Modern cosmetology gives them this opportunity. But, if a lady is faced with arthrosis of her hands, she will no longer be able to appear young.
Knobby, swollen fingers will immediately show age, or even “add” ten years. And although a face lift can be done, it is impossible to remove the “bumps” that have formed at the joints. And, as a matter of fact, women suffer from such arthrosis 10 times more often than men!
Arthrosis of the joints of the hands seriously impairs fine motor skills, and this greatly interferes both at work and at home. In advanced cases, it may be impossible to unscrew the cap from a bottle, hold a knife and fork, press buttons on the phone...
Fortunately, this development of events can be prevented. As with any other type of arthrosis, when the hands are affected, the articular cartilage is the first to suffer. When it becomes thin, the edges of the bones begin to grow - osteophytes appear. It is they who make the fingers lumpy, like a spindle. To prevent this from happening, it is important to avoid cartilage destruction. This can be done if you take care of your hands from a young age.
Features of the structure of the hands and fingers
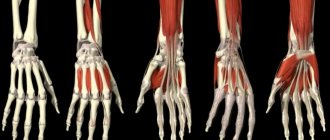
The structure of the hand is perhaps one of the most complex systems of the body; it is not for nothing that the hands are distinguished separately in traumatology. The brush consists of three sections:
- wrist,
- metacarpus,
- fingers.
The wrist consists of 8 bones, the number of metacarpal bones is similar to the fingers - there are 5 of them. Each finger has three phalanges, and only the thumb has two.
The muscles of the human hand form a complex system and are located on the palmar surface. The muscles of the hand are divided into three groups:
- muscles of the middle palm,
- muscles of the thumb,
- muscles of the little finger.
Muscles of the human hand - palm
Muscles of the human hand - top
The peculiarity of the movement of the fingers is that most of the muscles that move the phalanges are located in the forearm.
The muscles of the forearm are connected to the fingers by tendons through several joints. Thus, the fingers work like puppets; the finger muscles themselves do not perform independent movement.
In young age
The main risk factor is genetics.
Arthrosis itself is not inherited. But the characteristics of metabolism, the density and elasticity of articular cartilage, and their strength are largely determined genetically. Problems with the joints of the hands are more often observed in those women whose mothers and grandmothers also encountered this disease.
In your youth, think about choosing a profession. Even if a person is not predisposed to arthrosis, regular increased load on the hand increases the risk of getting sick. Pianists, office managers who constantly type on the keyboard, and masseuses suffer greatly in this regard. If your parents had arthrosis of the joints of the hands, it is better not to choose such professions.
Try to avoid injury. Injuries not only to the fingers themselves, but also to the wrist joint - the place where the hand connects to the forearm - can trigger the development of arthritis. Do not overuse fitness exercises with dumbbells. Be careful in icy conditions, because when falling, a person involuntarily puts his hands forward.
Top exercises to strengthen your hands and fingers at home
Wrist rotation
The technique is performed as a warm-up for muscles and joints. Clench your hands into fists and perform dynamic rotations at maximum amplitude. Perform rotation in one direction for one minute, then repeat for the same amount in the opposite direction.
Clenching fists
The exercise is performed without special equipment and allows you to train at home. Clench your fists at the same time, holding the maximum force for 1 to 2 seconds, and unclench your fingers, straightening your hand as much as possible. Perform the exercise for 1-2 minutes. Relax your muscles and repeat 2 more approaches.
Palm pressure
Bring your palms together tightly at chest level. Eliminate static tension by pressing your palms as much as possible from the fingers to the base of the hand. Hold the tension for 1-2 minutes, relax your hands for 1 minute. Repeat 2 more times.
One palm pressure
After applying simultaneous pressure from your hands, work each hand separately. One palm applies pressure to the second, tilting it back, and the second hand performs resistance. Alternate on each side for 5 seconds, and so on for 5-10 cycles.
Finger abduction
Remaining in the same position - palms at chest level, move your fingers away from each other as much as possible without lifting your palms. Perform the exercise dynamically, smoothly working your muscles, concentrating on the sensations in your palms and forearms. Perform the exercise 20-30 times in 3 approaches.
Pressure with fingers
Place your thumbs and index fingers on each hand. Perform maximum compression on the pads of your fingers, holding the pressure for 1-2 seconds, and so on for each finger, returning in the reverse order - from the little finger to the thumb. Perform 5-10 circles.
Flexion - extension of the hand without weight
Hold your hands in a fist, and your forearms parallel to each other, with your palms facing you. Bend your hands and bring them “toward you” as much as possible, then lower them “away from you” as much as possible. Perform the exercises for 1-2 minutes at full range.
If the first signs appear
Arthrosis of the joints of the hands is diagnosed when seals form on the fingers. But the disease begins long before that. At the first stage, aching pain appears in the joint, which subsides during the day and intensifies at night. There may be slight swelling, but the range of motion in the joint does not decrease.
Take protective medications. They are called chondroprotectors. Their components - glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate or a combination thereof - improve the regeneration of cartilage cells, increase the content of hyaluronic acid in it, which retains water, making cartilage more durable and elastic. Chondroprotectors are also used in the treatment of more advanced forms of arthrosis, but they are most effective in the early stages.
Conduct paraffin therapy sessions. Cosmetic paraffin slowly releases heat, warming problem areas. This promotes blood flow to the fingers and improves metabolism in the joint. In addition, paraffin, as it cools, contracts and gives a massage effect.
Knead your brush. Joints in which discomfort has appeared need moderate, properly selected physical activity no less than healthy ones. Lack of movement worsens the metabolism in cartilage, and this contributes to its accelerated destruction. In addition to special massage, it is useful to squeeze and unclench a rubber ball or expander. It’s great if you do this in a warm hand bath, you can take it for ten minutes. It is useful to sculpt from clay or plasticine. Just half an hour of such exercises a day will strengthen the muscles of the hand and stretch the joints.
Exercises for hands and fingers with equipment
Squeezing the ball with your fingers
Take a special expander ball or tennis ball, grasping the ball only with the pads of your fingers. Press the ball with your fingers for 5 seconds and relax. Repeat the movement 5-10 cycles on each hand.
Weight retention
Grasp the pancakes or some flat but heavy object with your fingers. Hold the weight until you feel a loss of strength, then lower the weight. Perform 3-4 approaches, loading the muscles of the hands to failure.
Push-ups on fingers
This type of push-up maximally strengthens the muscles of the hands, since it receives a large load under the pressure of its own weight. In this version, you should not concentrate too much on working the pecs and triceps, since the fingers may “give up” faster than the large muscles. Therefore, the option can be performed from your knees or hands on a hill.
Read more about finger push-ups →
Hanging on the bar
Hanging is a preparatory exercise for pull-ups, as it trains grip strength and strengthens the muscles of the hands. Perform the hang until your arms get tired. You can also hang on a towel or rope with one or two hands. Repeat 3-4 times.
Exercises with an expander
Choose a rubber or spring expander of high rigidity so that you can perform it at least 10 times. Squeeze the expander for 1-1.5 minutes on each hand, then relax your hands. Do these approaches 3-4 times for each hand.
Read more about the wrist expander in this article →
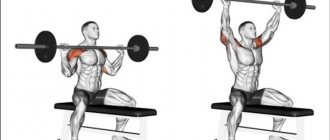
Curls with a barbell or dumbbells
The exercise affects the forearms to a greater extent, but also trains grip strength well. Choose any available equipment of sufficient weight - a barbell or dumbbells. Place your forearms on your thighs and hold the apparatus with an underhand grip. Bend your hands, bringing them closer to your shoulders 6-12 times, 3-4 approaches.
Reverse grip barbell extension
Grasp the barbell with an overhand grip, placing your forearms on your thighs. Relaxing your hands, lower the bar down, and with effort, lift the bar as far as possible towards you. Choose a weight for 8-12 repetitions, perform 3-4 sets.
Digging rice
This technique came to modern MMA and boxing from ancient times, and one of the best boxers, regardless of weight categories, Andre Ward, was once very familiar with it.
What you need to do:
- Take a large container of rice.
- Straighten your fingers and press them together and start digging the rice with your hands.
- While pulling your hand back, take a handful of rice in each hand, squeeze tightly, and then unclench, pouring the grain back out.
- Repeat these steps over and over again.
The more you do this exercise, the stronger your arms will become. This is a very useful procedure from a therapeutic point of view.
Carpal expander
Another simple and common way to strengthen your arms is to work with a hand-held resistance band. Constant resistance while clenching your fist is great for strengthening your forearms and increasing hand endurance.
In addition to the sports component, this also helps with everyday tasks, such as grasping/carrying various things, typing, and the like.
The manual expander is very convenient to use; you can exercise with it at any time and anywhere.
Diagnostics
Why weakness in the hands appeared can only be determined based on the data of a comprehensive comprehensive examination. After analyzing anamnestic information and a neurological examination, the neurologist makes a preliminary conclusion about the nature and origin of the pathology. Accurate verification of the lesion is provided by additional diagnostic methods:
- Laboratory research.
For myopathies in the blood, the level of creatine phosphokinase, hormones, glucose is assessed, and creatinine is examined. To confirm the nature of some conditions, DNA analysis and toxicological examination are performed. - Radiography.
Plain radiography is used as a routine method for identifying some causes of weakness in the arms - fractures, pathology of the cervical spine, joint diseases. Its resolution is not sufficient for more accurate visualization. - Tomography.
Volumetric processes, hematomas, consequences of traumatic brain injuries are found on. Magnetic resonance imaging is preferable for damage to nerves and soft tissues, spinal atrophy. - Electroneuromyography.
Helps evaluate nerve conduction and identify signs of peripheral motor neuron damage. Based on the results of ENMG, a decrease in the amplitude and speed of the impulse and muscle fasciculations are determined. - Ultrasonography.
Defects in surrounding structures in compression neuropathies can be detected using ultrasound of soft tissues. Diagnosis of vascular pathology is carried out by ultrasound scanning with assessment of blood flow parameters.
Patients with myasthenia gravis undergo a proserine test, and for carpal tunnel syndromes, a number of motor tests are performed. To identify atrophy and differential diagnosis of some myopathies and myodystrophies, a muscle biopsy can be performed. Damage to peripheral nerves and pathology of myoneural synapses should be distinguished from central paresis.
Electromyostimulation