in a vertical position;
- takes part in hip flexion;
- helps maintain a static body position;
- complements other muscles when performing movements.
General anatomical information
Due to the peculiarities of a person’s life, the most significant load falls on his lower limbs, which determines the special development of his femoral muscles. The thigh muscles support the human body in an upright position, are involved in the process of walking, and are the ones that bear the stress when running, jumping and other physical activities. In order to cope with all the functions assigned to them, the thigh muscles, in the process of evolution, grew together into large groups, united by common tendons.
Thus, the vastus lateralis muscle belongs to the quadriceps femoris muscle, which is classified as an anterior thigh muscle.
The vastus lateralis muscle is located on the anterolateral surface of the thigh and is one of the largest in its group. Its origin is on the femur in the area of the hip joint. The lower part of the muscle attaches to the lower leg, passing into the quadriceps tendon and, together with others, forming a ligament that supports the patella.
Characteristic
The quadriceps femoris muscle, a photo of which can be correlated with its location on the body, is called musculus quadriceps femoris. This muscle is part of the thigh muscle group and is located on the front of it, partially occupying the lateral surface of the upper leg. This muscle is the primary flexor of the knee and hip.
The largest muscle on one side is attached to the patella in the area of the tibia, and on the other hand - at the base of the pelvis on different sides. The muscle begins at the top in the form of 4 independent plexuses of muscle tissue or 4 different muscles, which combine into a single dense plexus and a rigid tendon at the knee.
This muscle is considered one of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body. It bears most of the load during movement, especially when playing sports. It also participates in fixing the body and helps to stand straight.
The quadriceps femoris muscle is considered one of the longest in the body and, due to its complex structure and location, is most often subject to injury. In the absence of treatment and prolonged immobility, it can gradually atrophy.
Exercises for muscle development
The main physiological function of the vastus lateralis muscle, exercises for which will be described below, is to bend the leg at the knee. Accordingly, any movements that involve flexion and extension of the legs are suitable for its development and strengthening.
One of the options for a set of exercises to strengthen the lateral femoral muscle:
- Squats. It is worth paying attention to the technique of performing the exercise: the back should remain straight, the knees and toes should be slightly turned to the sides, it is necessary to squat to a position in which the thigh is parallel to the floor. If classes last more than a month and take place in the gym, you can switch to squats with weights (barbell, body bar, etc.).
- Lunges forward or backward, in place or in motion. It is also important to keep your back straight, the knee of the leg that is behind you should touch the floor. The exercise can be performed either without sports equipment or using weights, dumbbells or a barbell.
- Stepping onto the platform. You can use any elevation as a platform - a chair, a bench, etc. You can step onto the stand with your feet alternately, or work first with one leg, then with the other.
- Exercise “pistol”. It is a squat on one leg with the other extended forward.
- Thrust with expander. It is carried out in a lying position. With one foot you need to hook onto the expander band and bend it at the knee, despite the resistance of the simulator.
- Squats with one leg on a stand. The passive leg is laid back and fixed on an elevation, which can be anything (table, chair, etc.). Squats are performed on the second, working leg.
- Jumping. To perform this movement, you need to squat down and jump out of this position with force.
- Jumping with alternating legs. From a standing position, you need to jump up, and then take a position like a lunge. During the next jump, the position of the legs must be changed.
- Leg spread. If you have the opportunity to train in the gym, there is a special machine for this exercise. An expander will do at home. In a lying position with the band just above the knees, you need to spread your legs as far as possible without lifting your feet from each other.
To avoid pain after training, it is necessary to properly stretch the muscles that were most involved in the exercises.
Grade
After taking the history, a thorough examination should be performed, including inspection, palpation, assessment of strength and movement. Quadriceps injuries may be accompanied by obvious deformity, such as a bulge or defect in the belly of the muscle.
- Palpation of the anterior thigh should include assessing the size of the injured muscle, locating the area of maximum tenderness, and looking for any defect in the muscle.
- Quadriceps strength testing should include assessment of resistance to knee extension and hip flexion. Adequate hip PM testing should include assessment of resistance to knee extension during hip flexion and extension. This is best done by assessing the patient in both the sitting and supine positions. The person is asked to straighten the leg at the knee against external resistance. If the femoral nerve is damaged, the quadriceps will not contract. The prone position also allows for optimal assessment of the mobility and elasticity of the quadriceps muscle.
- Pain is usually felt by the patient through resistance to muscle activation, passive stretching, and direct palpation of the injury site.
- Identifying tenderness, any perceptible defect, and strength early in the disease can determine the severity of the injury and provide direction for further examination and treatment.
- Assessing the quadriceps for imbalance may suggest a patellar problem. It is also necessary to examine the patient to identify an imbalance between the quadriceps and hamstrings.
- The quadriceps muscle can be used to test the femoral nerve.
- Functional tests include the Stand and Walk test and the Stair Climb test.
Treatment of muscle problems
If the vastus lateralis muscle hurts, the following methods are used to treat it:
- magnetic therapy (low- and high-intensity);
- ultraviolet irradiation of the injured area;
- diadynamic therapy (effect on the damaged muscle with full-wave current);
- inductothermy - used to eliminate the consequences of injury such as bruises and hemorrhages;
- paraffin therapy – also used in the post-traumatic period;
- cryotherapy (cold treatment).
All of the above methods are used in a hospital setting for serious muscle injuries. If the damage is minor, you can limit yourself to treatment at home using cold, a tight bandage that limits mobility, and ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect.
The duration of treatment and recovery period depends on the severity of the injury, the age of the patient, his general health and the time of treatment.
Prevention of painful conditions
To prevent strain and tear of the lateral thigh muscle, it is important to follow several recommendations:
- regularly train your muscles, since the more prepared they are for stress, the less likely they are to pull;
- in everyday life and in the gym, do not overload yourself;
- before starting a workout, any muscle needs to be warmed up;
- Beware of falls and sudden movements.
In a word, in order to stay healthy, you need to correctly assess your capabilities, keep your muscles in good shape and avoid unjustified risks.