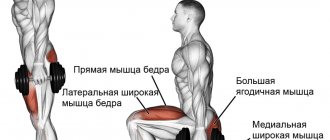
Examples of complex exercises combining aerobic and anaerobic exercise
- Kickboxing.
- A 20-30 minute workout alternating between easy jogging and sprinting.
When exercising on machines or with free weights (dumbbells, barbells), the general rule is as follows: Aerobic exercise - perform more repetitions with less weight and reduce the rest between sets. Signs indicating aerobic training will be increased heart rate (up to 90% of maximum) and sweating. You can calculate your maximum heart rate by subtracting your age from 220. For example, if you are 30, then your maximum heart rate will be 190 (220-30). Accordingly, your heart rate during aerobic exercise should not rise above 170
In addition to increasing your heart rate, pay attention to increased breathing. If your breathing does not increase, it means you are not training intensely enough.
And if you are unable to speak, then you should reduce the intensity of the workout. Anaerobic exercise - increase the weight, reduce the number of repetitions and do not forget to rest in between sets.
What types of aerobic exercise are the best?
This question has a clear and unambiguous answer: those as a result of which your pulse is at least 20 minutes (according to the basic norm of our program - 30 minutes, and if you need to lose weight, then 40-50 minutes), stays within the range of 60% to 90% of your maximum heart rate or maximum heart rate (MHR). If the pulse is less than 60%, it should not be considered a load, if more than 90%, then it will be considered a load, but it is dangerous for your heart, especially for poorly trained people.
There are different methods and tables for determining MHR. The easiest way to determine MHR is to subtract your age from 220. If you are 20, then MHR = 200, if 40, then 180, etc.
If you have special gadgets that automatically measure your pulse, for example, a smart watch, then everything is very simple. Firstly, they themselves will determine the MHR based on your profile data and average heart rate readings over a certain period. They will set their own heart rate zones. But you can participate in this. We recommend that you install the following zones:
- Zone 1 – initial level, warm-up (we do not consider it a load) – 50-60% of MHR
- Zone 2 – light, comfortable load – from 60 to 70%.
- Zone 3 – optimal aerobic activity – from 70 to 80%
- Zone 4 – high load, threshold value – from 80 to 90%
- Zone 5 is the maximum, acceptable only for short periods - from 90 to 100%.
Zones 2-4 are exactly those indicators within which your heart rate should be for 20-50 minutes, depending on your goals. If the goal is to strengthen the cardiovascular system, health and improve the quality of life, then 20-30 minutes in zone 3-4. If the goal is weight loss, then 40-50 minutes a day in zone 2-3. However, you will lose weight with the first option, as well as improve your health with the second. It is important to do all this regularly and with pleasure.
In the case of a smartwatch, the gadget will give you the results at the end of your workouts. The photo shows the results of our “bad” workouts: too relaxed and too intense!
The watch can be configured so that when entering the fifth zone, it will emit a sound and vibration signal, informing you that it is advisable to reduce the load level.
If you decide to purchase such a gadget, then we recommend Garmin as one of the undisputed leaders in this matter. Official representatives of Garmin in Russia are our partners and will be happy to provide you with a significant discount when you enter our promotional code. You can receive a promotional code by registering.
What about those who do not have the money or desire to purchase such a device? Firstly, there are a large number of free applications for smartphones, including those that measure heart rate. They are not as convenient to use as a watch, they are not as accurate, everything does not happen entirely automatically, but... for modest workouts that do not pretend to break records, this may be enough.
If you don't have a smartphone, use a regular stopwatch. Measure the distance (from 4 to 8 km for running, skiing, fast walking, from 10 to 20 km for cycling) and record the results, trying to gradually run/walk, cover the same distance faster. Or walk for 30 minutes, trying to run/ride further each time. In the absence of automatic gadgets, your assistants should be intense sweating and difficulty breathing. If this is not the case, then, apparently, you are not doing an aerobic workout, but taking a walk in the park.
Another good option is to use a treadmill and exercise bike, especially if they have a built-in heart rate monitor.
Focusing on various expert opinions and our own experience, we offer you our rating of the most useful and effective aerobic exercises. We pay special attention to the fact that we do not claim absolute objectivity - all types are good if the condition described above is met (pulse for at least 20 minutes at a level of 60-90% of MHR). So:
- Classic cross-country skiing. The best aerobic exercise. There is a minimum of injuries, the whole body is actively involved, there is no significant load on the spine and knee joints, as when running.
- Correct Nordic walking. Exactly the correct one, with the active involvement of the upper body in the work, and not just rearranging the poles at the level and behind you. Engaging the muscles of the upper body relieves the lower extremities and gives an excellent workout to the whole body.
- Swimming. Excellent load, without injury, perfectly develops all major muscle groups. By the way, Garmin watches work great in water, giving the same complete statistics at the end and during training. There is one “but”: according to widespread expert opinion and personal experience, the process of losing weight is slower than when training on land. Therefore, if the main goal is weight loss, then it is better, in addition to swimming, to include other types of aerobic exercise.
- Bike. Ideal for training the respiratory system and lower limbs without putting excessive stress on the joints.
- Run. A very effective aerobic exercise, during which it is difficult to “net”, unlike the above, but less useful than the previous ones for the spine and joints, primarily for the knees.
We have described here the simplest and most affordable options. If you come to the fitness center, you will be offered a wide variety of programs that effectively combine the required level of aerobic and anaerobic exercise. Compound exercises are most effective for burning fat and getting in good shape quickly.
If you love team sports and think that you have a sufficient level of exercise, since you play football, basketball, volleyball, tennis, etc. 2-3 times a week. then we are afraid that you may be wrong. Recreational play may not provide the required level of aerobic activity, and we strongly recommend testing yourself. How to do it? There are two options.
The ideal way is to use a smartwatch. By the way, the photo above shows the results of a football game. The game lasted 1 hour 15 minutes, the clock was set to auto-pause when the player stopped. Thus, from the statistics it is clear that the player was actively moving for 55 minutes (the sum of all minutes on the clock); Accordingly, he stood or moved very slowly for about 20 minutes, was in zones 2-4 for 41 minutes, and in maximum zone 5 for 14 minutes. From the point of view of the amount of aerobic exercise, everything is excellent here. However, 14 minutes in the maximum zone is not very good. So team sports are fraught not only with underperformance, but also with the risk of overdosing the load.
The second way is to test yourself at least once a week, using cyclic types of aerobic physical activity and comparing them with any available and adequate indicators, for example, GTO standards, Cooper test, Tecumseh test, etc. If you do not meet the standards for your age according to these indicators, you should think about and include cyclic aerobic training in your weekly program. Well, or participate in your games more actively.
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic process
Definition
Aerobic process refers to the process of cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic process refers to the process of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of free oxygen. Thus, this is the main difference between aerobic and anaerobic processes.
Type of organisms
Moreover, another important difference between aerobic and anaerobic process is that the aerobic process mainly occurs in higher organisms, whereas the anaerobic process mainly occurs in lower organisms, including bacteria, yeasts and parasites
cellular
Moreover, another difference between aerobic and anaerobic process is that the aerobic process occurs in the cytoplasm and inside the mitochondria, whereas the anaerobic process occurs in the cytoplasm.
Significance
The three stages of the aerobic process are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, while the two main types of anaerobic process are ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Chemical reaction
Moreover, the chemical reaction of aerobic process is C6HAC12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP, while the chemical reaction of ethanol fermentation is C6HAC12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 2ATP and the chemical reaction of lactic fermentation is C6HAC12O6 → 2C3HAC6O 3 + 2ATP.
molecular oxygen
It is important to note that the aerobic process requires molecular oxygen within the cell, while the anaerobic process does not require molecular oxygen
Substrate oxidation
In addition, while the aerobic process is responsible for the complete oxidation of the substrate, the anaerobic process is responsible for the incomplete oxidation of the substrate. Therefore, this is another difference between aerobic and anaerobic process.
NAD+ rebirth
In addition, NAD+ regeneration occurs in the electron transport chain of the aerobic process, while NAD+ regeneration occurs in the partial oxidation of pyruvate as a result of the anaerobic process.
ATP production during NAD+ degeneration
Additionally, another difference between aerobic and anaerobic process is that NAD+ regeneration of the aerobic process produces ATP, while NAD+ regeneration of the anaerobic process does not produce ATP.
ATP produced
The aerobic process produces 36 ATP molecules per glucose molecule, while the anaerobic process produces only 2 ATP per glucose molecule. This is also the difference between an aerobic and anaerobic process.
Water production
Additionally, water production is another difference between aerobic and anaerobic process. That is; the aerobic process produces six water molecules per glucose molecule, while the anaerobic process produces no water molecules because it does not use molecular oxygen in the electron transport chain.
Conclusion
An aerobic process is a type of cellular process that requires the presence of molecular oxygen within the cell. Aerobic respiration is a basic type of aerobic process that breaks down bonds in a glucose molecule to form ATP using the energy released. During aerobic respiration, 32 ATP molecules are produced per glucose molecule. In comparison, an anaerobic process is a type of cellular process that occurs in the absence of molecular oxygen. It produces fewer ATP molecules due to incomplete oxidation of glucose. Therefore, the main difference between aerobic and anaerobic process is the use of oxygen molecule for the process and efficiency.
Recommendations:
1. Scoville, Heather. “What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic processes?” ThoughtCo
, ThoughtCo, January 2, 2021,
Theory
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise. What is the difference?
These definitions show how the body obtains energy for movement. Energy is released by the breakdown of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a substance that is synthesized by the body from nutrients. Synthesis can occur with the participation of oxygen or without the participation of oxygen. In the first case, this is called aerobic metabolism, in the second - anaerobic .
A more natural and efficient process for the body is the "oxygen" or aerobic method of ATP synthesis. It can last for a long time, does not harbor any unpleasant consequences in the form of the formation of lactic acid in the muscles, and is 19 times more effective than the oxygen-free method (with it, 38 ATP molecules are formed from one glucose molecule, whereas with the oxygen-free method - only 2).
In what case is the oxygen-free method used and why? If we put the answer to this question in simple language, it will be this: the anaerobic method is used in the case when the cardiovascular system does not have time to deliver oxygen to its destination, and energy is needed. Then the body does the following:
- first uses all the ATP reserves in the muscles (this is only about 2-3 seconds, since ATP is not accumulated by the body);
- then uses the substance creatine phosphate for rapid ATP synthesis (another 7-8 seconds);
- then it begins to synthesize ATP from carbohydrates (through the breakdown of glucose) without oxygen. In this case, a by-product appears - lactic acid (lactate). Under these conditions, it accumulates faster than the body can neutralize it, and after a few minutes the anaerobic (lactate) threshold occurs, which is expressed in burning muscles, pain and fatigue. Even if you continue some movements, their intensity decreases due to fatigue, while the heart begins to beat faster, delivering oxygen to the cells more quickly. Thus, after some time there is a forced automatic transition to ATP synthesis with the participation of oxygen.
This means that anaerobic exercise is converted into aerobic exercise and that globally there is no such thing as pure aerobic and pure anaerobic exercise. In a generally simplified form, the scheme is as follows: with the beginning of any movement, the body uses existing and rapidly synthesized ATP, if during these 10 seconds it manages to supply oxygen to the muscles, the load becomes aerobic, if not, it will remain anaerobic. But after some time, either the movement stops, or as a result of an increase in heart rate and a decrease in intensity due to fatigue, the load will still become aerobic.
The effects of anaerobic strength training on the body.
Anaerobic exercise promotes muscle growth, strengthening and strengthening. But this growth is only possible with sufficient nutrition. Otherwise, the muscles you work on will grow at the expense of other muscles that are least used in the exercises. Girls should not be afraid to build large muscles - this is simply impossible due to low testosterone levels. During strength (anaerobic) training, fewer calories are consumed than during cardio (aerobic) training. But muscles themselves consume more calories. The more muscle mass you have, the more calories you burn throughout the day—when you sit, lie down, watch TV, and even sleep. Plus, the increased metabolism that helps burn fat lasts for an additional 36 hours post-workout! Thus, anaerobic training is very effective for losing weight. Muscle weighs more than fat. That is, body volume decreases even when weight does not fall. When losing weight, the result is usually measured in kilograms. But, you see, it’s unlikely that anyone will weigh you - what’s much more important is how many centimeters your waist will decrease :) Only with anaerobic exercises can you “sculpt” an ideal figure. Neither diet nor aerobics will help here. Anaerobic exercise is extremely beneficial for health...
- Increases bone density - bones will always remain strong.
- Strengthens the cardiovascular system.
- Prevents diabetes mellitus and helps in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
- Reduce the risk of cancer.
- Extend life.
- Improves mood and helps fight depression.
- Improves sleep quality and improves well-being if you don't get enough sleep.
- Help cleanse the body of toxins.
- Helps cleanse the skin.
Indications for aerobic training
Aerobic training is universal. They are often even prescribed as therapy for various diseases. Main indications for physical activity:
- The recovery period after prolonged illnesses with bed rest, injuries and surgical interventions.
- Sedentary work is the lack of physical activity in everyday life.
- Sleep disturbances, fatigue, constant stress and irritability.
- Excess body weight – it is aerobic exercise that helps burn fat tissue.
Interesting fact. In addition, aerobic exercise helps strengthen the immune system. They are often recommended for people who often get sick or have difficulty surviving various infections.
Combination of aerobic and anaerobic exercise
| Incorporating anaerobic exercise into an aerobic workout | Incorporating aerobic exercise into anaerobic training |
| Increasing the possibility of body correction, increasing strength endurance, enhancing the general health effect | Additional increase in endurance due to the aerobic component, improvement of the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, acceleration of weight loss due to fat burning during training |
The maximum positive effect from a combination of aerobic and anaerobic exercise can be obtained by properly designing a training program. However, I would like to warn the reader against the common practice when, after 30-40 minutes of aerobic exercise, a set of strength exercises is performed for 15-20 minutes. With this combination of loads, exercises are performed on tired muscles, which is not only ineffective, but also leads to overtraining.
Doing anaerobic and aerobic training on different days is a great way to achieve your fitness goals. But it is also necessary to avoid overtraining, that is, not loading the muscles involved in aerobic training with strength exercises for 24 hours before and after it.
For the most effective weight loss, it is best to combine aerobic and anaerobic exercise as follows:
- Interval training Interval training is alternating periods of high-intensity physical work with short periods of light (recovery) exercise. That is, anaerobic and aerobic exercises alternate with each other (for example, you run 20 seconds as hard as you can at a heart rate of 75–85% of the maximum value, and then 60–80 seconds at a relaxed pace). During one workout, you need to go through 5-12 such cycles of alternating intense work and recovery. The duration of each cycle depends on the intensity of the load and the physical training of the student. Calorie burning occurs both during interval training and after it due to the inclusion of the anaerobic component (though not as much and for less time than after standard anaerobic training). An additional advantage of interval training is significant time savings. Interval training should be done no more than two to three times a week, with at least two days of rest between interval training sessions. The number of other workouts must be reduced or eliminated altogether. After several weeks of intense interval training, you need to switch to regular training. Interval training involves very intense physical activity and is not suitable for beginners (at least a year of sports experience is desirable). It is recommended that you consult your doctor before starting interval training.
- Dividing the lesson into two parts: in the first part, anaerobic exercises are done, in the second, aerobic exercises. Anaerobic strength exercises of the first part are aimed at increasing muscle mass and maximizing the consumption of stored glycogen. Aerobic exercises of the second part are aimed at burning fat. The advantage of the method is that during anaerobic exercise, glycogen reserves were used up, so working in aerobic mode can almost immediately begin with burning fat reserves. The duration of aerobic exercise depends on the duration of anaerobic exercise. In some cases, 5-10 minutes will be enough. A small disadvantage of this method is a slight decrease in the effectiveness of strength training for the growth of muscle mass and strength.
weight loss is not a goal
muscles
An anaerobic workout followed by 10 minutes of aerobic exercise is a great way to increase muscle mass along with aerobic endurance. Such training comprehensively strengthens physical and mental health, and especially the cardiovascular system.
Whichever of these methods you choose, do not forget to warm up before training - this will help prepare your body for the load and avoid injury. Flexibility exercises at the end of the session will help to quickly utilize lactic acid and prevent a decrease in muscle elasticity.
The benefits of aerobic exercise
The main goal of aerobic exercise is to train and strengthen the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. The practical goal is to burn excess calories and get the body into good athletic shape.
In addition, during aerobic exercise the following positive changes occur in the body:
Improved blood condition:
Reducing the risk of other diseases:
- increasing bone density – reducing the risk of osteoporosis;
- strengthening muscles – reducing the risk of injury;
- cleansing of waste and toxins through sweating - reducing the risk of cancer, diabetes and other diseases.
Improvement in general condition:
- improved appearance, increased vitality;
- improved mood and mental state;
- reducing stress levels, preventing depression;
- improved sleep, general health;
- increased endurance, decreased fatigue.
What is aerobic and anaerobic training
There are three systems of energy supply for all types of human activity.
Almost all of the changes that occur in the body due to exercise are related to the demands placed on these energy-producing systems in the human body.
Moreover, the effectiveness of a training regimen can be assessed by its ability to provide adequate stimulus for change within these three energy systems.
Typically, it is an activity that lasts more than 90 seconds and is characterized by low to moderate power output or intensity.
Examples of aerobic exercise include running on a treadmill for 20 minutes, swimming 1 mile, and watching TV.
During anaerobic training, energy is produced without the participation of oxygen. An activity in which most of the energy is obtained anaerobically is called anaerobic.
Attention!
Typically an activity that lasts less than two minutes and has a moderate to vigorous power output and intensity. There are two fundamentally different ways of producing energy during anaerobic training: lactic acid and phosphagen.
Examples of anaerobic exercise are represented by running 100 meters, squats, and pull-ups.
Our main goal here is to look at how aerobic and anaerobic training affects physical performance variables such as strength, power, speed and endurance. We also believe that comprehensive physical fitness and optimal health necessitate training each physiological system on a regular basis.
It is worth noting that all three energy systems are involved in any activity, although one of them dominates. The interaction of these systems can be complex, but even a simple comparison of aerobic and anaerobic exercise characteristics can be beneficial.
However, it has been observed that as a result of excessive aerobic exercise, athletes lose muscle mass, strength, speed and power. It is not that uncommon for a marathon runner to have a vertical jump of only a couple of tens of centimeters, and a bench press score that is well below the average for most athletes. Aerobic training also reduces anaerobic capacity.
This is not ideal for athletes or individuals interested in comprehensive physical fitness and maintaining optimal levels of health.
Anaerobic activity also improves cardiovascular function and reduces the amount of subcutaneous fat. Anaerobic activity is a unique tool for significantly increasing power, speed, strength and muscle mass. Anaerobic training allows us to exert maximum effort in a short period of time.
Important!
Perhaps most noteworthy is the fact that anaerobic training does not reduce aerobic performance! In fact, properly designed anaerobic training can be used to develop a high degree of aerobic fitness without the loss of muscle mass that accompanies excessive aerobic exercise!
Basketball, football, gymnastics, boxing, athletics in disciplines up to 1.6 km, swimming within 370 meters, volleyball, wrestling, weightlifting, etc. - all of these are sports in which the majority of training time is spent in an anaerobic state.
Long and very long distance running, cross-country skiing, and swimming over 1400 m are activities that require aerobic training of a volume that produces results that are unacceptable to athletes and individuals interested in comprehensive physical fitness and optimal health.
Aerobic and aerobic exercise
Recommended intensity for aerobic exercise
Entry-level athletes often ask questions about the recommended intensity for aerobic exercise, as well as the impact of intensity on performance. Several methods have been developed to help a person determine the intensity of training. One of them is the principle of using a point system for assessing well-being after each exercise. If we take the maximum intensity as 100%, then in this case, during aerobic training you need to adhere to an intensity in the range of 45-60% of the maximum
Approximate intensity
- 0% - no movement
- 10% - very light load
- 20% - light load
- 30% - average load
- 40% - medium-heavy load
- 50-60% - heavy load
- 70-90% - very heavy load
- 100% is the maximum limit.
Another way to measure the approximate intensity of exercise is a speech test, which implies that during high-intensity training, the athlete is sure to lose his breath, and because of this, difficulties arise with speech pronunciation.
Complex techniques require specialized medical equipment, the results of which are based on determining the pulse during exercise. There is a connection between oxygen consumption and heart rate changes during physical activity. There is also information that training in the desired pulse zone is most effective for heart function. Leaving a certain pulse zone means either the ineffectiveness of the training or its excessive intensity.
The maximum permissible heart rate described above is a relatively abstract indicator. Well-trained athletes during aerobic training can increase the values by 10-15 beats/min. from the calculated pulse zone without harm to health. You can also apply the Karvonen formula. With its help, oxygen consumption is calculated at a certain intensity of exercise. The maximum allowable heart rate is calculated in a calm state. The operating range is calculated as 60-90% of the calculated value. After which, the resting heart rate is added to the percentage.
If you doubt the accuracy of your own calculations, contact a competent trainer. First, you can measure your pulse during exercise, for example, at your wrist or at the carotid artery in your neck. Secondly, special sensors, usually built into cardio equipment, can be used to measure heart rate. And thirdly, in sports stores you can buy heart rate monitors that measure your heart rate with maximum accuracy, even on your wrist.
The American Sports Cardiology Association recommends training in a heart rate zone that is between 70-90% of your maximum heart rate, or in the range of 50-80%, based on the Karvonen formula. Low intensities should generally be used by people with reduced fitness levels.
What does this mean?
Aerobic activities include running, walking, cycling, swimming, tennis, football, dancing and kickboxing. Exercises on a stepper, orbitrek, as well as step aerobics in the gym also involve many muscle groups, so there is plenty to choose from. It’s worth listening to yourself and choosing the type of load that will be fun!
Basic nutrition rules for gaining muscle mass
Even if you don’t go to the gym and don’t have special exercise equipment at home, you can always find suitable complexes for working at home. It can be jumping, step aerobics or dancing, the main thing is desire! Watch aerobic exercises on video and start training!
Nutrition during aerobic exercise
Read more about nutrition in the relevant articles from the “Healthy Eating” section and in the “Ideal Day GREENPORTAL.pro” article. Here we will briefly say that the correct way would be to eat carbohydrate foods before training and protein-carbohydrate foods after. If you eat food 30-40 minutes before training (as a rule, this happens if you train in the morning), then the best option would be a small snack with foods with an average glycemic index - so-called fast carbohydrates, for example, bananas. The ideal option, which we recommend in the morning, half an hour before training, is a green smoothie.
If the workout is in the evening, then consume a good supply of slow carbohydrates 1.5-2 hours before it - buckwheat, brown rice, durum wheat pasta. You will need them to conduct your classes effectively.
Keep in mind that after aerobic exercise, the body continues to actively break down fats and carbohydrates for some time. This process lasts about 2 hours. If at this moment you consume some quick source of energy - the same banana - then this process will stop. Therefore, if your goal is to lose weight, then try not to eat anything for 2 hours after training. If there is no such goal, then proteins in combination with slow carbohydrates (60 to 40) are an excellent option within 30-40 minutes after training. If you are planning to lose weight, but cannot withstand 2 hours without food, then a better option would be predominantly protein foods, for example, dairy and fermented milk products, a small piece of fish or poultry with a side dish of fresh vegetables.